Today’s Current Affairs: 4th February 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Qaumi Waqf Board Taraqqiati Scheme (QWBTS):

Implemented by The Ministry of Minority Affairs through the Central Waqf Council (CWC)
- Under this scheme, a dedicated online portal has been developed.
- This dedicated online portal is the Waqf Assets Management System of India (WAMSI) for computerization, digitization of records of Waqf properties and Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping of Waqf properties to prevent encroachment.
- The Waqf property details on WAMSI have been entered by the respective State Waqf Boards (SWBs).
- As per Section 40 of the Waqf Act 1995 (as amended in 2013) the State Waqf Board is empowered to decide any question which arises as to whether a particular property is a Waqf property or not or whether a Waqf is a Sunni Waqf or a Shia Waqf.
- The decision of the Board on a question, unless revoked or modified by the Tribunal, be final.
Central Waqf Council (CWC):
- It is a statutory body under the Ministry of Minority Affairs.
- It was set up in 1964 as per the provision given in the Waqf Act, 1954 as Advisory Body to the Central Government on matters concerning the working of the Waqf Boards and the due administration of Auqaf.
- The Council has been empowered to advise the Central Government, State Governments and State Waqf Boards.
- It will now issue directives to the boards/ State Government to furnish information to the Council on the performance of the board particularly on their financial performance, survey, revenue records, encroachment of Waqf properties, Annual and Audit report etc.
Judicial Majoritarianism:

As the recent majority judgment of the Supreme Court on demonetisation comes under criticism, the minority judgment by J. Nagarathna is being hailed for its challenge to the RBI’s institutional acquiescence to the Central government.
Judicial Majoritarianism:
- As opposed to standard matters heard by Division Benches consisting of two judges, numerical majorities are of particular importance to cases which involve a substantial interpretation of constitutional provisions.
- In such cases, Constitutional Benches, consisting of five or more judges, are set up in consonance with Article 145(3) of the Constitution.
- Such Benches usually consist of 5, 6, 9, 11 or even 13 judges.
- This is done to facilitate decision-making by ensuring numerical majorities in judicial outcomes.
- Article 145(5) of the Constitution states that no judgment in such cases can be delivered except with the concurrence of a majority of the judges but that judges are free to deliver dissenting judgments or opinions.
What Is Angel Tax?

The Section 56 (2) (vii b) in the Income Tax Act is referred to as Angel tax.
- These taxes are imposed on startups.
- During Union Budget 2023, Finance Minister Smt Nirmala Sita Raman proposed to amend the Angel tax.
- Now, the equity amount received by the startups will be subjected to income taxes and not angel taxes.
- Meaning, the entire 50 crores of rupees, that is, the total amount the startup received by selling the shares is subjected to income tax! Earlier, only 30 cores were subjected to taxes.
- Most of the investors of the startups, that is, the share buyers are from foreign countries.
- Already startup investments have been decreasing.
- In 2022, it fell by 33%.
- The new change in Angel Tax is to further affect the startup investment.
Amrit Bharat Station Scheme : 15 Railway Stations Selected To Be Developed

Recently, 15 railway stations under Tiruchi Division Railway Division were selected to be developed under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme.
- The Union Ministry of Railways launched Amrit Bharat Station Scheme in December 2022 to modernize over 1,000 small stations over the coming years.
- The scheme will subsume all previous redevelopment projects where work is yet to begin.
- Key features for these proposed stations:
- provisions for roof top plazas,
- longer platforms,
- ballastless tracks; and
- 5G connectivity.
Red Sanders : Smuggled

About 20,000 tonnes of Red Sanders were smuggled from India between 2016 and 2020 according to The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) report.
- Red Sanders is a flora species that are endemic to a distinct tract of forests in the Eastern Ghats region of Andhra Pradesh.
- Geographical conditions required: It usually grows in rocky, degraded and fallow lands with Red Soil and a hot and dry climate.
- Protection Status:
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- CITES: Appendix II
- Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972: Schedule IV
What Is a Pioneer Investor?
 International Seabed Authority has officially designated India as a Pioneer Investor
International Seabed Authority has officially designated India as a Pioneer Investor
- Pioneer Investor is An early investment made in any new sector or technology. E.g. Polymetallic nodules at the ocean bed.
India’s Step for PMN and Blue Economy:
- The International Seabed Authority (ISA) and the Ministry of Earth Sciences also exchanged PMN (Polymetallic Nodules) exploration extension contract
- India is framing the Blue Economy policy framework, which aims at covering the coastal economy, tourism, marine fishery, deep-sea mining etc.
- As a part of the Deep Ocean Mission, India concluded the world’s first locomotive trials of a deep-sea mining system in the central Indian ocean last year (2022).
Deep Ocean Mission:
- It would develop a manned submersiblethat can carry three people to a depth of 6,000 meters in the ocean for exploring and, then, extracting minerals in the deep seabed.
- It also aims to explore marine biodiversity for the sustainable use of resources.
- It has recently been allocated Rs 600 Cr(Budget 2023-24)
International Seabed Authority:
- ISA (HQ: Jamaica, est. 1994) is an intergovernmental body of 167 member states and the European Union established under the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea and its 1994 Agreement on Implementation
- It comes under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)for monitoring all activities related to mineral resources in the deep sea.
- The international seabed is the area that lies beyond the limits of national jurisdiction and represents around 50% of the total area of the world’s oceans.
Bal Mitra : Delhi Commission For Protection Of Child Rights

