Today’s Current Affairs: 4th November 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Global One-Stop Centres:

The Ministry of External Affairs’ proposal to establish nine One-Stop Centres (OSCs) has received approval from the Empowered Committee of the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- These centres aim to provide comprehensive assistance to women in vulnerable situations, addressing their immediate needs and offering critical support.
- Out of the nine proposed OSCs, seven will include shelter homes and will be set up in Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia (with centres in both Jeddah and Riyadh).
- The remaining two centres, located in Toronto and Singapore, will operate without shelter home facilities.
- To facilitate the rollout of these initiatives, the Ministry of External Affairs has opened a dedicated budget line for these missions.
- The Indian Community Welfare Fund (ICWF) will play a vital role in extending welfare measures to distressed Indian nationals, particularly women.
- The ICWF has significantly expanded its scope to address a wide range of issues faced by overseas Indians.
- The fund now covers emergency assistance such as boarding and lodging, air travel for those stranded, legal aid, medical care, and the repatriation of mortal remains.
- The ICWF guidelines include specific provisions for legal assistance and counselling for women abandoned by their overseas Indian or foreign spouses.
- Legal panels have also been established in countries with large Indian diasporas to provide timely and efficient support.
- In cases involving minor legal infractions, the fund allows for the payment of fines to secure the release of Indian nationals.
Nazca Lines : Study

Artificial intelligence was used by the researchers to discover more mysterious Nazca geoglyphs in Peru.
- Nazca Lines are a group of geoglyphs, or large designs made on the ground by creators using elements of the landscape such as stones, gravel, dirt or lumber.
- These are located in the arid Peruvian coastal plain, some 400 km south of Lima.
- The Nazca Lines were discovered by hikers in the mid 1920s and later on Peruvian archaeologist Toribio Mejia Xesspe studied them systematically in 1926.
- These are believed to be the greatest known archaeological enigma, owing to their size, continuity, nature and quality.
- They depict creatures from both the natural world and the human imagination.
- They include animals such as the spider, hummingbird, monkey, lizard, pelican and even a killer whale. Ancient artisans also depicted plants, trees, flowers and oddly shaped fantastic figures, as well as geometric motifs, such as wavy lines, triangles, spirals and rectangles.
- The vast majority of the lines date from 200 B.C. to A.D. 500, to a time when a people referred to as the Nazca inhabited the region.
- The earliest lines, created with piled up stones, date as far back as 500 B.C.
- The Lines were declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1994.
High Risk Food Category:

The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has decided to treat the packaged drinking and mineral water segment as a “High Risk Food Category”.
- Food products that come under the “High Risk” category are subjected to mandatory risk-based inspections.
- They include dairy, meat, fish egg, and food items intended for nutritional use, prepared food, Indian sweets and nutrients, and related preparations such as fortified rice kernel.
- In its order, the FSSAI has made amendments in its Risk-Based Inspection Policy to include the packaged drinking water and mineral water categories.
- This means that these products will now be subject to mandatory inspections and third-party audits.
- All centrally licensed manufacturers under high-risk food categories shall get their businesses audited annually.
- This aims to improve the safety and quality standards of these products for consumers.
- Previously, the packaged drinking water industry had called for simplified regulations, requesting the removal of dual certification requirements from both BIS and FSSAI.
Jim Corbett National Park : Misuse Of Drones And Cameras Planted

A study has concluded that the drones and cameras originally planted in the Jim Corbett National Park for conservation activities, such as monitoring animals, are being deliberately misused by local government officials and men to surveil women without consent.
- Jim Corbett National Park is located at the foothills of the Himalayas in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand.
- It is the first national park of India, established in 1936. It was named Hailey National Park then.
- In 1957, the park was rechristened Corbett National Park in memory of the late Jim Corbett, a great naturalist and eminent conservationist.
- Known for housing the endangered Bengal tiger, Corbett National Park is part of the larger Corbett Tiger Reserve.
- It was the first place where Project Tiger was launched in 1973.
Exercise Harimau Shakti:

