Today’s Current Affairs: 4th Dec 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Anthrobots:
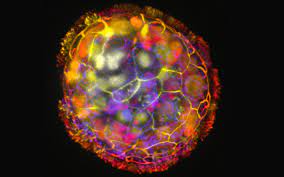
Researchers have developed miniature robots using human cells and termed them as anthrobots.
- Anthrobots are constructed from human tracheal cells which are bio-robots that possess self-assembly capabilities.
- These are capable of both movement and healing neurons within a laboratory setting.
- They can spontaneously fuse together to form a larger structure called a superbot, which was able to encourage the growth of neurons.
- They are measuring between the width of a human hair and the tip of a sharpened pencil.
- The anthrobots displayed diversity in structure and behavior. Some took on a spherical shape fully covered in cilia, while others resembled a football shape irregularly adorned with cilia.
- These anthrobots are different from Xenobots, which are created from embryonic stem cells of frog.
- They hold promise for regenerative medicine, wound healing, and disease treatment.
Leadership Group For Industry Transition (LeadIT) 2.0:

India and Sweden launched Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT) 2.0 during the COP28 World Climate Action Summit, hosted in Dubai.
- The LeadIT initiative, initially centered around pivotal sectors such as iron, steel, cement, and aluminum, focused on industry transition and knowledge sharing.
- LeadIT has played a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of low-carbon technologies, aligning with global environmental goals.
Three core areas of LeadIT 2.0:
- Inclusive and Just Industry Transition: Ensuring that industry transitions are not only efficient but also equitable, promoting fairness and inclusivity in the process.
- Low Carbon Technology Development and Transfer: Placing renewed emphasis on the development and seamless transfer of low-carbon technologies, crucial for achieving sustainable practices across industries.
- Emerging Economy Technology Transfer: Facilitating the expedited transfer of innovative solutions to emerging economies, assisting in their transition to more sustainable practices.
- It serves as a platform for public-private collaboration, fostering sector-specific and cross-sectoral learning, especially concerning innovation opportunities and new technologies.
Chess Grandmaster Title: Brother-Sister Duo In History

Vaishali Rameshbabu and her younger brother Rameshbabu Praggnanandhaa have become the first-ever Grandmaster brother-sister duo in history.
- Chess Grandmaster title is the highest title or ranking that a chess player can achieve.
- The Grandmaster title and other chess titles is awarded by the International Chess Federation, FIDE (acronym for its French name Fédération Internationale des Échecs),
- The title is the badge of the game’s super-elite, recognition of the greatest chess talent on the planet, which has been tested and proven against a peer group of other similarly talented players in the world’s toughest competitions.
- Besides Grandmaster, the Qualification Commission of FIDE recognises and awards seven other titles: International Master (IM), FIDE Master (FM), Candidate Master (CM), Woman Grandmaster (WGM), Woman International Master (WIM), Woman FIDE Master (WFM), and Woman Candidate Master (WCM) are also be given.
- All the titles, including that of Grandmaster, are valid for life, unless a player is stripped of the title for a proven offence such as cheating.
Voice Over 5G:

Reports indicate Reliance Jio, India’s largest mobile carrier, has been testing Voice over New Radio (VoNR) behind the scenes.
- Voice over 5G is also known as Voice over New Radio (VoNR).
- This standard allows voice calls over 5G networks instead of the current standard that uses 4G.
- Vo5G takes all the improvements of 5G – speed, capacity, responsiveness – and applies them squarely to voice.
- It aims to have all that infrastructure and interoperability ready well in advance.
- To use Vo5G, you need three things: a phone that supports Vo5G, a carrier that offers Vo5G, and a 5G signal in your area.
- VoNR brings clear advances over VoLTE with 5G’s substantially higher bandwidth and lower latency compared to 4G LTE.
- It utilizes more advanced audio codecs that provide superior clarity and fidelity based on 5G’s increased data capacity.
- It promises faster call connection times, ensuring a seamless and prompt user experience.
- Vo5G aims to eliminate the notorious call drop issues, particularly during transitions between 5G and 4G.
- Lower packet loss contributes to better reliability, minimising the occurrence of voice cutouts during calls.
International Maritime Organisation:

India was re-elected to the International Maritime Organisation (IMO) Council with the highest tally at elections held at its Assembly in London for the 2024-25 biennium.
- International Maritime Organisation is a specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for measures to improve the safety and security of international shipping and to prevent pollution from ships.
- It is the global standard-setting authority for the safety, security and environmental performance of international shipping.
- Its main role is to create a regulatory framework for the shipping industry that is fair and effective, universally adopted and universally implemented.
- It was established as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization (IMCO) in 1948, became a specialized agency of the United Nations in 1959 and was renamed International Maritime Organization in 1982.
- It is the highest Governing Body of the IMO. It consists of all Member States, and it meets once every two years in regular sessions.
- The Assembly is responsible for approving the work program, voting the budget and electing the Council.
- It is the Executive Organ of the IMO and is responsible, under the Assembly, for supervising the work of the Organization.
- Funding for the organization comes from contributions by Member States, as well as voluntary donations and commercial activities.
- It currently has 175 Member States.
- Headquarters: London.
Dopamine : New Study

A new study shows that dopamine release in the human brain plays a crucial role in encoding both reward and punishment prediction errors.
- Dopamine is a neurotransmitter.
- It is a chemical messenger that helps in the transmission of signals in the brain and other vital areas.
- It is found in humans as well as animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates.
- It plays a role as a “reward center” and in many body functions, including memory, movement, motivation, mood, attention, and more.
- Dopamine is released when your brain is expecting a reward. When you come to associate a certain activity with pleasure, mere anticipation may be enough to raise dopamine levels.
- Dysfunction of the dopamine system has been implicated in different nervous system diseases.
- High or low dopamine levels are associated with diseases including Parkinson’s disease, restless legs syndrome, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Neurons in the region at the base of the brain produce dopamine in a two-step process.
- First, the amino acid tyrosine is converted into another amino acid, called L-dopa.
- Then L-dopa undergoes another change as enzymes turn it into dopamine.
- In other parts of the body, dopamine acts as a type of hormone called catecholamine. Catecholamines are made in the adrenal glands- small hormone production factories that sit on top of the kidneys.
- There are three main catecholamines: Dopamine, Epinephrine (adrenaline), and Norepinephrine.
- These hormones get released into the bloodstream when the body is physically or mentally stressed.
- They cause biochemical changes that activate the so-called fight-or-flight response.
- That’s the body’s natural reaction to real or perceived stress.
Aarogya Maitri Aid Cube: World’s First Portable Hospital

The world’s first portable hospital, ‘Aarogya Maitri Aid Cube’, was unveiled recently in Gurugram.
- Aarogya Maitri Aid Cube is the world’s first portable hospital.
- Designed indigenously under Project BHISHM (Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog Hita and Maitri), the modular trauma management and aid system is made up of 72 detachable mini-cubes, each being a specialized station for emergency response and humanitarian efforts.
- It contains medical equipment and supplies such as a mini-ICU, an operation theatre, cooking station, food, water, a power generator, blood test equipment, an X-ray machine, and more.
- The cubes are capable of handling patients with severe injuries up to 25 major burns, long limb fractures, chest injuries, spinal injuries and approximately 10 head injuries.
- It can treat as many as 200 patients.
- These cubes are light and portable, and can be rapidly deployed anywhere, from airdrops to ground transportation.
Iyothee Thass Pandithar:

The Tamil Nadu government installed a statue of Dalit rights and anti-caste activist Iyothee Thass Pandithar at Gandhi Mandapam in Chennai.
- Iyothee Thass Pandithar was born on 20 May 1845 in Madras presidency.
- He was a prominent anti-caste activist and a practitioner of Siddha medicine.
- In the 1870s, Iyothee Thass organised the Todas and other tribes of the Nilgiri Hills into a formidable force for the freedom movement.
- In 1876, Thass established the Advaidananda Sabha and launched a magazine called Dravida Pandian in collaboration with Rev. John Rathina.
- He established the “Dravida Mahajana Sabha ” in 1891 along with Rettamalai Srinivasan.
- He established the Sakya Buddhist Society in Madras, with branches all over South India.
- The Sakya Buddhist Society, also known as the Indian Buddhist Association, was established in 1898.
- To manage and coordinate the functioning of society, he began a weekly magazine, Tamizhan, in 1907
Codex Alimentarius Commission : Global Standards For Millets