Delhi Commission for Protection of Child Rights (DCPCR) launched ‘Bal Mitra’, a WhatsApp Chatbot to provide communication support to children and parents in Delhi.
It will include:
- Complaint registration
- Searching for information and tracking complaint status
- Seeking information on admissions
- Providing authentic information on various matters related to children and their rights
- This initiative can be used as an example for showing “how technology can help in securing child’s rights and creating awareness”.
- It can also be used as an example of e-governance initiatives.
Government e-Marketplace:

Government e-Marketplace achieves a Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of Rs. 1.5 Lakh Crores.
- GeM has been effectively contributing to the government’s commitment of “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance”.
Gross Merchandise Value (GMV):
- GMV refers to the value of goods sold via customer-to-customer or e-commerce platforms.
- It is calculated prior to the deduction of any fees or expenses.
- It is a measure of the growth of the business or use of the site to resell products owned by others through consignment.
Government e-marketplace (GeM):
- The GeM is an online platform launched by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India in 2016 to facilitate procurement of goods and services by various government departments and organisations.
- It is open to all government departments, public sector undertakings, autonomous bodies and other organisations.
- Currently, GeM stands at the third position after Singapore’s GeBIZ.
Exercise Trishakti Prahar:

The Indian military recently concluded exercise Trishakti Prahar — a joint training exercise in North Bengal (close to the strategic ‘Siliguri’ corridor).
- The aim of the exercise was to practise battle preparedness of the security forces, using latest weapons and equipment in a networked, integrated environment, involving the Army, the IAF and CAPFs.
- The exercise concluded with an Integrated Fire Power Exercise at the Teesta Field Firing Ranges, aimed at synergising the firepower assets of the Indian Armed Forces and CAPFs to orchestrate an integrated battle.
- The Siliguri corridor or Chicken’s neck (West Bengal) is a stretch of land bordering Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal, measuring approximately 170×60 km; at the narrowest it is about 20-22 km.
Space Debris Orbiting Earth:
The Government of India has announced that 111 payloads and 105 space debris have been identified as Indian objects orbiting Earth.
- All orbiting debris will affect the future of outer space and future missions.
- Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has also been carrying out several studies on the impact of growing space debris on the space environment.
- Space debris refers to man-made objects in Earth’s orbit that no longer serve a useful purpose.
- This includes defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments of debris from collisions or other events.
- The floating space debris is a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- This overpopulation of space with objects and debris is referred to as Kessler Syndrome.
- The accumulation of space debris in specific orbital regions can limit the availability of desirable orbital slots for future missions.
- The increasing amount of space debris makes it more challenging for satellite operators and space agencies to accurately track and predict the orbits of objects in space.
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris.
- ISRO also carried out 21 collision avoidance manoeuvres of Indian operational space assets in 2022 to avoid collisions with other space objects.
- ISRO has also set up a Centre for Space Debris Research to monitor and mitigate the threat of space debris.
- ‘Project NETRA’ is also an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
Macrosomia:
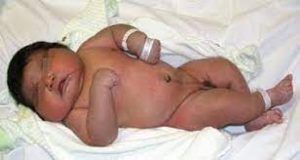
A mother in Brazil gave birth to a two-foot-tall baby weighing 16lb (7.3kg)
- Macrosomia term used to describe giant babies is macrosomia (Greek for the large body). Any baby that weighs more than 4kg, regardless of its gestational age, is said to have macrosomia.
- Factors that cause Macrosomia:
- The mother’s body weight: Obese mothers are more likely to have children with Macrosomia.
- Mothers with gestational diabetes: High blood sugar that arises during pregnancy, this increases to between 15 per cent and 45 per cent of births.
- Being older when pregnant also increases the odds of having a baby with macrosomia.
- Overdue pregnancies: Those that run past the typical 40 weeks – also increase the risk of a baby being macrosomic, particularly at 42 weeks or more.
- Previous pregnancies increase the risk of macrosomia because, with each successive pregnancy, birth weight increases.
- Macrosomic baby may cause permanent harm to shoulders of a baby.
- While the baby is stuck, it cannot breathe and the umbilical cord may be squeezed.
- Mothers are also at increased risk of vaginal tears during delivery, which then increases the risk of postpartum haemorrhage (bleeding)
NASA’s Juno spacecraft : Lost Images Taken During a Jupiter Flyby

