Today Current Affairs: 7th June 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
US Suspends Retaliatory Tariffs On India:

The US suspended imposition of retaliatory tariffs against six countries, including India, that had begun imposing digital services tax on companies such as Google and Facebook.
- Other than India, the countries slapped with this tariff proposal are Austria, Italy, Spain, Turkey, and the United Kingdom.
- Tariffs were imposed after the office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) noted that the Digital services taxes adopted by India, Italy, and Turkey discriminate against US companies and are inconsistent with international tax principles.
- Under Section 301 of the Trade Act of 1974, the USTR enjoys a range of responsibilities and authority to investigate and take action to enforce US national interests under trade agreements and respond to certain foreign trade practices.
Digital Services Taxes:
- DSTs are the adopted taxes on revenues that certain companies generate from providing certain digital services. E.g. digital multinationals like Google, Amazon and Apple etc.
- The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is currently hosting negotiations with over 130 countries that aim to adapt the international tax system. One goal is to address the tax challenges of the digitalization of the economy.
- Some experts argue that a tax policy designed to target a single sector or activity is likely to be unfair and have complex consequences.
- Further, the digital economy cannot be easily separated out from the rest of the global economy.
Incredible India Tourist Facilitator Certification Programme (IITFC):

On the occasion of World Environment Day (5th June), the Tourism Minister appreciated the Incredible India Tourist Facilitator Certification Programme (IITFC).
- IITFC Programme is a digital initiative of the Ministry of Tourism (MoT), for the citizens of India to become a part of the booming Tourism Industry.
- It is an online programme where one can learn about tourism at their own time, space, path and pace.
- The successful completion of this programme would enable the learner to become a Certified Tourist Facilitator of the Ministry of Tourism.
Tourism & Hospitality Sector in India:
- In FY20, the tourism sector in India accounted for 39 million jobs, which was 8% of the total employment in the country. By 2029, it is expected to account for about 53 million jobs.
- According to WTTC (World Travel and Tourism Council), India ranked 10th among 185 countries in terms of travel & tourism’s total contribution to GDP in 2019. During 2019, the contribution of travel & tourism to GDP was 6.8% of the total economy.
- By 2028, international tourist arrivals are expected to reach 30.5 billion and generate revenue over USD 59 billion.
UN Global Compact’s CEO Water Mandate:

India’s largest power utility, NTPC Ltd, has become a signatory of UN Global Compact’s CEO Water Mandate.
- CEO Water Mandate is a UN Global Compact initiative that demonstrates the commitment and efforts of companies to enhance their water and sanitation agendas in line with Sustainable Development Goals.
- It has been designed to assist companies in developing, implementing and disclosing comprehensive water strategies and policies.
- It provides a platform for companies to link with like-minded businesses, public authorities, UN agencies, civil society organizations etc.
The UN Global Compact initiative:
- It is a non-binding United Nations pact to encourage businesses and firms worldwide to adopt sustainable and socially responsible policies and to report on their implementation.
- Launched in 2000.
- It is a principle-based framework for businesses, stating ten principles in the areas of human rights, labor, the environment and anti-corruption.
- Under the Global Compact, companies are brought together with UN agencies, labor groups and civil society.
- Cities can join the Global Compact through the Cities Programme.
- NTPC has already taken a series of measures across its plant locations on sound water management.
- NTPC will further imbibe the 3 R’s (reduce, reuse, recycle) for water conservation and management while carrying out its core business activity of power generation.
- The NITI Aayog report on ‘Composite Water Management Index (2018)’ underlines that over 600 million Indians face high to extreme water stress.
- According to a World Bank report, the amount of water currently available to an individual will fall below half of the 1,588 cubic meters per year by 2030. This will create unimaginable disaster for the majority people in India.
- India has 4% of the world’s freshwater which has to cater to 17% of the world’s population.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj:

