Today’s Current Affairs: 7th June 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Musankwa sanyatiensis : Dinosaur Fossil
Fossils found on the shoreline of Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe represent a completely new dinosaur species named Musankwa sanyatiensis.
- Musankwa sanyatiensis is a new dinosaur species which has been identified from fossils discovered along the shores of Lake Kariba in Zimbabwe.
- The dinosaur’s genus name, “Musankwa,” was the name of the houseboat scientists used during their expeditions to the research site.
- In addition, its species name, “sanyatiensis,” alludes to the Sanyati River that flows into Lake Kariba.
- It is the first dinosaur to be named from the Mid-Zambezi Basin of northern Zimbabwe in over 50 years.
- Additionally, it is only the fourth dinosaur to be named from Zimbabwe, following the descriptions of “Syntarsus” rhodesiensis in 1969, Vulcanodon karibaensis in 1972, and, most recently, Mbiresaurus raathi in 2022.
- The rocks yielding this new specimen date back to the Late Triassic period, approximately 210 million years ago.
- Musankwa sanyatiensis is represented by the remains of a single hind leg, including its thigh, shin, and ankle bones.
- Evolutionary analysis reveals that it was a member of the Sauropodomorpha, a group of bipedal, long-necked dinosaurs that were widespread during the Late Triassic.
- Interestingly, it appears to be closely related to contemporaries in South Africa and Argentina.
- Weighing in at around 390 kg, the plant-eating Musankwa sanyatiensis was one of the larger dinosaurs of its era and mostly lived in swamp areas.
Maharani Temple : Destroyed

The iconic Maharani Temple in Gulmarg, located atop a hillock was distroyed.
- Maharani Temple is situated on a small hillock in the heart of Gulmarg town in the Baramulla district of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Also known as the Rani Temple or Mohineshwar Shivalaya, the temple is dedicated to Lord Shiva and his consort, Parvati.
- It was constructed by Mohini Bai Sisodia, wife of the former ruler of Kashmir, Maharaja Hari Singh, in 1915.
- This temple was once a royal temple of the Dogra dynasty of the erstwhile princely state of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It has been constructed in such a way that it can be seen from all corners of Gulmarg.
- The temple’s intricate carvings and designs reflect a beautiful blend of Indian and Persian styles.
- It is an example of religions intertwined with a Muslim priest performing rituals in the temple.
- The Indian Army collaborated with local communities in 2021 to restore this 106-year-old temple. Apart from renovating the temple structure, the Indian Army also undertook the redesigning of pathways leading to the temple.
UNESCO State Of Ocean Report 2024:

UNESCO’s ‘State of Ocean Report, 2024’ provides crucial insights into the current state of global oceans, emphasising the challenges posed by climate change and human activities.
The key finding of the report:
- The upper 2,000 meters of the oceans have experienced significant warming, with the rate increasing from 0.32 ± 0.03 watt per square meter (W/m²) from 1960 to 2023 to 0.66 ± 0.10 W/m² in the last two decades.
- Oceans are absorbing about 90% of the Earth’s excess energy, causing increased deoxygenation and threatening marine ecosystems and human economies dependent on them.
- Ocean acidification is on the rise globally, particularly in the open ocean, with a noted pH decline since the late 1980s; more comprehensive data from coastal areas is needed.
- Sea levels have risen consistently since 1993, necessitating improved monitoring systems at all scales.
- There’s growing interest in marine carbon dioxide removal (mCDR) technologies, but their ecological impacts and effectiveness remain uncertain.
Tele-MANAS:

A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) and the Ministry of Defence (MoD) to facilitate collaboration between the two ministries in operating a special cell of Tele MANAS.
- The Tele Mental Health Assistance and Networking Across States (Tele-MANAS) initiative was launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in October 2022.
- It aims to provide free tele-mental health services all over the country round the clock, particularly to people in remote or underserved areas.
- Tele-MANAS will be organised in a two-tier system:
- Tier 1 comprises state Tele-MANAS cells, which include trained counsellors and mental health specialists.
- Tier 2 will comprise specialists at the District Mental Health Programme (DMHP)/Medical College resources for physical consultation and/or e-Sanjeevani for audio-visual consultation.
- Currently, there are 51 operational Tele-MANAS cells functioning across all 36 States and UTs, offering services in 20 different languages.
- A toll-free, 24/7 helpline number (14416) is available as part of the initiative, allowing callers to select the language of choice for availing services.
- The service is also accessible at 1-800-891-4416.
- This call will be an Interactive Voice Response system (IVRS) based audio call only, with a timely auto-call back approach.
- Through the automated callback service, the caller will first be attended to by a trained counsellor.
- Based on the level of care required, the counsellor will either provide the care needed within their capabilities or refer the caller for specialist care.
- If the caller requires specialized care, the call will be handled by a mental health specialist (clinical psychologist, psychiatric social worker, psychiatric nurse, or psychiatrist). This level of service will contain both audio- and video-based options.
- In case the caller requires urgent in-person intervention/complex evaluations and management, they will be referred to the nearest in-person service for a physical consultation, and/or an audio-visual consultation with a specialist will be arranged through eSanjeevani.
- These centers will range from Health and Wellness Centre (HWCs) to tertiary care centers as part of the DMHP.
Air Of The Anthropocene Initiative:

“Air of the Anthropocene” project uses light painting to visualise air pollution in India, Ethiopia, and the UK, highlighting severe health risks and sparking global discussions on air quality.
- The “Air of the Anthropocene” project is an international initiative combining art and science to visualise air pollution through light painting.
- Artists and researchers collaborated to produce photographic evidence using digital light painting techniques and low-cost air pollution sensors.
Particulate Matter:
- Particulate matter (PM) is a complex mixture of small solid particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air.
- It includes both organic and inorganic particles such as dust, pollen, soot, smoke and liquid droplets, which vary greatly in size, composition and origin.
Impact of Air Pollution:
- Impact on Public Health: Particulate matter, particularly 5, is linked to severe health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, stroke and respiratory illnesses.
- It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates that 99% of the global population breathes air that exceeds WHO guideline limits, with about 7 million premature deaths annually linked to air pollution.
H5N2 Bird flu:
The first-ever human case of H5N2 has been reported in Mexico City, involving a 59-year-old man who died from the infection.
- Bird Flu or avian flu, is an infectious viral disease caused by the Avian Influenza A virus.
- It mainly infects and spreads among poultry and some wild birds.
- Occasionally, a form of the flu virus jumps from wild birds to poultry farms.
- It then quickly evolves into a highly pathogenic flu virus that causes a larger wave of illness and death among birds.
- Avian influenza can also infect humans due to direct contact with infected birds or contaminated environments.
H5N2 Bird flu:
- H5N2 is a subtype of the Avian Influenza A virus.
- Influenza A viruses are categorised by subtypes based on the proteins on their surfaces.
- There are 18 different hemagglutinin (H) and 11 different neuraminidase (N) subtypes, including H5N2.
- Hemagglutinin is a glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza viruses and neuraminidase is an enzyme found on the surface of the viruses that enable them to be released from the host cell.
- H5N2 has been first reported in poultry in Mexico.
UN Convention On Combating Desertification (UNCCD) Report On Rangelands And Pastoralists:

A UN Convention on Combating Desertification (UNCCD) report on rangelands and pastoralists has said that millions of pastoralists in India need better recognition of their rights and access to markets.
Key Findings of the UNCCD Report:
- Rangelands cover 80 million square kilometres, which is 54% of the earth surface, constituting the largest land cover/use type in the world. Of this:
- 78% occur in the drylands, mainly in the tropical and temperate latitudes
- 12% is protected rangelands worldwide.
- Around 40-45% of these lands are degraded, posing a threat to one-sixth of the world’s food supply and one-third of the planet’s carbon reservoir.
- Rangelands generate 16% of global food production and 70% of feed for domesticated herbivores, most significantly in Africa and South America.
Almost half of the world’s rangelands are degraded due to climate change, population growth, land-use change and growing farmlands. - In India, rangelands occupy about 1.21 million square kilometres, from the Thar Desert to Himalayan meadows.
- As per report, less than 5% of India’s grasslands are within protected areas, and the total grassland area decreased from 18 million hectares to 12 million hectares between 2005 and 2015.
- The area used for grazing is estimated at around 40% of the total land surface of India.
State of Pastoralist and Economic Contributions in India:
- Globally, an estimated 500 million pastoralists are involved in livestock production and allied occupations.
- There are around 13 million pastoralists in India, across 46 groups including Gujjars, Bakarwals, Rebaris, Raikas, Kurubas, and Maldharis.
- According to the 2020 report “Accounting for Pastoralists in India,” India holds 20% of the world’s livestock population and approximately 77% of the animals are raised in pastoralist systems, where they are either herded or allowed to graze on common lands.
- Pastoralists contribute to the economy through livestock rearing and milk production.
- The livestock sector contributes 4% to the national GDP and 26% to the agricultural GDP.
- The report highlighted that laws, such as the Forest Rights Act of 2006, have aided pastoralists in securing grazing rights across various states in the country.
About Rangelands:
- Rangelands are vast natural landscapes primarily used for grazing livestock and wildlife.
- They are dominated by grasses, shrubs, and open-canopy trees.
About Pastoralists:
- Pastoralists are people who raise livestock on natural pastures.
- They often lead a nomadic or semi-nomadic lifestyle, moving their herds seasonally to access fresh pastures and water sources.
Leading Edge Actuators & Airbrake Control Module:

The Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)’s Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) handed over the first batch of the indigenous Leading Edge Actuators and Airbrake Control Module to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The successful completion of flight trials for Leading Edge Actuators and Airbrake Control Modules has paved the way for production clearance, enabling HAL to gear up for equipping the Mk-1A variant of Light Combat Aircraft -Tejas.
- It used to control the leading edge slats on aircraft wings.
- These are developed in collaboration with Research Centre Imarat (RCI), Hyderabad, and Central Manufacturing Technology Institute (CMTI), Bengaluru.
- RCI is a Hyderabad based (DRDO) premier lab.
- CMTI is a Research & Development organization under the aegis of the Ministry of Heavy Industries.
Oleg Kononenko (Russian Cosmonaut) : 1st Person To Spend 1,000 Days In Space

Oleg Kononenko, a 59-year-old Russian cosmonaut, recently achieved a historic landmark by becoming the first person to spend 1,000 days in space.
- This milestone was reached during Kononenko’s fifth mission to the International Space Station (ISS) which commenced on September 15, 2023.
- Kononenko has been traveling in space since his first trip in 2008, and he has always made improvements to space research.
- His total amount of space-time was longer than Gennady Padalka’s record of 878 days, which had been held since 2015, until February 2024.
- Kononenko will have been in space for a total of 1,110 days if his mission ends on September 23, 2024, as planned.
Hydroxyurea : To Treat Sickle Cell Disease
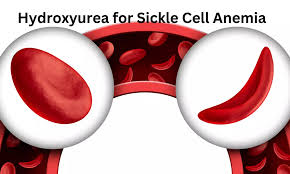
The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) is seeking to develop a pediatric oral formulation of hydroxyurea to treat sickle cell disease in India, where over 20 million individuals are affected.
- Currently, hydroxyurea is mainly available in 500 mg capsules or 200 mg tablets, making dosing for children challenging.
- This initiative is crucial, especially with the launch of the National Mission to eliminate Sickle Cell Anemia/SCD by 2047.
SCD (Sickle Cell Disease):
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder that affects the shape of red blood cells, causing them to become sickle-shaped instead of round.
- This abnormal shape can lead to various complications, including pain, anemia, and organ damage.
- SCD is one of the most common inherited blood disorders and can result in serious health issues, including stroke and organ failure.