NASA’s Juno spacecraft experienced a glitch that caused it to lose over 200 images taken during a Jupiter flyby.
- Juno Probe was launched in 2011, the Juno spacecraft initially embarked on a 5-year journey to the largest planet in our solar system.
- Towards the end of its primary mission, the spacecraft’s objectives evolved, and it transitioned into a full Jupiter system explorer with flybys of Jovian moons.
- Goal is Understand the origin and evolution of Jupiter, look for a solid planetary core, map the magnetic field, measure water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe auroras.
Jupiter:
- Jupiter, a gas giant planet covered in thick red, brown, yellow and white clouds, boasts a diameter of about 89,000 miles.
- Interior models based on Juno data indicated Jupiter has a large “diluted” core representing about 5 to 15 % of the planet’s mass comprised of rocky and icy material unexpectedly mixed with light elements like hydrogen and helium.
Mission For The Welfare Of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups:

Union Finance Minister recently announced a mission for the welfare of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in the 2023-24 Union Budget.
- Pradhan Mantri PVTG Development mission will be launched as part of ‘Reaching The Last Mile’, one of the seven Saptarishi priorities enlisted in this year’s Budget.
- The mission will saturate the particularly vulnerable tribal groups with safe housing, clean drinking water, education, nutrition, road and telecom connection and livelihood.
- A Budget of Rs 15,000 crore will be dedicated to this mission in the next three years.
- The scheme will benefit 3.5 lakh tribals.
Saptarishi priorities (seven priorities) enlisted in the 2023-24 budget:
- Inclusive Development
- Reaching the Last Mile
- Infrastructure and Investment
- Unleashing the Potential
- Green Growth
- Youth Power
- Financial Sector
PVTG (Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups):
- PVTGs are more vulnerable among the tribal groups who are in need of greater support and development.
- Out of the 705 Scheduled Tribes in India, 75 have been identified as PVTGs and are spread across 17 states and one Union Territory.
- Government of India follows the following criteria for identification of PVTGs
- Pre-agricultural level of technology
- Low level of literacy
- Economic backwardness
- A declining or stagnant population.
Subsidiary Of EXIM Bank:

Union Finance Minister recently announced the setting up of a subsidiary of EXIM Bank and data embassies at GIFT City in Gujarat.
- EXIM Bank is the premier export finance institution of the country.
- It was established by the Government of India, under the Export-Import Bank of India Act, 1981
- EXIM Bank wholly owned by the Government of India.
- EXIM Bank provides financial assistance to exporters and importers.
- It extends Lines of Credit (LOCs) to overseas financial institutions, regional development banks, sovereign governments and other entities overseas, to enable buyers in those countries to import developmental and infrastructure projects, equipment, goods and services from India, on deferred credit terms.
- It functions as the principal financial institution for coordinating the work of institutions engaged in financing export and import of goods and services with a view to promoting the country’s international trade.
- The operations of the Bank are governed by a Board of Directors.
- The Board of Directors consists of a chairman, a managing director, two deputy managing directors; one director each nominated by the Reserve Bank of India; IDBI Bank Ltd. and ECGC Ltd.; and not more than 12 directors nominated by the Central Government.
Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City):
- It is located in the state of Gujarat, between Ahmedabad and Gandhinagar, on the bank of river Sabarmati.
- The GIFT city is built on 886 acres and has a multi-service Special Economic Zone (SEZ).
- It is home to India’s first International Financial Services Centre(IFSC) and also has Domestic Tariff Area (DTA)
Senior Citizen Savings Scheme:

The maximum investment limit for the Senior Citizen Savings Scheme (SCSS) has been increased from Rs 15 lakh to Rs 30 lakh in Budget 2023.
- Senior Citizen Savings Scheme was launched with the main aim of providing senior citizens in India a regular income after they attain the age of 60 years old.
- Eligiblility:
- Indian citizens above the age of 60 years.
- Retirees in the age bracket of 55-60 years who have opted for Voluntary Retirement Scheme (VRS) or Superannuation.
- Retired defence personnel above 50 years and below 60 years of age.
- It has a maturity period of five years. But, a depositor can extend one’s maturity period for another three years.
- Individuals are allowed to operate more than one account by themselves or open a joint account with their spouse.
- Eligible investors can make a lump sum deposit
- Minimum Deposit– Rs. 1,000 (and in multiples thereof)
- Maximum Deposit– Rs. 15 Lakh or the amount received on retirement, whichever is lower(Increased to Rs 30 lakh in Budget 2023).
- Under SCSS, the interest amount is paid to the accountholders quarterly.
- After one year of opening the account, premature withdrawal is allowed.
- Deposits in SCSS qualify for deduction u/s 80-C of Income Tax Act.