The 4th edition of Exercise HARIMAU SHAKTI commenced at Bentong camp, Pahang district, Malaysia.
- Exercise Harimau Shakti is a joint military exercise conducted between India and Malaysia.
- Indian contingent comprising personnel is being represented by a Battalion of MAHAR Regiment.
- It is an annual training event conducted alternatively in India and Malaysia. Last edition was conducted in November 2023 at Umroi Cantonment in Meghalaya, India.
- Aim of the Joint Exercise is to enhance joint military capability of both sides to undertake counter insurgency operations in jungle terrain under Chapter VII of the United Nations Mandate. The exercise will focus on operations in the jungle environment.
- The 2024 exercise will be conducted in two phases.
- The first phase will be focused on cross training between both the Armies including lectures, demonstrations, and practices of various drills in jungle terrain.
- In the final phase both the Armies will take active part in a simulated exercise, wherein troops will execute various drills including Anti-MT Ambush, Occupation of Harbour, Carrying out Recce Patrol, Ambush and an Attack on area taken over by the terrorists.
- It will enable both sides to share best practices in Tactics, Techniques and Procedures of conducting joint operations.
- It will facilitate developing inter-operability, bonhomie and camaraderie between the two armies.
Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users’ Conference:
The 14th Asia-Oceania Meteorological Satellite Users’ Conference (AOMSUC-14) is being held from December 4-6, 2024, in New Delhi, India.
- The first AOMSUC was held in Beijing, China, in 2010. Since then, it has been hosted annually in various locations across Asia-Oceania.
- The AOMSUC has become a premier event for meteorologists, earth scientists, satellite operators, and students from across the region and the globe.
- This year’s conference is hosted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD), Ministry of Earth Sciences, and it will feature high-quality oral and poster presentations, panel discussions, and a training workshop focused on applying current satellite data for meteorological and climatologically applications.
- The conference aims to:
- Promote the importance of satellite observations
- Advance satellite remote sensing science
- Provide a platform for dialogue and collaboration between satellite operators and users
- Inform the community about the current status and future plans of international space programs
- Encourage the development of new technologies for weather satellite sensing
- Engage young scientists in the field
National Housing Bank:

