Today’s Current Affairs: 12th February 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Kashmir Hand-knotted Carpet:

The Geographical Indications Registry Chennai has granted a new logo for the Kashmir hand-knotted carpet in order to preserve the exclusivity of the famed Kashmir carpets.
- The origin of hand knotted carpets, locally known as “Kal baffi” dates back to 15th century after which it progressively attained the high degree of perfection.
- It is said that Sultan Zain-ul-Abidin brought carpet weavers from Persia and central Asia in to Kashmir to train the local inhabitants.
- The loom used in Kashmir carpet weaving is composed of two horizontal wooden beams between which the wrap threads are stretched, one beam in front of the weaver and the second behind the first.
- The difference between a carpet and other hand woven rugs lies in the fact that short lengths of the thread or yarn are tied to wrap chains to form the pile of the carpet.
- These are commonly called knots though it is a loop rather than an actual knot.
- In Kashmir, the primary type of knot used in carpet weaving is called the “Farsi baff” or the “Sehna” knot, which is a Persian system of knotting.
- Very simple tools are used to thread these knots – a wood or a metal comb to push knots and weft tightly together and a pair of short scissors to cut the pile of the carpet to an even form once it is finished.
Euthanasia : For Rabies Patients
The Supreme Court recently agreed to hear a plea in seeking passive euthanasia for rabies patients.
- Euthanasia is defined as the hastening of death of a patient to prevent further suffering.
- The term “euthanasia” comes from the Greek phrase “eu thanatos”, in which “eu” means “good” and “thanatos” translates into “death.” Literally speaking, the maxim translates to “easy death”.
- The practice of euthanasia can be classified into the following two categories:
- Active euthanasia is a method that involves taking active steps to end a life.
- This involves taking positive steps to end a patient’s life, such as by administering them a dose of medication through their intravenous line that will kill them.
- Active euthanasia is also sometimes referred to by the term “aggressive euthanasia”.
- Passive Euthanasia is defined as the deliberate act of causing someone’s death by withholding or withdrawing artificial life support, such as a ventilator, from a patient who is terminally ill.
- In a case like this, something that is essential to save a patient’s life is not done.
Quipu:

Astronomers recently identified what could be the largest structure ever found in the known universe, named Quipu.
- It is a recently discovered superstructure in which galaxies group together in clusters and clusters of clusters (superclusters).
- It contains nearly 70 galactic superclusters.
- It is the largest known structure in the universe in terms of length.
- Quipu stretches an astonishing 3 billion light-years across and contains an estimated 200 quadrillion solar masses.
- It is over 13,000 times the length of the Milky Way.
- It is also hundreds of thousands of times more massive than a single galaxy.
- Inspired by the Incan counting system of knotted cords, the structure mirrors its namesake with a long central filament and multiple branching filaments.
- Despite its vast size, Quipu will not last forever. Scientists believe it will eventually break into smaller, collapsing units.
- They describe it as a “transient configuration” that will change over time.
- Studying Quipu may help refine cosmological models.
- It could offer new insights into galaxy evolution and large-scale cosmic dynamics.
R-37M Missile:

Russia has reportedly offered the R-37M missile, one of the world’s best air-to-air missiles, to India.
- The R-37M missile, known by its NATO reporting name AA-13 Axehead, is a long-range air-to-air missile developed by Russia.
- It is designed to eliminate enemy fighter jets and drones beyond visual range (BVR).
- It evolved from the earlier R-33 missile and is designed to engage high-value targets such as AWACS, tanker aircraft, and other support platforms, thereby keeping the launching aircraft out of the range of enemy fighters.
- It has a weight of approximately 510 kilograms and a length of over 4 meters, with a warhead weighing 60 kilograms.
- The guidance system of the R-37M is a combination of inertial navigation with mid-course updates, an active radar homing head, and semi-active radar guidance for the terminal phase.
- It features a jettisonable rocket booster that allows it to achieve a range of 300 to 400 kilometers, making it one of the longest-reaching air-to-air missiles in service globally.
- Its speed can reach hypersonic levels, up to Mach 6, which is crucial for intercepting fast-moving targets.
Morand-Ganjal Irrigation Project:

The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has warned that the Morand-Ganjal Irrigation Project in Madhya Pradesh will submerge vital tiger habitats Satpura and Melghat Tiger Reserves.
- A dam-based irrigation project aimed at improving agricultural productivity in Madhya Pradesh.
- Rivers Involved: Morand and Ganjal Rivers.
- Both the Morand and Ganjal rivers are considered major tributaries of the Narmada River.
- The Ganjal being a left bank tributary and the Morand being a significant tributary of the Ganjal.
- It Covers Hoshangabad, Betul, Harda, and Khandwa districts in Madhya Pradesh.
Revised Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) Guidelines:

The Government has revised the Market Intervention Scheme (MIS) guidelines, increasing the procurement limit from 20% to 25% and expanding procurement agencies.
Revised Market Intervention Scheme (MIS):
- Increased Procurement Limit: Procurement coverage raised from 20% to 25% of total production.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) Option: States can now pay farmers directly for the price difference between the Market Intervention Price (MIP) and market price.
- Expanded Procurement Agencies: Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), Farmer Producer Companies (FPCs), State-nominated agencies, and Central Nodal Agencies (NAFED, NCCF) will procure TOP (Tomato, Onion, Potato) crops.
- Reimbursement of Storage & Transport Costs: Central Nodal Agencies (CNA) will reimburse costs for transporting crops from producing to consuming States.
Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) : Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign
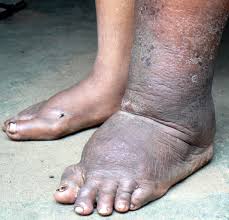
India has launched a nationwide Mass Drug Administration (MDA) campaign covering 111 endemic districts across 13 states, with the goal of eliminating Lymphatic Filariasis (LF) by 2027.
- Lymphatic Filariasis (LF), also called Elephantiasis, is a parasitic disease caused by filarial worms that infect the human lymphatic system, leading to severe swelling and disability.
- India is among the highest-burden countries for LF, contributing significantly to the global caseload.
- Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Odisha are among the states with the highest number of LF cases
- The government aims to eliminate LF by 2027 through mass drug administration, morbidity management, and vector control strategies.
- Causes and Transmission:
- Caused by Wuchereria bancrofti (most common), Brugia malayi, and Brugia timori parasites.
- Transmitted through mosquito bites (Anopheles, Culex, Aedes species).
- Requires repeated mosquito bites over months or years for infection to establish.
- Symptoms:
- Asymptomatic in early stages but leads to chronic lymphatic damage over time.
- Common symptoms:
- Lymphedema: Swelling of arms, legs, breasts, or genitals.
- Elephantiasis: Thickening of the skin and severe swelling.
- Hydrocele: Swelling of the scrotum (in males).
- Recurrent infections due to weakened immunity.
- Prevention and Treatment
- Mass Drug Administration (MDA): Annual distribution of anti-filarial drugs (Diethylcarbamazine + Albendazole).
- Triple Drug Therapy in select districts to accelerate LF elimination efforts.
- Triple Drug Therapy include diethylcarbamazine (DEC) + Albendazole + Ivermectin.
- Morbidity Management & Disability Prevention (MMDP): Ensuring access to care for affected individuals.
- Surgical intervention: Hydrocelectomy under Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY scheme.
- Vector Control: Use of mosquito nets, insecticides, and community awareness.
NITI Aayog Report on Higher Education:

The NITI Aayog report, “Expanding Quality Higher Education through States and State Public Universities,” highlights disparities in state-wise spending on higher education, urging increased public investment, especially in State Public Universities (SPUs).
Key Findings:
- States Allocating the Most to Higher Education (% of GDP): Jammu & Kashmir (8.11%), Manipur (7.25%), Meghalaya (6.64%), Tripura (6.19%).
- States with the Lowest Higher Education Expenditure (% of GSDP): Telangana (0.18%), Gujarat (0.23%), Rajasthan (0.23%).
- States with the Highest Higher Education Budget (Absolute Amount): Maharashtra (₹11,421 crore), Bihar (₹9,666 crore), Tamil Nadu (₹7,237 crore).
- States with the Lowest Higher Education Budget (Absolute Amount): Sikkim (₹142 crore), Arunachal Pradesh (₹155 crore), Nagaland (₹167 crore).
- Growth in Per Youth Spending on Higher Education: Increased from ₹2,174 (2005-06) to ₹4,921 (2019-20), with widening disparities among states.
- States with Consistently High Per Youth Spending: Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana.
- States Lagging in Higher Education Investment: Rajasthan, Punjab, Chhattisgarh.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension:
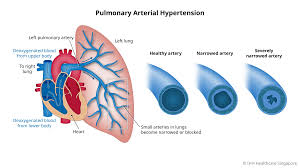
The Natco Pharma has received U.S. Food and Drug Administration final approval for Bosentan tablets for oral suspension, its generic version of Actelion Pharmaceuticals US Inc.’s pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) drug Tracleer.
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension is a specific type of pulmonary hypertension that is caused when the tiny arteries in your lung become thickened and narrowed.
- This blocks the blood flow through the lungs which raises the blood pressure in the lungs and causes the heart to work harder to pump blood through those narrowed arteries.
- The exact cause of PAH is unknown but it is believed that PAH occurs when there is injury to the cells that line the blood vessels of the lung, which over time results in this blood vessel disease.
- It can also develop in association with other medical conditions including congenital heart disease, liver disease, HIV and connective tissue diseases — such as scleroderma and lupus.
- PAH can even be associated with past or present drug use, such as the use of methamphetamine or certain diet pills.
- Symptoms: Blue fingers or lips, Chest pain, Dizziness or fainting, Fatigue, Shortness of breath that gets worse over time etc.
- Treatment: While there are treatment options for PAH, there is no known cure.
Yashas:

Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) recently renamed its flagship HJT-36 jet training aircraft as ‘Yashas’, following significant upgrades
- It is the flagship jet training aircraft of the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The aircraft, previously known as Hindustan Jet Trainer (HJT)-36, has undergone extensive modifications aimed at improving its departure characteristics and spin resistance across the aircraft envelope, leading to its rechristening as ‘Yashas.’
- It is fully equipped for Stage II pilot training, which includes a variety of specialized operations such as counter-insurgency, counter-surface force operations, and armament training.
- It has been upgraded with state-of-the-art avionics and a modern cockpit, enhancing both the training effectiveness and operational efficiency of the aircraft.
- The modifications also include a reduction in weight and the replacement of imported equipment with Indian-made Line Replaceable Units (LRUs), ensuring a more self-reliant and sustainable system.
- Its capabilities extend to aerobatics and armament carriage, supporting up to 1,000 kg of payload.
- It is powered by a Full Authority Digital Engine Control (FADEC)-controlled AL55I Jet engine, providing best-in-class thrust-to-weight ratio, optimised thrust management, and reliability.
- Additionally, the aircraft boasts a stepped-up rear cockpit with a drooped nose, providing improved all-around vision and enhanced situational awareness.
Exercise Cyclone 2025:

India and Egypt will hold Exercise Cyclone 2025 from February 10 to 23 in Rajasthan.
- Exercise Cyclone 2025 is a joint military exercise held between India and Egypt army.
- This is the third edition of Cyclone exercise.
- The first edition of the exercise was conducted in 2023 (In India) and second edition (In Egypt) was in 2024.
- The goal of the exercise is to improve coordination between the two armies. Training will include real-world scenarios and tactical drills.
- Motto of Exercise Cyclone 2025: “Together we train, together we excel”
- The exercise will involve the special forces of both countries.
- The Indian Army and the Egyptian Army would train together in desert conditions.
- The focus will be on counter-terrorism, high-intensity combat, and survival techniques.
- Military cooperation between India and Egypt has strengthened in recent years.
- Both countries have emphasised the need to strengthen security efforts.
- The exercise will allow both forces to operate together in simulated combat situations.
Paris AI Summit 2025:

India, co-chairing the Paris AI Action Summit (Feb 10-11, 2025), seeks to amplify the Global South’s voice on AI governance, innovation, and equitable AI access.
- Paris AI Summit is the third global AI safety summit, following UK (2023) and South Korea (2024) meetings.
- Organized by France, focusing on AI safety, ethics, governance, innovation, and economic impact.
- Significance of the Summit:
- AI Safety & Governance: Establishes norms and risk management frameworks for AI development.
- Equitable AI Access: Addresses global AI divide, advocating for open-source AI and cross-border collaboration.
- Economic & Strategic Impact: Shapes future of AI-driven industries, trade policies, and international regulations.
- Geopolitical Balancing: Counterbalances US-China AI dominance, promoting multilateral cooperation.
Swavalambini:
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), in collaboration with NITI Aayog launched “Swavalambini” in Assam, Meghalaya and Mizoram.Swavalambini is a women entrepreneurship program that aims to empower females in Northeast Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) with an entrepreneurial mindset, resources, and mentorship for business success.MSDE, in collaboration with Indian Institute of Entrepreneurship (IIE), Guwahati and NITI Aayog, launched a stage-wise entrepreneurial process including Entrepreneurship Awareness Programme (EAP), Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP), Faculty Development Programme (FDP), and funding.
US Agency for International Development:
The US President Donald Trump has imposed a 90-day freeze on foreign aid, halting US Agency for International Development (USAID) programs worldwide.The US has announced that it will not attend the 2025 G20 Foreign Ministers’ meeting in Johannesburg, South Africa.USAID is the primary US agency for global humanitarian and development aid. In 2024, USAID was allocated USD 44.2 billion, just 0.4% of the total US federal budget, but accounted for 42% of all humanitarian aid tracked by the United Nations.
Taranaki Maunga Mountain Gains Legal Personhood:
Taranaki Maunga (New Zealand’s 2nd-highest mountain in North Island) was granted legal personhood becoming the third natural feature (after Te Urewera park in 2014 and Whanganui River in 2017) in the country to receive this status.It will now be officially recognized by its Māori name, replacing the colonial name Mount Egmont. Māori are the indigenous tribes (Iwi) of New Zealand.
Eurasian Otters in Kashmir Valley:
Eurasian otters have been spotted in Gurez Valley (Kashmir) with the first live documentation in 25 years.It was spotted feasting on fish in the Kishanganga River (Originating from Krishansar lake, Ganderbal district (J&K).The river flows northwards through the Tulail and Gurez Valleys of Kashmir before entering PoK.Otters are members of the mammalian family called Mustelidae and inhabit both marine and freshwater.
100 GW Solar Power Capacity:
India has crossed 100 GW of installed solar capacity, marking a key milestone toward its 500 GW non-fossil energy goal by 2030.It surged over 35 times in the last decade, rising from 2.82 GW in 2014 to 100 GW in 2025.The grand total of solar and hybrid projects stands at 296.59 GW.Muft Bijli Yojana enabled 9 lakh rooftop solar installations across households.Solar power contributes 47% of India’s total renewable energy capacity.Top Solar States: Rajasthan, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh. Solar module production capacity surged from 2 GW in 2014 to 60 GW in 2024.
India-UK Defence Agreements:
India and the UK have signed multiple defence agreements at Aero India 2025, including the launch of Defence Partnership–India (DP-I), collaboration on next-generation weapons, and the establishment of an ASRAAM missile assembly facility in Hyderabad.
Over 54.5 Crore Jan Dhan Accounts Opened till Jan 15:
As of January 15, 2025, the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) has surpassed a significant milestone, with over 54.58 crore bank accounts opened. What makes this achievement even more remarkable is that 55.7% of these accounts belong to women, highlighting the scheme’s role in promoting financial inclusion, especially among marginalized communities. Since its launch in August 2014, PMJDY has transformed from a basic financial access initiative into a foundation for various government welfare programs, social security schemes, and digital transactions.
Balancing Freebies and Welfare:
There is a rising trend among the political parties to promise a barrage of freebies or subsidies to lure the electorate as seen in the Delhi Assembly elections 2025.Electoral freebies (or “revdi culture”) are debated—some see them as harmful to development, while others view them as essential for socio-economic progress.The RBI defines ‘freebies’ as “a public welfare measure that is provided free of charge.”