On the occasion of the anniversary of Maratha king’s coronation day (6th June), the Goa government has released a short film on Chhatrapati Shivaji.
- He was born on 19th February, 1630 at Shivneri Fort in District Pune in the present-day state of Maharashtra.
- He was born to Shahaji Bhonsle, a Maratha general who held the jagirs of Pune and Supe under the Bijapur Sultanate and Jijabai, a pious woman whose religious qualities had a profound influence on him.
- He displayed his military zeal for the first time in 1645 when as a teenager, he successfully got control of the Torna Fort which was under Bijapur.
- He also acquired the Kondana Fort. Both these forts were under Adil Shah of Bijapur.
- He raided Mughal territory near Ahmednagar and in Junnar, 1657.
- Aurangzeb responded to the raids by sending Nasiri Khan, who defeated the forces of Shivaji at Ahmednagar.
- Shivaji defeated a large force of Shaista Khan (Aurangzeb’s maternal uncle) and the Bijapur army in Pune,1659.
- In 1664, the wealthy Mughal trading port of Surat was sacked by Shivaji.
- In June 1665, the Treaty of Purandar was signed between Shivaji and Raja Jai Singh I (representing Aurangzeb).
- As per this treaty, many forts were relinquished to the Mughals and it was agreed that Shivaji would meet Aurangzeb at Agra. Shivaji also agreed to send his son Sambhaji as well.
- When Shivaji went to meet the Mughal emperor at Agra in 1666, the Maratha warrior felt he was insulted by Aurangzeb and stormed out of the court.
- He was arrested and kept prisoner. The clever escape of Shivaji and his son from imprisonment in disguise out of Agra is legendary today.
- After that there was peace between the Marathas and the Mughals until 1670.
- The jagir of Berar which was granted to Sambhaji by the Mughals was taken back from him.
- Shivaji in response attacked and recovered many territories from the Mughals in a short span of four months.
- Through his military tactics, Shivaji acquired a large part of the land in the Deccan and western India.
- He was crowned as the king of the Marathas on 6th June , 1674, at Raigad.
- He took on the titles of Chhatrapati, Shakakarta, Kshatriya Kulavantas and Haindava Dharmodhhaarak.
- The Maratha Kingdom founded by Shivaji grew larger over time and became the dominant Indian power in the early 18th century.
- He died on 3rd April 1680.
Project 75 India:

The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has approved the issuance of a Request For Proposal (RFP) for the construction of six conventional submarines under Project-75I (India).
- RFP is a project announcement posted publicly by an organization indicating that bids for contractors to complete the project are sought.
- This project envisages indigenous construction of submarines equipped with the state-of-the-art Air Independent Propulsion system at an estimated cost of Rs. 43,000 crore.
- Project 75 (I), approved in 2007, is part of the Indian Navy’s 30 year Plan for indigenous submarine construction.
- It will be the first under the strategic partnership model which was promulgated in 2017 to boost indigenous defence manufacturing.
- The strategic partnership model allows domestic defence manufacturers to join hands with leading foreign defence majors to produce high-end military platforms to reduce import dependence.
- Acquisitions under the Strategic Partnership model refer to participation of private Indian firms along with foreign OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) in ‘Make in India’ in defence.
Significance:
- One of the Largest ‘Make in India’ Projects:
- It will serve to facilitate faster and more significant absorption of technology and create a tiered industrial ecosystem for submarine construction in India.
- To Ensure Self-Reliance:
- From a strategic perspective, this will help reduce current dependence on imports and gradually ensure greater self-reliance and dependability of supplies from indigenous sources.
- To Protect Indo-Pacific:
- This is keeping in mind the rapid increase of nuclear submarine arsenal by People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) (CHINA) and to protect the Indo-Pacific from future domination by the adversary.
About 30-year Submarine Plan:
- The Cabinet Committee on Security, in June 1999, had approved a 30-year submarine-building plan which included the construction of 24 conventional submarines indigenously by 2030.
- P75I succeeded the P75 under which six diesel-electric attack submarines of the Kalvari class, based on the Scorpene class, were being built at MDL (Mazagon Dock Limited) – the third submarine, INS Karanj, was commissioned in March 2021.
- Of the total 24 submarines to be built in India, six will be nuclear-powered.
- India has only one nuclear submarine, INS Arihant, at the moment. The INS Arighat, also a nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine, is to be commissioned soon.
- INS Chakra, a nuclear submarine, which is taken on lease from Russia, is believed to be on its way back to the country of origin.
Green Railways:

Indian Railways (IR) is working in mission mode to become the “largest Green Railways” in the world and is moving towards becoming a “net zero carbon emitter” before 2030.
- Railway Electrification which is environmentally friendly and reduces pollution has increased nearly ten times since 2014. Railways have planned to electrify balance Broad Gauge (BG) routes by December 2023 to achieve 100% electrification of BG routes.
- Green certification: 19 Railway Stations have also achieved Green Certification including 3 Platinum, 6 Gold, and 6 Silver ratings. 27 Railway Buildings, Offices, Campuses, and other establishments are also Green certified.
- Green certification mainly covers the assessment of parameters having a direct bearing on the environment, such as energy conservation measures, use of renewable energy, Green House Gas emission reduction, water conservation, waste management, material conservation, recycling, etc.
Chemical Weapons:

Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) has told the United Nations Security Council that it investigated 77 allegations against Syria, and concluded in 17 cases chemical weapons were likely or definitely used.
- Syria was pressed to join the chemical weapons convention in 2013 by its close ally Russia after a deadly chemical weapons attack that the West blamed on Damascus.
- In 2014, President Bashar al-Assad’s government declared that the destruction of its chemical weapons was completed.
- But Syria’s initial declaration to the OPCW has remained in dispute.
- In April 2021, the OPCW suspended Syria’s rights until all outstanding issues are resolved.
Organisation For The Prohibition Of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- OPCW is an intergovernmental organization and the implementing body for the Chemical Weapons Convention, which entered into force on 29 April 1997.
- Mandate: It oversees the global endeavor to permanently and verifiably eliminate chemical weapons.
- Headquarters: The Hague, Netherlands.
- Member states 193 (All states party to the CWC are automatically members. 4 UN Member States are non-members: Egypt, Israel, North Korea, and South Sudan. Of these Israel signed CWC but didn’t ratify it, the rest 3 are non-signatories).
- Nobel Peace Prize: The organisation was awarded the 2013 Nobel Peace Prize “for its extensive efforts to eliminate chemical weapons with most recent being in Syria civil war”.
- The OPCW–The Hague Award: It is an annual award founded by the OPCW as a result of their being presented with the 2013 Nobel Peace Prize.
- The Award honors individuals and institutions that have significantly contributed towards the goal of a world free of chemical weapons.
Citizenship Under The Citizenship Act, 1955:

Migrants belonging to six non-Muslim minority communities from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh who came to India on long term visa (LTV) before 2014 are eligible to apply online for citizenship under the Citizenship Act, 1955 from any part of the country, Home Ministry said.
- The six communities are Hindus, Christians, Sikhs, Jains, Buddhists, and Parsis.
- Citizenship is a Home Ministry subject but it can delegate powers to States for a specific objectives.
Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA)
- The official asserted that this particular awareness drive was not related to the Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 (CAA) that is intended to benefit undocumented (illegal migrants) from the six persecuted communities who entered India before December 31, 2014.
- The CAA is yet to come into force as the rules that govern the law have not been notified by the Ministry yet.
Long term visa (LTV)
- For foreigners of non-Indian origin, a longer-term visa is classed as one that permits the holder to stay in India for longer than 180 days (six months) continuously.
- The main visas that provide this are the Employment, Entry, and Student visas.
Market Based Economic Despatch (MBED):

Ministry of Power has circulated discussion Paper on Market Based Economic Despatch (MBED) on 1st June 2021 to all concerned stakeholders for obtaining their inputs and comments.
- Power despatch meaning: Since electricity cannot be stored in power lines, the entity operating the power grid must continuously adjust the output of its power plants to meet electricity demand. This process is called the “dispatch” of power plants.
- The existing electricity scheduling and despatch mechanisms in the country are siloed and the day-ahead procedures result in sub-optimal utilization of the country’s generating resources.
- It has been observed that the states very often end up committing and utilizing costlier generation plants, while cheaper generation plants are not fully scheduled/utilized across the country.
- MBED will ensure that the cheapest generating resources across the country are despatched to meet the overall system demand.
- This will be a win-win for both the distribution companies and the generators and ultimately result in estimated annual savings in excess of INR 12,000 crores for the electricity consumers. MBED shall also facilitate larger integration of variable renewable energy
- Implementing Market-Based Economic Despatch (MBED) will ensure a “One Nation, One Grid, One Frequency, One Price” framework.
- It has been suggested to implement MBED in phases.
- The Ministry of Power intends to implement Phase 1 of MBED from 1 April 2022.
- The first phase of MBED would involve only the thermal fleet of central generating stations to test the efficacy of the mechanism and allow for necessary infrastructure and systems to be built out and tested before scale-up.
National Council Of Science Museums (NCSM):