Aviom India Housing Finance has informed its creditors about an ongoing audit by the National Housing Bank (NHB) following the discovery of fraudulent transactions during a recent onsite supervisory inspection.
- National Housing Bank (NHB) is an apex agency established to promote housing finance companies (HFCs) in India.
- It is an All-India Financial Institution (AIFl) wholly owned by the Government of India (GoI).
- It supervises HFCs, while regulation of HFCs is with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The National Housing Policy, 1988, envisaged the setting up of NHB as the apex-level institution for housing.
- In pursuance of the above, NHB was set up on July 9, 1988, under the National Housing Bank Act, 1987.
- RBI contributed the entire paid-up capital.
- The broad functions of NHB as a part of its objective of building a strong, healthy, cost-effective, and viable Housing Finance System include:
- Supervision and grievance redressal regarding HFCs
- Financing
- Promotion and Development.
- NHB RESIDEX: It is the country’s first official housing price index (HPI). It captures movements in the prices of residential real estate prices.
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis : Data
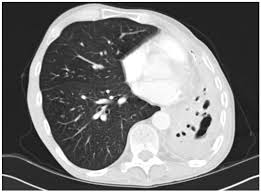
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA) claims over 340,000 lives annually, with a recent study revealing its severe impact on individuals with pre-existing lung diseases.
- Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CPA) is a fungal infection of the lungs, caused by Aspergillus, a common type of mold.
- Aspergillus is commonly found in households, workplaces, and public spaces, as well as in outdoor areas.
- People who have chronic lung conditions, such as emphysema, bronchitis, or tuberculosis, are most at risk of developing CPA.
- CPA is not contagious.
- It cannot be passed from person to person.
- CPA doesn’t always cause symptoms in the early stages.
- When symptoms do occur, they can vary from person to person.
- The most common symptom of CPA is coughing up blood.
- For most people, CPA is a lifelong condition, and long-term management is needed. However, for a small number of people, CPA may sometimes resolve completely.
- Antifungal medications are the most common treatment for CPA.
- Surgery is an option to remove the fungal mass.
- This is done when CPA causes bleeding in the lungs.
Global Cooperation in Space Debris Management:
The issue of increasing satellites and space debris in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) has gained international attention, with experts warning that without global cooperation, this vital region of space may become unusable.In October 2024, a United Nations panel on space traffic coordination called for urgent measures to address this challenge.
Global Plastic Treaty:
Global plastic treaty talks failed to reach a consensus at the 5th meeting of the United Nations(UN) Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-5) in Busan, South Korea.A resolution adopted in 2022 at the UN Environment Assembly in Nairobi aimed to establish global rules to curb plastic pollution by the end of 2024, but nations were unable to reach an agreement.
The delegations agreed that another session would be scheduled in 2025, tentatively being calling “INC-5.2,” to finalize the treaty.
WIPO World Intellectual Property Indicators 2024 Report:
India has gained notable recognition in the global intellectual property (IP) arena, ranking among the top 10 nations for patents, trademarks, and industrial designs, as per the WIPO World Intellectual Property Indicators (WIPI) 2024 report.The report highlights continued growth in global IP filings, reflecting innovation resilience despite economic challenges. This increase was largely driven by residents in China, the US, Japan, South Korea, and India.
India Adopts CubeSat Standard:
India adopted the global CubeSat standard, marking a significant step in its ambition to enhance its footprint in the global space economy.CubeSat standards define a modular satellite framework (1 unit (U) = 10 cm³, ≤1.33 kg) compatible with standard deployers, requiring uniform dimensions, low-outgassing materials, kill switches, and rigorous testing. The standard CubeSat size uses a “one unit” or “1U” measuring 10x10x10 cms and is extendable to larger sizes like 1.5, 2, 3, 6, and even 12U.
Paryatan Mitra and Paryatan Didi:
The Ministry of Tourism highlighted a national responsible tourism initiative called Paryatan Mitra/Paryatan Didi in the Lok Sabha.Paryatan Mitra/Paryatan Didi launched in September 2024, aims to provide a better tourist experience through training local stakeholders to be tourist-friendly ambassadors and storytellers. It Special emphasis on training women and youth to create innovative tourism products like heritage walks, food tours, and nature treks.
Design Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme: In News
India’s first indigenously designed 3GPP compliant modem system-on-chip (SoC), developed by WiSig Networks under the government’s Design Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme, faces production challenges despite significant funding.Supports the growth of domestic companies, startups, and MSMEs in semiconductor design, fostering import substitution and value addition in the electronics sector.Provides financial incentives and infrastructure for semiconductor design, including Integrated Circuits (ICs), chipsets, System on Chips (SoCs), IP cores, and other linked designs, over five years.
Ratapani Tiger Reserve:
The Madhya Pradesh government has officially notified the Ratapani Wildlife Sanctuary as the state’s 8th Tiger Reserve. Ratapani Tiger Reserve Situated in the Vindhyachal Mountain Ranges across Raisen and Sehore districts of Madhya Pradesh. Initially declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1976, extended in 1983, and received NTCA’s approval for a tiger reserve in 2008.
Inner Line Permit System:
The Manipur government launched a review of the ILP system following violations, highlighting the importance of stringent implementation. Inner Line Permit (ILP) is a travel document required by Indian citizens from outside certain states to enter and stay for a limited period in protected regions. Originated during the colonial era under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation Act, 1873, to protect Crown interests.
India Launches First ‘Uber Shikara’ Service in Srinagar:
Uber has launched Asia’s first water transport service, Uber Shikara, in the scenic Dal Lake in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir. This innovative initiative aims to offer a seamless and modern way for tourists to experience the traditional shikara ride, a popular attraction in the region, combining technology with Kashmir’s cultural heritage. With this new service, Uber seeks to uplift tourism and provide greater accessibility, making the shikara experience more convenient and hassle-free for visitors.
Oxford Picks “Brain Rot” as 2024’s Top Word:
Oxford University Press (OUP) has announced ‘brain rot’ as the Oxford Word of the Year 2024, reflecting a defining cultural and societal theme of the year. The term gained prominence due to concerns over the detrimental effects of consuming excessive amounts of low-quality online content, especially via social media. Selected through a global public vote involving over 37,000 participants and expert analysis of language trends, ‘brain rot’ captures the zeitgeist of 2024, where digital consumption and its consequences have been central topics of discussion.
RBI Lifts Supervisory Restrictions on Navi Finserv:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) lifted the supervisory restrictions imposed on Navi Finserv, a non-banking financial company (NBFC) led by Sachin Bansal. This decision comes after the company took significant corrective measures to address the regulatory concerns that had led to the imposition of restrictions on October 17, 2024, primarily related to loan pricing practices and non-compliance with lending norms.
Pavan Kampelli Wins Bronze in eFootball at Asian Esports Games:
India’s Pavan Kampelli has made history by securing a bronze medal in eFootball at the 2024 Asian Esports Games held in Bangkok. This marks India’s first-ever podium finish in the eFootball category, a monumental achievement in the country’s esports journey. Known as ‘Mr Tomboy’, Pavan showcased his exceptional skill and determination throughout the competition, battling some of the best eFootball players in Asia.
UNESCO Declares West Bengal a Top Heritage Tourism Destination:
West Bengal’s tourism sector has received international recognition with UNESCO declaring it a top destination for heritage tourism. Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee emphasized the state’s significant progress in religious, heritage, and tea tourism. This development has not only boosted tourism but also generated employment for thousands of youth. West Bengal’s focus on enhancing iconic religious sites and heritage spots is driving its tourism to new heights, fostering job creation, and making it a key player in India’s tourism landscape.
Indian Council of Social Science Research : Implementation of the 7th Central Pay Commission revised pay scales

