Today Current Affairs: 2nd May 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Hatti Community : Request For Inclusion In The List Of Scheduled Tribes

Centre is considering the Himachal Pradesh’ government’s request for inclusion of the Hatti community in the list of Scheduled Tribes in the state.
- The community has been making the demand since 1967, when tribal status was accorded to people living in the Jaunsar Bawar area of Uttarakhand, which shares a border with Sirmaur district.
- Their demand for tribal status gained strength because of resolutions passed at various maha Khumblis over the years.
- The Hattis are a close-knit community who got their name from their tradition of selling homegrown vegetables, crops, meat and wool etc. at small markets called ‘haat’ in towns.
- The Hatti community, whose men generally don a distinctive white headgear during ceremonies, is cut off from Sirmaur by two rivers called Giri and Tons.
- Tons divides it from the Jaunsar Bawar area of Uttarakhand.
- The Hattis who live in the trans-Giri area and Jaunsar Bawar in Uttarakhand were once part of the royal estate of Sirmaur until Jaunsar Bawar’s separation in 1815.
- The two clans have similar traditions, and inter-marriages are commonplace.
- There is a rigid caste system among the Hattis — the Bhat and Khash are the upper castes, while the Badhois are below them.
- Inter-caste marriages have traditionally remained a strict no-no.
- Due to topographical disadvantages, the Hattis living in the Kamrau, Sangrah, and Shilliai areas lag in education and employment.
- The Hattis are governed by a traditional council called Khumbli, which like the khaps of Haryana, decide community matters.
- The Khumbli’s power has remained unchallenged despite the establishment of the Panchayati Raj System.
East Kolkata Wetlands (EKW) And The Sunderbans : Violates Environmental Norms

A recent audit report of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) has pointed out illegal construction and violations of environmental norms in two Ramsar sites in West Bengal, the East Kolkata Wetlands (EKW) and the Sunderbans.
- The EKW, a unique peri-urban ecosystem that lies on the eastern fringes of Kolkata, covers an area of about 12,500 hectares.
- It is spread over 37 mouzas of the State’s South and North 24 Parganas districts.
- The CAG report pointed out that failure to delineate boundaries of the EKW and uncontrolled transfer of land resulted in its change of character and lack of effective action by the EKWMA (East Kolkata Wetland Management Authority).
- In absence of effective measures by EKWMA, waterbodies were dried up and filled illegally.
- Since 2007, EKWMA has identified 357 cases of violation, out of which 101 cases were identified between December 2015 and March 2020, the audit said.
Wildfires In Himachal Pradesh:

The prolonged dry spell coupled with unusually high temperatures in recent days has triggered many wildfires in Himachal Pradesh, destroying several hectares of forest cover across many parts of the hill State.
- The early onset of summer this year in the hills posed a major challenge to the State government’s efforts to control forest fires and with dry weather conditions and high temperatures expected to continue, the task has become more difficult.
- Till April 28 this year, as many as 719 incidents of forest fires have been reported across the State, affecting close to 5,662 hectares under forest circles of Shimla, Chamba, Bilaspur, Dharamshala, Hamirpur, Kullu Mandi, Rampur, Nahan and the Great Himalayan National Park at Shamshi in the Kullu region.
- The estimated loss so far has been pegged at around ₹1.4 crore.
- In 2018-19, the State witnessed as many as 2,544 forest fire incidents while in 2019-20 the figure was down to 1,445. In 2020-21, there were 1,045 forest fire incidents and in 2021-22 as many as 1,275 fire instances were reported.
- The maximum number of forest fires are human-generated — many accidental but a few deliberate ones. In several areas, there is a practice of burning the pasture lands to get rid of the dry leaf litter to ensure fresh grass growth for livestock.
- Usually, when there is intermittent rainfall, such fires do not go out of control but when there’s prolonged dry weather, many of these fires go out of control.
SemiconIndia Conference 2022:

Prime Minister of India Shri Narendra Modi inaugurated SemiconIndia Conference 2022, the global semiconductor conclave designed to bring together key stakeholders to showcase existing capabilities, ideate innovations and discuss global best practices.
- The flagship conclave with the theme Catalyzing India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem, is being held in Bengaluru from 29th April to 1st May 2022.
- Inaugurating the conference, Narendra Modi, Prime Minister of India said, We have earmarked USD 10 billion for India Semiconductor Mission and are creating an environment that encourages growth to create a vibrant semiconductor ecosystem and steer India into the future.”
- The conference aligns with the larger national narratives such as Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat and is pegged as the launchpad to India Semiconductor Mission (ISM).
- IESA launched an industry report on ‘Semiconductor manufacturing supply chain – India’s opportunity in the global market”.
- During the conference, the below Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) were inked:
- MOU signed between SEMI and ELCINA to promote semiconductor ecosystem in India
- MOU between CDAC and Qualcomm for partnership in semiconductors which will target semiconductor design startups, in line with the objectives of the PLI scheme
- MOU between AICTE and SEMI and ISM for training and skilling tech workforce for the semiconductor sector
Atal New India Challenge (ANIC 2.0):

