Today’s Current Affairs: 2nd April 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Digital India Trust Agency (DIGITA) : RBI

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is considering establishing a Digital India Trust Agency (DIGITA) to combat the proliferation of illegal lending apps and curb growing cyber fraud.
- This proposed agency aims to verify digital lending apps, maintain a public register of verified apps, and promote transparency and accountability within the digital lending sector.
- In recent years, India has witnessed a surge in fraudulent activities and unethical practices in the digital lending sector.
- The RBI has taken various measures to address this issue, including collaborating with the IT Ministry and Google to whitelist legitimate digital lending apps and remove unauthorised ones from the Google Play Store.
- Once established, DIGITA would be responsible for the following:
- Verification of digital lending apps: DIGITA would vet digital lending apps to ensure compliance with RBI regulations and guidelines.
- The agency would maintain a public register of verified digital lending apps, making it easier for consumers to identify legitimate apps.
- Apps lacking the verified mark from DIGITA would be considered unauthorised for law enforcement purposes, serving as a crucial checkpoint in combating financial crimes in the digital domain.
Hockey India Awards 2023:

The Hockey India Awards 2023 were held in New Delhi on March 31, 2024 to celebrate the outstanding Indian hockey players from the previous calendar year.
- The event saw several players being recognized for their exceptional performances and contributions to the sport.
- Mens Player of the Year: Hardik Singh, the vice-captain of the Indian mens team, was named the Player of the Year.
- He was part of the bronze medal-winning team at the Tokyo 2023 Olympics and the gold medal-winning team at the Asian Games 2023.
- Womens Player of the Year: Salima Tete, an Olympian, was awarded the Player of the Year for her role in the Indian womens team that won the bronze medal at the Asian Games in Hangzhou last year.
Schengen Area:
Romania and Bulgaria partially joined the Schengen Area, Europe’s ID-check-free travel zone. This marks a significant step in the two countries’ integration with the European Union (EU).
- Land border checks will remain in place due to opposition from Austria, which has long blocked their bid over concerns about illegal migration.
- Romania and Bulgaria joined the EU in 2007, while Croatia joined in 2013.
- The Schengen Area, established in 1985, comprised 23 of the 27 EU member countries, along with Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein before the partial admission of Romania and Bulgaria.
- Around 3.5 million people cross an internal border each day within the Schengen Area.
- The European Commission has stated for more than a decade that Romania and Bulgaria meet the technical criteria for full accession to the Schengen Area.
- Full accession requires unanimous support from all member states.
- Both countries have agreed to implement random security screening at airports and maritime borders to combat illegal migration and cross-border crime.
Conservation Of The Caracal Species:

There was a concern regarding the conservation of the Caracal species.
- Caracal is an elusive, primarily nocturnal animal which has traditionally been valued for its litheness and extraordinary ability to catch birds in flight. In India, it is called siya gosh, a Persian name that translates as ‘black Ear’.
- They typically use abandoned porcupine burrows and rock crevices for maternal dens, but can be found with their young in dense vegetation.
- The most suitable habitat for caracals in Rajasthan, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh is located in Kutch, the Malwa Plateau, the Aravalli hill range and the Bundelkhand region,
- It is found in several dozen countries across Africa, the Middle East, Central and South Asia.
- They live in woodlands, savannahs and in scrub forests.
- Large-scale hunting, illegal trading and loss of natural habitats are considered significant threats to the species.
- Conservation status: The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule
Hume AI:

A New York-based research lab and technology company Hume, has introduced what can be called the ‘first conversational AI with emotional intelligence’.
- Hume AI is the world’s first emotionally intelligent voice AI.
- It accepts live audio input and returns both generated audio and transcripts augmented with measures of vocal expression.
- It is essentially an API that is powered by its proprietary empathic large language model (eLLM).
- This eLLM reportedly understands and emulates tones of voices and word emphasis to optimise human-AI conversations.
- It is trained on human reactions to optimize for positive expressions like happiness and satisfaction. EVI will continue to learn from users’ reactions.
- By processing the tune, rhythm and timbre of speech, EVI unlocks a variety of new capabilities, like knowing when to speak and generating more empathic language with the right tone of voice.
Organic Electrochemical Transistor:
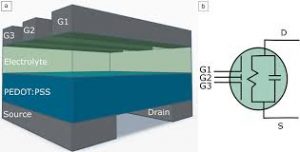
Researchers recently outlined a new strategy to fabricate high-density and mechanically flexible Organic Electrochemical Transistor (OECTs).
- Organic Electrochemical Transistor is an emerging class of transistor based on organic superconducting materials known for their ability to modulate electrical current in response to small changes in the voltage applied to their gate electrode.
- It is a device capable of simultaneously controlling the flow of electronic and ionic currents.
- They have various notable advantages, including promising amplification and sensing capabilities, low power consumption, low driving voltages and a versatile structure.
- They can be used to create biosensors, wearable devices and neuromorphic systems.
- Transistor is a semiconductor device for amplifying, controlling and generating electrical signals.
- It is the active components of integrated circuits or “microchips,” which often contain billions of these minuscule devices etched into their shiny surfaces.
Tentative UNESCO List Of World Heritage Sites:

6 new sites from Madhya Pradesh have found place in the Tentative UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites (WHS).
- The sites included in the new list included Gwalior Fort, Historical Group of Dhamnar Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple, Rock Art Sites of Chambal Valley, Khooni Bhandara, Burhanpur, and Gond monuments of Ramnagar, Mandla.
Gwalior Fort:
- It is renowned for its formidable walls, stands atop a hill providing panoramic views of the surrounding city.
- Historically, it is believed that the fort’s first foundations were laid in the 6th century AD by Rajput warrior Suraj Sen.
- Suraj Sen was the local chieftain who suffered from a severe leprosy but was healed by a hermit-saint named Gwalipa. In gratitude for this event, he established the Gwalior City named after him.
Historical Group of Dhamnar:
- It comprises 51 rock-cut caves, stupas, chaityas, and dwellings dating back to the 7th century AD.
- Among these, the colossal statue of Gautam Buddha in the nirvana pose is a significant highlight.
- Noteworthy caves include the Bari Kacheri and Bhima Bazar on the northern bank, known for their historical importance and architectural features.
- Bhojeshwar Mahadev Temple: It is dedicated to Lord Shiva and boasts a massive Linga carved from a single stone.
- Commissioned by Raja Bhoj in the 11th century, this temple is revered for its grandeur and unique architecture.
Rock Art Sites of the Chambal Valley:
- It hosts the world’s largest concentration of rock art sites, showcasing scenes from various historical periods and civilizations.
- These sites, spanning across Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, provide insights into ancient human life and cultural evolution.
Burhanpur’s Khooni Bhandara:
- It is an underground water management system comprising eight waterworks built by Abdurrahim Khankhana in the historical city of Burhanpur.
- It was built using the Persian qanat approach and designed by Persian geologist, Tabkutul Arz
- During the Mughal era, technologies like Persian Qanats from Iran and Iraq were imported to India as useful public utilities.
Gond Memorial of Ramnagar, Mandla:
- The region formerly known as the Central Provinces of India and covering parts of the present-day states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra; was historically called Gondwana, the home of the largest heterogenous tribe of India, the Gond tribe.
Tripura’s Matabari Pera And Pachra Receive GI Tag:

The Tripura Chief Minister announced that two traditional items from the state, Matabari Pera and Pachra, have been honoured with the Geographical Indication (GI) tag marking a significant milestone for local artisans and weavers.
- Matabari Pera, a dairy-based confectionery that served as prasad at the Tripurasundari temple, and Pachra, a handwoven cloth used by Indigenous communities, have been recognised with the prestigious GI tag.
- The GI tag ensures legal protection against unauthorised imitation or misuse of the product, safeguarding its authenticity and preserving the cultural heritage associated with it.
- This recognition also facilitates market access and promotion, both domestically and internationally, fostering economic opportunities for local communities involved in its production.
- Tripura’s iconic queen pineapple was previously honoured with the GI tag, along with 13 other products from the Northeast, highlighting the region’s diverse and unique offerings.
India’s First Small-Scale Liquefied Natural Gas (SSLNG) Unit:

The Union Minister for Petroleum and Natural Gas recently inaugurated India’s first small-scale liquefied natural gas (SSLNG) unit at GAIL (India) Ltd’s Vijaipur complex in Madhya Pradesh.
- This development is part of the government’s broader initiative to promote the use of natural gas in various sectors and increase its share in the country’s primary energy mix to 15% by 2030.
- SSLNG involves liquefying and transporting natural gas on a smaller scale, catering to areas without pipeline connections using specialised trucks and vessels.
- Starting from large-scale LNG import terminals, SSLNG can supply LNG directly to consumers via cryogenic road tankers or small vessels, either as a liquid or regasified for traditional uses.
- It will lead to reduced dependency on costly gas imports, especially if it replaces a significant portion of diesel consumption, leading to substantial foreign exchange savings.
- It also promotes cleaner energy and supports India’s transition towards sustainable fuel sources.
- LNG is increasingly used as a fuel for ships and vessels, especially in emission-controlled areas, due to its lower emissions of sulphur oxides (SOx) and particulate matter compared to traditional marine fuels.
- LNG is used as a fuel for trucks, buses, and other heavy-duty vehicles, offering reduced emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and greenhouse gases compared to diesel.
- LNG is used in gas-fired power plants to generate electricity, providing a cleaner alternative to coal or oil-fired power plants with lower emissions of pollutants.
- LNG can be used in industrial processes for heating and cooling applications, such as in manufacturing, food processing, and refrigeration.
- LNG can complement renewable energy sources like wind and solar by providing backup power when renewable generation is intermittent or unavailable.