National Council of Science Museums (NCSM) is collaborating with the Science Museum Group, London for an international traveling exhibition ‘Hunt for the Vaccine’. The exhibition will tell the story of the global effort to find new ways to develop vaccines and look at vaccinations more broadly with a historical and contemporary view.
- National Council of Science Museums (NCSM) is a premier institution in the field of science communication.
- It is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Culture, Govt. of India.
- It is Headquartered in Kolkata.
- It was established in 1978.
- It is primarily engaged in popularizing Science and Technology through a network of science centres and Mobile Science Exhibitions (MSE) units that visit rural schools.
- Presently NCSM administers and manages 25 science museums/centres spread across the country and is the “world’s largest network of science centres and museums that functions under a single administrative umbrella” with an annual reach of about 15 million people.
Performance Grading Index (PGI):
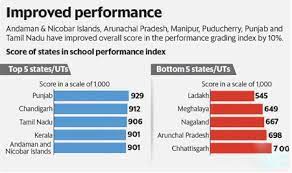
The Union Education Minister has approved the release of the Performance Grading Index (PGI) 2019-20 for States and Union Territories.
- The PGI is a tool to provide insights on the status of school education in States and UTs including key levers that drive their performance and critical areas for improvement.
About the Performance Grading Index (PGI):
- The PGI for States and Union Territories was first published in 2019 with reference year 2017-18.
- The PGI : States/UTs for 2019-20 is the third publication in this series.
- The PGI exercise envisages that the index would propel States and UTs towards undertaking multi-pronged interventions that will bring about the much-desired optimal education outcomes.]
- The PGI helps the States/UTs to pinpoint the gaps and accordingly prioritise areas for intervention to ensure that the school education system is robust at every level.
- It is initiated by the Department of School Education and Literacy (DoSEL).
Important Findings of the PGI 2019-20:
- Shows that 33 States and UTs have improved their PGI scores in 2019-20 compared to the previous year.Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Puducherry, Punjab and Tamil Nadu have improved their overall PGI scores by 10%.
- Inter-state Differential:
- On a maximum possible of 1000 points, the range between the States and UTs with the highest and the lowest score is more than 380 points in the year 2019-20.
- Domain-wise Performance:
- Access: Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep and Punjab have shown improvement of 10% or more in the ‘Access’ domain.
- Infrastructure and Facilities: Thirteen states and UTs have shown improvement by 10% or more in ‘Infrastructure and Facilities’ while Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Odisha have improved their scores in the domain by 20% or more.
- Equity: In ‘Equity’, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur and Odisha have shown an improvement of more than 10%.
- Governance Process: 19 states have shown improvement by 10% or more.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Punjab, Rajasthan and West Bengal have shown improvement by at least 20%.
Srivilliputhur-Megamalai Tiger Reserve and Vaigai River:

The recently declared Srivilliputhur-Megamalai Tiger Reserve in Tamil Nadu will provide protection to Megamalai, the Vaigai’s primary catchment, in turn helping water levels to rise in the river.
About Vaigai River:
- It originates in the Western Ghats (Varushanad Hills).
- It travels through the Pandya Nadu region of Tamil Nadu.
- Its main tributaries are Suruliyaru, Mullaiyaru, Varaganadhi, Manjalaru, Kottagudi, Kridhumaal and Upparu.
- The Vaigai is 258 kms long and finally empties into the Palk Strait near the Pamban Bridge in Ramanathapuram district.
- Its deterioration happened at the end of the 18th century when the British started deforesting the Megamalai region which acts as a major catchment for Vaigai. Consequently, the water flow in the river reduced gradually.
- Some 2,00,000 people died in this region during the Great Famine of 1876-77.
- Following the famine, the British Crown proposed diverting water from the Periyar river (Kerala) and feeding it to the Vaigai through a tunnel.
- The Vaigai presently gets about 80% of its water from the Periyar dam. The balance 20% is obtained from the major watershed of the Megamalai region during the northeast monsoon season.
- The Srivilliputhur-Megamalai Tiger Reserve will protect wild animals and the natural forests, their habitats which act as watersheds.
Srivilliputhur-Megamalai Tiger Reserve:
- It was established in February 2021. It was jointly declared by the Centre and Tamil Nadu governments.
- For this, the Megamalai WLS and the adjoining Srivilliputhur WLS were clubbed together.
- Srivilliputhur-Megamalai Tiger Reserve is the fifth Tiger Reserve of Tamil Nadu, and 51th tiger reserve of India.
- Animals seen here are Bengal tiger, elephants, gaur, Indian giant squirrel, leopard, Nilgiri Tahrs, etc.
- It has a mix of tropical evergreen forests and semi-evergreen forests, dry deciduous forests and moist mixed deciduous forests, grassland.