The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC) praised India’s Standards on Millets and accepted its proposal for the development of global standards for millets during its 46th session held in Rome, Italy.
- India has framed a comprehensive group standard for 15 types of millets specifying 8 quality parameters, which received resounding applause at the international meet.
- India put forward a proposal for the development of global standards for millets, particularly for Finger millet, Barnyard millet, Kodo millet, Proso millet and Little millet as group standards as in the case of pulses.
- Codex Alimentarius Commission:
- It is an international food safety and quality standard-setting body.
- It was created by the World Health Organisation and Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations in May 1963.
- Objective is protecting consumer’s health and ensuring fair practices in food trade.
- It consists of 189 member countries.
- Membership of the Commission is open to all Member Nations and Associate Members of FAO and WHO which are interested in international food standards.
- The Commission meets in regular sessions once a year, alternating between Geneva and Rome.
- The programme of work of the Commission is funded through the regular budgets of WHO and FAO, with all work subject to the approval of the two governing bodies of the parent organisations.
- The Commission works in the six official languages of the UN.
- Currently, it has standards for sorghum and pearl millet.
Peace Agreement With United National Liberation Front (UNLF):

The Government of India and Government of Manipur signed a Peace Agreement with United National Liberation Front (UNLF) , which is oldest valley-based insurgent group of Manipur.
- United National Liberation Front (UNLF) was formed in 1964, and is distinct from the insurgent groups active in the state’s Naga-dominated and Kuki-Zomi dominated hills.
- The UNLF is one of the seven “Meitei Extremist Organisations” banned by the Union government under the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act, 1967.
- The UNLF has been operating both within and outside Indian Territory.
- It is believed that the UNLF initially received training from the NSCN (IM), the largest insurgent group among the Naga factions.
- It operates in all the valley areas of Manipur and some villages in the Kuki-Zomi hill districts.
- It is a banned group It mostly operates from camps and training bases in Myanmar’s Sagaing Region, Chin State, and Rakhine State, with support from the Myanmar military.
- The agreement is anticipated to bring about a significant boost in ushering in a new era of peace, particularly in Manipur and the North East region.
- This marks the first instance where a Manipuri armed group from the valley has chosen to abandon violence, returning to mainstream society while committing to respect the Constitution of India and abide by the country’s laws.
- The agreement will not only bring an end to hostilities between UNLF and security forces which have claimed precious lives on both sides over the last more than half a century but also provide an opportunity to address the longstanding concerns of the community.
- The return of the UNLF to the mainstream will also encourage other valley-based armed groups to participate in the peace process.
- A Peace Monitoring Committee (PMC) will be constituted to oversee enforcement of the agreed ground rules.
40th Coast Guard Commanders Conference:

The Union Defence Minister inaugurated the 40th Coast Guard Commanders’ Conference.
- The conference agenda covers vital topics such as improving maritime safety and security, including search and rescue, pollution response, combating contraband and drug trafficking, ensuring the safety of fishermen and seafarers at sea, optimizing coastal security, promoting inter-agency coordination, and enhancing Maritime Domain Awareness.
- ICG was established in 1978 by the Coast Guard Act, 1978 as an independent Armed force of India.
- As the fourth largest Coast Guard in the world, it has played a significant role in securing the Indian coasts and enforcing regulations in the maritime zones of India.
MAHASAGAR : Indian Navy’s Outreach Initiative

The Indian Navy’s outreach initiative, MAHASAGAR, conducted its maiden edition as a virtual interaction between the Indian Chief of the Naval Staff, and heads of navies and maritime agencies from the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) littorals.
- Participating nations included several members of IORA such as Bangladesh, Comoros, Kenya, Madagascar, Maldives, Mauritius, Mozambique, Seychelles, Sri Lanka, and Tanzania.
- They emphasized the importance of harmonizing capacities in the IOR, aligning with India’s vision of SAGAR.
- India’s SAGAR (announced in 2015), which stands for ‘Security and Growth for All in the Region,’ is a vision and policy framework designed to enhance maritime cooperation and security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- The initiative emphasizes the importance of promoting collective security and sustainable development for the benefit of all nations in the region.
ASW Shallow Water Craft (CSL) Project:

The first three ships of the ASW Shallow Water Craft (CSL) project for the Indian Navy, named Mahe, Malvan, and Mangrol, were simultaneously launched on November 30, 2023, at Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), Kochi.
- Mahe class ships are part of the 08 x ASW Shallow Water Craft project and are equipped with indigenously developed underwater sensors for anti-submarine and maritime operations.
- The project aims for ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ with over 80% indigenous content.
- The first ship is expected to be delivered in 2024.
- Aim is to undertake anti-submarine operations in coastal waters, Low-Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO) and Mine Laying Operations.




