Today Current Affairs: 30th August 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Small Cells:
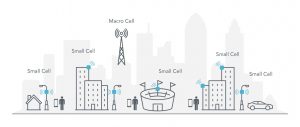
To expedite the roll-out of 5G, telecom operators in the country will leverage street furniture such as poles, advertisement hoardings and bus shelters for deploying low-power base stations called ‘small cells’ that will help bring the network closer to the consumers.
- Small cells are needed for deploying 5G as opposed to earlier generations such as 4G, because of the frequency.
- The higher the frequency, the lower the wavelength, which means that the distance they travel is less.
- Small cells are low-powered radio access nodes or base stations that have a coverage range from a few metres up to a few hundred metres.
- They are portable, easy to deploy and help provide localised coverage.
- As per the TRAI paper, small cells provide coverage for very short distances and therefore they are installed in a large number — even more than 200 per square kilometre — for good geographical coverage to provide highly reliable and high-capacity broadband.
Positive Indigenisation List (PIL):

Defence Minister Rajnath Singh approved the third Positive Indigenisation List (PIL) of 780 strategically important line replacement units (LRU), sub-systems and components, with a timeline beyond which they will only be procured from the domestic industry.
- This is different from the three PILs announced for the armed forces.
- This was done in line with the effort to promote self-reliance in defence manufacturing, and minimising imports by the defence public sector undertakings (DPSUs).
- This list is in continuation to the two PILs of LRUs, sub-systems, assemblies, sub-assemblies and components that were published in December 2021 and March 2022.
- These lists contain 2,500 items which are already indigenised and 458 (351+107) items which will be indigenised within the given timelines.
- Out of the 458 items, 167 items (163 from the first PIL, and four from the second PIL) have been indigenised, so far.
- The Ministry explained that indigenisation of these items will be taken up through different routes under the ‘Make’ category of procurement procedure.
National Sports Day 2022:

The National Sports Day or Rashtriya Khel Divas is celebrated on 29th August every year in India as a tribute to hockey legend Major Dhyan Chand who was born on this date in 1905.
- The day was first designated and celebrated in 2012 as India’s National Sports Day.
- The nation celebrates the day honouring our sports stars.
- The president gives away sports awards such as the Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award, Arjuna Award, Dronacharya Award, and Dhyan Chand Awards on this occasion.
- The primary motto of National Sports Day is to promote awareness about the significance of sports and being physically active in day-to-day life.
- The Government of India organises various programs, events, seminars etc to raise awareness about the significance of National Sports Day.
Third Consecutive La Nina Event:

Australia’s Bureau of Meteorology (BOM) predicted, that a third consecutive event of La Nina could be underway which could lead to unusual weather effects in various countries.
- There is an extended period of La Nina in 2022.
- It is the first time that this has happened since the 1950s when the event started to be recorded. The years 1973-76 and 1998-2001 were consecutive La Nina years.
La Nina and El Nino:
- In the neutral state (neither El Niño nor La Niña) trade winds blow east to west across the surface of the tropical Pacific Ocean, bringing warm moist air and warmer surface waters towards the western Pacific and keeping the central Pacific Ocean relatively cool.
- Warm sea surface temperatures in the western Pacific pump heat and moisture into the atmosphere above.
- In a process known as atmospheric convection, this warm air rises high into the atmosphere and, if the air is moist enough, causes towering cumulonimbus clouds and rain.
- The pattern of air rising in the west and falling in the east with westward moving air at the surface is referred to as the Walker Circulation.
La Nina:
- La Nina means the Little Girl in Spanish. It is also sometimes called El Viejo, anti-El Nino, or simply “a cold event.”
- La Nina events represent periods of below-average sea surface temperatures across the east-central Equatorial Pacific.
- It is indicated by sea-surface temperature decreased by more than 0.9℉ for at least five successive three-month seasons.
- La Nina event is observed when the water temperature in the Eastern Pacific gets comparatively colder than normal, as a consequence of which, there is a strong high pressure over the eastern equatorial Pacific.
- There are increased temperatures in Western Pacific, Indian Ocean and off the Somalian coast.
EL Nino:
- El Nino is a climate pattern that describes the unusual warming of surface waters in the eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It is the “warm phase” of a larger phenomenon called the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
- It occurs more frequently than La Nina.
Aadhaar-Voter ID Linkage:

The Election Commission (EC) started a campaign to promote the linkage of Voter ID and Aadhaar.
- Further, Government officials have asked individuals to link them Aadhaar with their Voter IDs and failure to link voter ID with Aadhar could lead to the cancellation of their Voter ID card.
- The linking project would help the Election Commission, which conducts regular exercises to maintain an updated and accurate record of the voter base.
- To weed out duplication of voters, such as migrant workers who may have been registered more than once on the electoral rolls in different constituencies or for persons registered multiple times within the same constituency.
- As per the government, linkage of Aadhaar with voter IDs will assist in ensuring that only one Voter ID is issued per citizen of India.
Exercise Vajra Prahar 2022:

India – USA Joint Special Forces conducted the 13th edition of exercise Vajra Prahar 2022 culminated at Bakloh (Himachal Pradesh).
- It’s an annual exercise is hosted alternatively between Special Forces India and the United States.
- Special Forces are the units of a country’s armed forces that undertake covert, counterterrorist, and other specialized operations.
- The 21-day joint training provided an opportunity for the Special Forces from both nations to train in Air Borne Operations, Special Operations and Counter Terrorism operations in a joint environment under United Nations Charter.
- It was conducted in two phases;
- The first phase involved combat conditioning and tactical level special missions training exercises,
- The second phase included 48 hours of validation of training received by both contingents in the first phase.
Cyber Threat To Mobile Banking:

The lack of adequate cybersecurity and the dearth of talent in banking could potentially lead to a further rise in cyberattacks on user devices.
- According to a 2020 Statista survey across 25 States in India, two-third respondents said they had a smartphone.
- Of these, half said they sent and received money digitally, and about 31% said they had a mobile app for banking.
- Nearly 14% said they used their mobile phones for banking-related purposes.
- Global cybersecurity firm Kaspersky warns of an increase in cyberattacks on Android and iOS devices in the Asia Pacific (APAC) region.
- One mobile banking trojan, called Anubis, has been targeting Android users since 2017.
- Roaming Mantis is another prolific malware targeting mobile banking users.
- There is push from regulators to make payment platforms interoperable at a time when the demand for technical experts is a serious concern in the banking industry.
Intended Nationally Determined Contribution:

India has formally submitted an updated Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) target to UNFCCC
- India’s INDC to be achieved primarily by 2030
- A total of 40% of the installed capacity for electricity will be from non-fossil fuel sources was Original target.
- As per new Target 50% by 2030 with help from international finance (Global climate fund) and transfer of technology
- To reduce the emissions intensity of the GDP by 33-35% was original target
- As per new target 45% of GDP by 2030
- Propagating a sustainable way of living: mass movement for ‘LIFE- Lifestyle for environment’ using traditions and values of conservation is new target.
- India also promised an additional carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent through additional forest and tree cover by the year 2030.
- India announced the goal of reaching net-zero by 2070
INDC:
- The INDCs are the primary means for governments to communicate internationally the steps they will take to address climate change in their own countries.
Identifying a Forest:

The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has objected to Chhattisgarh for its transfer of land without following due process from its Forest to the Revenue Department.
- In March 2022, Chhattisgarh Chief Minister announced in his Budget speech that the state government has transferred over 300 sq km an area larger than Raipur in the Bastar region from the Forest department to the Revenue department to ensure easy availability of land for setting up industries and building infrastructure.
- In August 2022, the Union Environment Ministry’s Integrated Regional Office asked the state to stop the transfer of land, saying it was in violation of the Forest Conservation Act, 1980 and multiple Supreme Court orders, and return the land already transferred.
- The move has now run into a hurdle, even as paperwork is underway for transferring more land to other parts of the state.
- At present, in India, there is no clear nationally-accepted definition of ‘forest’.
- States are responsible for determining their definition of forests.
- The prerogative of the states to define forests stems from a 1996 Supreme Court order called the T.N. Godavarman Thirumulkpad vs the Union of India judgment.
- In the judgement, the Supreme Court interpreted that the word “forest” must be understood according to its “dictionary meaning”.
- This description covers all statutorily recognised forests, whether designated as reserved, protected or otherwise.
- Forests are included in the Concurrent List in the (Seventh Schedule) of the Constitution of India.Through the 42nd Amendment Act, 1976 Forests and Protection of Wild Animals and Birds were transferred from State to Concurrent List.
- State Forest Departments have jurisdiction over two types of forests notified under the Indian Forest (IF) Act, 1927: Reserve Forests (RF), where no rights are allowed unless specified, and Protected Forests (PF), where no rights are barred unless specified.
- Certain forests, such as villages or nagarpalika forests, are managed by state Revenue Departments.