Atal Innovation Mission launched the phase 1 of the 2nd edition of the Atal New India Challenge (ANIC 2.0) on 28th April 2022.
- Atal New India Challenge is a flagship program of Atal Innovation Mission, NITI Aayog.
- The program aims to seek, select, support and nurture technology-based innovations that solve sectoral challenges of national importance and societal relevance.
- One of the primary goals of the ANIC program is to support innovations in areas critical to India’s development and growth – Education, Health, Water and Sanitation, Agriculture, Food Processing, Housing, Energy, Mobility, Space Application etc.
- Launching the Challenge, Dr S. Chandrasekar, Secretary, DST in his address said that Government will hand-hold the path breaking innovations and asked the start-ups to take up hard challenges.
- The Atal New India Challenge aims to address the Commercialization Valley of Death – supporting innovators scale over the risks associated with access to resources for testing, piloting and market creation.
Mission SAGAR IX:

With the overarching aim of providing critical medical aid to Sri Lanka during the ongoing crisis, INS Gharial as part of Mission SAGAR IX reached Colombo.
- Mission SAGAR IX: INS Gharial reaches Colombo, delivers critical medical aid to Sri Lanka
- It delivered over 760 kgs of 107 types of critical lifesaving medicines.
- The shipment was received by Sri Lankan Health Minister Channa Jayasumana.
- In line with the Government’s vision of SAGAR – Security And Growth for All in the Region – the Indian Navy undertakes several deployments titled Mission SAGAR to assist friendly countries.
- Since May 2020, the Indian Navy has successfully concluded eight such missions, deploying ten ships to 18 Friendly Foreign Countries.
State Of Employment In India:

According to the latest data from the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), India’s labor force participation rate (LFPR) has fallen to 40% from 47% in 2016.
- According to the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), the labor force consists of persons who are of age 15 years or older, and belong to either of the following two categories:
- Are employed
- Are unemployed and willing to work and are actively looking for a job.
- LFPR is defined as the percentage of persons in the labor force in the population.
- LFPR includes those who are employed and those who are unemployed
- Worker Population Ratio (WPR) is defined as the percentage of employed persons in the population.
- Unemployment Rate (UR) is defined as the percentage of persons unemployed among the persons in the labor force.
- Chhattisgarh has the country’s lowest unemployment rate.
- The world over, LFPR is around 60%. In India, it has been sliding over the last 10 years and has shrunk from 47% in 2016 to just 40% as of December 2021.
- According to CMIE data, as of December 2021, while the male LFPR was 67.4%, the female LFPR was 9.4%.
- It means, less than one in 10 working-age women in India are demanding work.
India’s Forex Reserves:

India’s foreign exchange (forex) reserves declined for the seventh consecutive week.
- Forex or foreign exchange reserves are assets held by the central bank in foreign currencies as a reserve.
- According to the latest data from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), India’s forex reserves stood at $600.42 billion as of April 22, 2022.
- All components in India’s forex reserves witnessed a fall in the week ending April 22, 2022.
- The forex reserves were at an all-time high of $642.453 billion on September 3, 2021.
- The components of forex reserves are:
- Foreign currency assets (FCA)
- Gold holdings
- SDRs (special drawing rights) of the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Reserve tranche position (RTP) in the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
- Foreign currency assets (FCA) are maintained as a multi-currency portfolio comprising major currencies, such as the US dollar, Euro, Pound sterling, Japanese yen, etc.
- Foreign currency assets (FCA) are expressed in terms US dollar.
- Forex reserves are usually used for backing the exchange rate and influencing monetary policy.
Rules For Resignation And Reinstatement Of An Officer:

Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer Shah Faesal, who resigned from the service in protest against the “unabated” killings in Kashmir in 2019, has been reinstated.
- Faesal’s resignation, in January 2019, had not been accepted by the government, pending investigation into some of his posts on social media.
- The resignation of an officer of any of the three All-India Services — IAS, the Indian Police Service (IPS) and Indian Forest Service — is governed by Rules 5(1) and 5(1)(A) of the All India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958.
- An officer serving in a cadre (state) must submit his/her resignation to the chief secretary of the state.
- An officer who is on central deputation is required to submit his/her resignation to the secretary of the concerned Ministry or Department.
- Before forwarding the resignation to the central government, the concerned state is supposed to send information on the issues of dues and vigilance status, along with its recommendation.
- The state checks to see if any dues are outstanding against the officer, as well as the vigilance status of the officer or whether any cases of corruption etc. are pending against him/her.
- In case there is such a case, the resignation is normally rejected.
- Minister of State at the Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) in respect of the IAS, the Minister for Home Affairs in respect of the IPS, and the Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change in respect of the Forest Service.
- The central government may permit an officer to withdraw his/her resignation “in the public interest”
Laser Communications Relay Demonstration:

NASA recently demonstrated its Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD). It was launched in December 2021.
- It is the agency’s first-ever laser communications system.
- The LCRD will help the agency test optical communication in space.
- LCRD is a technology demonstration that will pave the way for future optical communications missions.
- The LCRD payload is hosted onboard the US Department of Defense’s Space Test Program Satellite 6 (STPSat-6).
- It will be in a geosynchronous orbit, over 35,000km above Earth.
- Optical communications systems are smaller in size, weight, and require less power compared with radio instruments.
- A smaller size means more room for science instruments.
- Less weight means a less expensive launch.
- Less power means less drain on the spacecraft’s batteries.
- With optical communications supplementing radio, missions will have unparalleled communications capabilities.
Ban On Menthol Cigarettes And Flavored Cigars : US

The US Food and Drug Administration issued a proposal to ban menthol cigarettes and flavored cigars.
- India has not banned the sale of menthol cigarettes.
- In 2012, Brazil became the first country in the world to ban menthol cigarettes.
- In 2019, the Centre banned electronic cigarettes and in addition, different states have their own rules in place banning hookah consumption, including flavored hookahs, in public places.
- It aims to prohibit menthol as a characterizing flavor in cigarettes and prohibit all characterizing flavors (other than tobacco) in cigars.
- The proposed rules would help prevent children from becoming the next generation of smokers and help adult smokers quit.
- The proposed rules represent an important step to advance health equity by significantly reducing tobacco-related health disparities.
- The proposed ban does not cover electronic cigarettes.
- The rules will not be enforced against individual consumers for possession or use of menthol cigarettes or flavored cigars.
- The rules will only “address manufacturers, distributors, wholesalers, importers and retailers who manufacture, distribute, or sell such products.
RBI’s Report On Currency And Finance:

According to recent Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Report on Currency and Finance (RCF), the Indian economy may take more than a decade to overcome the losses caused by the outbreak of Covid-19 pandemic.
- The theme of the report is “Revive and Reconstruct” in the context of nurturing a durable recovery post-Covid-19 and rising trend growth in the medium-term.
- Covid-19, Worst Health Crises: The Covid-19 pandemic will go down in history as one of the worst health crises the world has ever faced.
- The pre-Covid trend growth rate works out to 6.6% and excluding the slowdown years it works out to 7.1%.
- Taking actual growth rate of (-) 6.6% for 2020-21, 8.9% for 2021-22 and assuming growth rate of 7.2% for 2022-23 and 7.5% beyond that, India is expected to overcome Covid-19 losses in 2034-35.
- Its economic impact may linger for many more years and confront Indian Economy with the challenges of rebuilding livelihoods, safeguarding businesses and reviving the economy.
- India suffered among the biggest pandemic induced losses in the world in terms of output, lives and livelihoods, which may take years to recover.
- The Russia-Ukraine conflict has also dampened the momentum of recovery, with its impact transmitting through record high commodity prices, weaker global growth outlook and tighter global financial conditions.
- Concerns surrounding deglobalisation impacting future trade, capital flows and supply chains have amplified uncertainties for the business environment.
GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation:
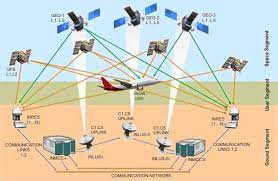
Airports Authority of India (AAI) Successfully conducted a light trial using GAGAN {GPS (Global Positioning System) Aided GEO Augmented Navigation} based LPV (Localizer Performance with Vertical Guidance) Approach Procedures.
- Many airports including the ones under Regional Connectivity Scheme are being surveyed for the development of GAGAN-based LPV Instrument Approach Procedures.
- This is being done so that suitably equipped aircraft can derive maximum benefit in terms of improved safety during landing, reduction in delays, diversions and cancellations, reduction in fuel consumption, etc.
- LPV is a Satellite Based Procedure which has been used by aircraft for landing purposes.
- LPV approaches make aircraft possible to land at airports not equipped with expensive Instrument Landing Systems, which includes many small regional and local airports.
- Lowering the decision height up to 250 ft provides a substantial operational benefit in poor weather and low visibility conditions.
- Thus, any airport which hitherto would require higher visibility minima, will be able to accept aircraft benefiting remote airports which are devoid of precision approach capability equipment.
- GAGAN is a Space Based Augmentation System (SBAS) jointly developed by ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) and AAI to provide the best possible navigational services over Indian FIR (Flight Information Region) with the capability of expanding to neighboring FIRs.
- GAGAN is a system of satellites and ground stations that provide GPS signal corrections, giving you better position accuracy.
- It is the first such system developed for India and neighboring countries in the equatorial region.
- GAGAN System was certified by DGCA (Directorate General of Civil Aviation) in 2015 for Approach with Vertical Guidance (APV 1) and en-route (RNP 0.1) operations.
- There are only four Space-Based augmentation systems available in the world namely India (GAGAN), US (WAAS) Europe (EGNOS) and Japan (MSAS).
- Aviation, Forest management, Railways signaling, Scientific Research for Atmospheric Studies, Natural Resource and Land Management, Location based services, Mobile, Tourism.
- GAGAN GEO footprint expands from Africa to Australia and GAGAN system has capability to cater 45 reference stations for expansion to neighboring countries.
- GAGAN provides a civil aeronautical navigation signal consistent with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPs) as established by the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) Panel.
National Behaviour Change Communication (BCC) Framework For Garbage Free Cities:

Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0), has launched the ‘National Behaviour Change Communication (BCC) Framework for Garbage Free Cities’ to strengthen the ongoing jan andolan for ‘Garbage Free Cities’.
National Behaviour Change Communication Framework:
- The BCC Framework for Garbage Free Cities shall serve as a guiding document and blueprint for States and Cities to undertake large scale multimedia campaigns along with intensive and focused inter-personal communication campaigns.
- The framework focuses on intensifying messaging around the key focus areas of source segregation, collection, transportation, and processing of waste, plastic waste management, and remediation of legacy dumpsites to transform the urban landscape of India.
- SBM-U 2.0, announced in Budget 2021-22, is the continuation of SBM-U first phase.
- It was launched on 1st October 2021 to achieve the vision of ‘Garbage Free Cities’ over the next five years.
- The government is also trying to tap safe containment, transportation, disposal of faecal sludge, and septage from toilets.
- It will be implemented over five years from 2021 to 2026 with an outlay of Rs.1.41 lakh crore.
- SBM-U first phase was launched on 2nd October 2014 aiming at making urban India Open Defecation Free (ODF) and achieving 100% scientific management of municipal solid waste. It lasted till October 2019.
- Aim:
- It focuses on source segregation of garbage, reduction in single-use plastic and air pollution, by effectively managing waste from construction and demolition activities and bioremediation of all legacy dump sites.
- Under this mission, all wastewater will be treated properly before it is discharged into water bodies, and the government is trying to make maximum reuse a priority.
- All statutory towns will become ODF+ certified (focuses on toilets with water, maintenance and hygiene).
- All statutory towns with less than 1 lakh population will become ODF++ certified (focuses on toilets with sludge and septage management).
- 50% of all statutory towns with less than 1 lakh population will become Water+ certified (aims to sustain toilets by treating and reuse of water).
- All statutory towns will be at least 3-star Garbage Free rated as per MoHUA’s Star Rating Protocol for Garbage Free cities.
- Bioremediation of all legacy dumpsites.
MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification Scheme:

Ministry for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises has launched the MSME (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) Sustainable (ZED-Zero Defect Zero Effect) Certification Scheme.
- This Scheme is an extensive drive to enable and facilitate MSMEs adopt ZED practices and motivate and incentivize them for ZED Certification while also encouraging them to become MSME Champions.
- MSME Sustainable (ZED) Certification can be attained in Three Levels after registering and taking the ZED Pledge:
- Certification Level 1: BRONZE
- Certification Level 2: SILVER
- Certification Level 3: GOLD
- After taking the ZED Pledge, the MSME can apply for any Certification Level if it feels that it can fulfil the requirements mentioned in each level.
- The intent of taking a ZED Pledge is to take a “pre-commitment” or a solemn promise by MSMEs to uphold the values of Zero Defect Zero Effect in their practices and to urge them to move ahead on the journey of ZED.
- Under the Scheme, MSMEs get subsidy as per the following structure, on the cost of ZED certification:
- Micro Enterprises: 80%
- Small Enterprises: 60%
- Medium Enterprises: 50%
- A provision of up to Rs. 5 lakhs (per MSME) will be made available for handholding and consultancy support for MSMEs under ZED Certification for assisting them to move towards Zero Defect Zero Effect solutions.
- The MSMEs can also avail themselves of several other incentives offered for ZED Certification by States & UTs, Financial Institutions etc. and can also apply for free Certification under the MSME KAWACH (COVID-19 Support) initiative.
Zero Defect Zero Effect Scheme:
- Launched in 2016 by the Ministry of MSME, the scheme is an integrated and comprehensive certification system.
- The scheme accounts for productivity, quality, pollution mitigation, energy efficiency, financial status, human resource and technological depth including design and IPR (Intellectual Property Rights) in both products and processes.
- Its mission is to develop and implement the ‘ZED’ culture in India based on the principles of Zero Defect & Zero Effect.