Faculty and staff members from Indian Council of Social Science Research (ICSSR) institutions have written to the Minister of Education expressing concern over the delay in implementation of the 7th Central Pay Commission revised pay scales.
- Indian Council of Social Science Research (ICSSR)was established in the year 1969 by the Government of India to promote and fund research in the social sciences in the country.
- It was established on the recommendation of Prof. V. K. R. V. Rao Committee.
- It is an autonomous organisation working under the aegis of the Department of Higher Education, Ministry of Education
- It provides grants for projects, fellowships, international collaboration, capacity building, surveys, publications, etc. to promote research in social sciences in India.
- An all-India network of 24 frontline research institutes and six regional centres is maintained, and five recognized institutes are programmatically supported by the ICSSR.
- The Documentation center of ICSSR – National Social Science Documentation Centre (NASSDOC)-provides library and information support services to researchers in social sciences.
- ICSSR has developed the ICSSR Data Service to serve as a national data service for promoting a powerful research environment through the sharing and reuse of data among the social science community in India.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
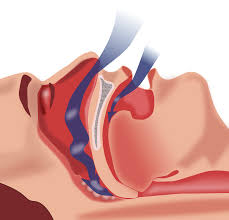
Obstructive sleep apnea contributes to the development of dementia among adults—particularly women, a study suggests
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder.
- People with OSA repeatedly stop and start breathing while they sleep.
- OSA occurs when a blockage in your airway keeps air from moving through your windpipe while you’re asleep.
- The blockage and lack of airflow can cause your blood oxygen levels to drop, triggering a survival reflex in your brain that wakes you up just enough to breathe again.
- This happens off and on many times during sleep.
- While that reflex is key in keeping you breathing, it also disrupts your sleep.
- When your breathing is reduced and you’re not taking enough oxygen, it’s called hypopnea. If your breathing completely stops, it’s called apnea.
- Snoring is one of the biggest symptoms of OSA.
- Anyone at any age can have OSA. But it’s most common in middle-aged and older adults.
- OSA has significant implications for cardiovascular health, mental illness, quality of life, and driving safety.
- Treatments for OSA are available.
- One treatment is a device that uses positive pressure to keep the airway open during sleep.
- Another option is a mouthpiece to thrust the lower jaw forward during sleep.
- In some people, surgery might be an option too.
First In The World Challenge Initiative:
Aimed at encouraging Indian scientists to come up with innovative ideas for finding solutions to difficult health problems, the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has announced a new initiative called “First in the World Challenge”.
- The “First in the World” Challenge, inspired by the success of Chandrayaan-3, is a major initiative of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) designed to promote the development of groundbreaking health technologies.
- The scheme aims to foster novel, out-of-the-box, futuristic ideas, new knowledge generation, and discovery/development of breakthrough health technologies (vaccines, drugs/therapeutics, diagnostics, interventions, etc.) that have never been thought of, tested or tried in the world till date.
- This high-risk, high-reward program will provide funding for projects at various stages, from proof-of-concept to prototype and final product development.
- The proposal must have bold research ideas with significant wide-ranging impact and, if successful, should have potential ‘first of its kind’ biomedical and technological innovations for better health outcomes in the global context.
- Proposals aiming for ‘incremental’ knowledge’ or ‘process innovation ‘will not be funded through this scheme.
- The proposals can be submitted by an individual or by a team of researchers either from a single institute or from multiple institutes
- Every team application must designate one Principal Investigator from the team who will be responsible for technical, administrative, and financial deliverables.
- A selection committee will be formed by experts of high repute, innovators, policymakers and scientists with outstanding record of conducting research and innovation in the biomedical domain.
- This initiative will inspire our scientists to come up with innovative ideas for finding solutions to difficult health problems.
Sendai Framework For Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030:

India is committed to the Sendai Framework for disaster risk reduction, the Prime Minister’s Principal Secretary said recently, while calling for increased international collaboration to enhance disaster resilience.
- Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 was the first major agreement of the post-2015 development agenda and provides member states with concrete actions to protect development gains from the risk of disaster.
- It was adopted by the UN member states at the Third UN World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction in Sendai, Japan, on March 18, 2015.
- It is the successor instrument to the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) 2005-2015.
- The Sendai Framework advocates for:
- The substantial reduction of disaster risk and losses in lives, livelihoods, and health and in the economic, physical, social, cultural, and environmental assets of persons, businesses, communities, and countries.
- It recognizes that the State has the primary role to reduce disaster risk, but that responsibility should be shared with other stakeholders, including local government, the private sector, and other stakeholders
Gastrodia lohitensis : New Leaf Of Orchid Species
A team of Indian botanists has identified a new leafless orchid species, Gastrodia lohitensis, in Arunachal Pradesh’s Lohit district.
- Gastrodia lohitensis is a leafless orchid species found in bamboo thickets around Tezu and it is named after Lohit district.
- The orchid presents unique adaptations, thriving without sunlight by extracting nutrients from fungi in decomposing leaf litter.
- It grows 50-110 cm tall, the orchid’s defining features include a pair of linear calli and ridges on its flower lip, setting it apart from closely related species in Southeast Asia.
- It flourishes only in dense, shaded bamboo canopies, underlining its limited ecological niche.
- With just a small range in the district, Gastrodia lohitensis faces pressures from local land use, including bamboo harvesting and agriculture.
- Conservationists stress that the survival of this rare orchid depends on protecting its fragile habitat in Arunachal Pradesh’s biodiverse landscape.
Kodo millet : Cause Of Death Of Elephant

The Principal Chief Conservator of Forests (Wildlife) said that the deaths of elephants in Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve could have been caused by “mycotoxins associated with kodo millet”.
- Kodo millet is also known as Kodra and Varagu in India.
- It is one of the “hardiest crops, drought tolerant with high yield potential and excellent storage properties,” It is rich in vitamins and minerals.
- It is a staple food for many tribal and economically weaker sections in India.
- The tropical and subtropical regions are best suited for Kodo millet cultivation.
- It is grown on poor soils, and widely distributed in arid and semi-arid regions.
- The millet is believed to have originated in India and Madhya Pradesh (MP) is one of the largest producers of the crop, according to a 2020 research paper.
- Apart from MP, the millet is cultivated in Gujarat, Karnataka, Chhattisgarh, and parts of Tamil Nadu.
- The crop is grown in India, Pakistan, the Philippines, Indonesia, Vietnam, Thailand, and West Africa.
- According to the research paper, “CPA (Cyclopiazonic acid) is one of the major mycotoxins associated with the kodo millet seeds causing kodo poisoning which was first recognised during the mid-eighties”.
- Kodo poisoning occurs mainly due to the consumption of Kodo grains, when “maturing and harvesting if the grains had encountered with rainfall, resulting in a fungal infection leading to ‘poisoned Kodo’ which is locally known as ‘Matawna Kodoo’ or ‘Matona Kodo’ in northern India.”
- Kodo poisoning mainly affects the nervous and cardiovascular systems and the chief symptoms include “vomiting, giddiness, and unconsciousness, small and rapid pulse, cold extremities, shaking of limbs and tremors.”




