Today’s Current Affairs: 2nd June 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Birch Glacier : Destroyed

A large chunk of the Birch Glacier largely destroyed an Alpine village in Switzerland.
- Birch Glacier is located in the Lötschental valley in northern Switzerland.
- The collapse of the glacier blocked the flow of the Lonza River, which runs through the valley.
- The Birch glacier was a special case: the only Swiss glacier that was advancing rather than shrinking. However, this was not because of extra snowfall.
- Its advance “was quite likely due to the pre-loading with rockfalls from this mountain, which has finally collapsed.
- Glaciologists have repeatedly expressed concerns about a thaw in recent years, attributed in large part to global warming, that has accelerated the retreat of glaciers in Switzerland.
- Switzerland, a landlocked Alpine country has the most glaciers of any country in Europe, and saw 4% of its total glacier volume disappear in 2023.
- That was the second-biggest decline in a single year after a 6% drop in 2022.
ULLAS – Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram:

The State of Goa become fully literate under the ULLAS – Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram (New India Literacy Programme), marking a significant milestone in India’s journey towards achieving full literacy by 2030.
- Understanding Lifelong Learning for All in Society(ULLAS) is a centrally sponsored scheme implemented from 2022-2027.
- The scheme, aligned with NEP 2020, targets adults (aged 15 years and above) who can’t go to school.
- It aims to empower those adults aged 15 years and above from all backgrounds who could not get due schooling and mainstream them with society to be able to contribute more to the growth story of the country.
- The scheme has five components – Foundational Literacy and Numeracy, Critical Life Skills, Basic Education, Vocational Skills and Continuing Education.
- The vision of the ULLAS Scheme is to make India Jan Saakshar and is based on the spirit of Kartavya Bodh and is being implemented on volunteerism.
- The ULLAS app can be used for registration of learners and volunteers either through self-registration or by surveyors.
- It will serve as a digital gateway for learners to engage in diverse learning resources through the DIKSHA portal of NCERT.
Preeclampsia:
World Preeclampsia Day (May 22) was observed, to increase awareness about preeclampsia.
- Preeclampsia is a serious condition that develops during pregnancy, usually after 20 weeks or so.
- It is often marked by high blood pressure and protein in the urine and this condition can also affect other organs of the body including the kidneys, liver and brain.
- Untreated preeclampsia can have serious, even fatal consequences for the mother and baby.
- In some women, preeclampsia may develop after the delivery of the baby; this is known as postpartum preeclampsia.
- The exact cause of preeclampsia remains unknown, but researchers believe it may have come from a problem with the health of the placenta(the organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy and is responsible for providing oxygen and nutrients to the fetus).
- Many people with preeclampsia do not have any symptoms.
- For those that do, some of the first signs of preeclampsia are high blood pressure, protein in the urine and retaining water (this can cause weight gain and swelling).
- Other signs of preeclampsia include Headaches, Blurry vision or light sensitivity, Dark spots appearing in your vision, Right side abdominal pain, Swelling in your hands and face (edema) and Shortness of breath.
- The only cure for preeclampsia is to give birth.
- Even after delivery, symptoms of preeclampsia can last 6 weeks or more.
- Treatment, if necessary, is based on how far along the pregnancy is, and may include induced labor or a Caesarean section (C-section).
Krishi Nivesh Portal:

In a bid to boost and expedite investments in the agriculture sector, the government is working to integrate schemes from various ministries and state governments under a unified digital platform the Krishi Nivesh portal.
- It is an initiative by the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare to facilitate farmers and investors.
- The portal will cater to diverse stakeholders, including farmers, entrepreneurs and industries, by providing easy access to information regarding various Central and State Government schemes.
- There are many government schemes for farmers’ welfare through which the investors can avail the subsidized benefits provided by various departments, divisions and ministries.
- This portal is a one-stop place for availing the benefits promulgated by different Government departments and ministries in the agriculture sector.
- It is a comprehensive platform designed to enhance agribusinesses, attract investments, and improve farmers’ income.
- It serves as a centralized interface to track investment opportunities, monitor the status of applications and access information on schemes — all from a single source.
- It is designed to streamline the investment process, making it more transparent and efficient.
- The portal features a user-friendly interface, real-time assistance through chatbot and interactive dashboards for data-driven decision-making.
- It currently provides information on 17 flagship agri-sector schemes, including the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund, Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund, PM Kisan Sampada Yojana, and PM-KUSUM (Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan), covering initiatives from seven ministries on a single platform.
- Currently, the portal is being utilised by multiple ministries, including those of agriculture, food processing, rural development, jal shakti, new and renewable energy and fertilisers.
Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary:

A rare Arctic seabird, the Sabine’s Gull, was spotted at Gujarat’s Nalsarovar Wildlife Sanctuary recently — its first recorded sighting in India since 2013, when it was seen in Kerala.
- It is located approximately 64 km west of Ahmedabad in Gujarat.
- It is a natural lake with shallow waters and muddy lagoons, dotted by 360 islets.
- Spread over an area of 120.82 sq km, this sanctuary is a paradise for bird watchers and nature enthusiasts.
- The history of Nalsarovar dates back to the 15th century, when the lake was created as a result of the construction of a check dam across the Sabarmati River.
- The lake was initially used for irrigation and as a source of drinking water for nearby villages.
- Over time, the lake became an important habitat for a variety of bird species, and local communities recognized its ecological significance.
- In the early 20th century, the British colonial administration recognized the importance of Nalsarovar as a wetland ecosystem and established it as a protected area.
- In 1969, the Gujarat government declared Nalsarovar a bird sanctuary to primarily protect its bird population.
- The Ramsar Convention designation of Nalsarovar Bird Sanctuary in 2012 recognized its ecological importance as a wetland habitat for birds and other wildlife.
IndiaAI Mission:

The selection of three new startups for building India’s own Foundation Model, the IndiaAI Mission, has taken a significant leap toward strengthening indigenous AI capabilities.
- IndiaAI Mission was initially launched as a joint initiative between the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and Nasscom in 2023.
- This initiative aims to bolster India’s AI ecosystem by making high-end computing resources accessible to startups and researchers.
- The mission’s key goals are:
- “Making AI in India” – Encouraging domestic AI development.
- “Making AI Work for India” – Ensuring AI benefits various sectors in the country.
- Implementing agency: IndiaAI, an independent business division under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), serves as the implementing agency for the IndiaAI Mission.
- It will help to democratize the benefits of AI, strengthen India’s position as a global AI leader and promote ethical and responsible AI use across sectors.
Zangezur Corridor:
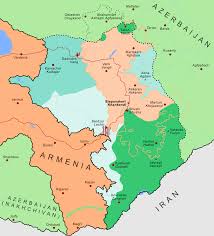
The Zangezur Corridor has become a topic of discussion following a recent meeting between Armenia’s Security Council Secretary and India’s National Security Advisor in New Delhi.
- Zangezur Corridor is a proposed transport route designed to connect Azerbaijan’s mainland with its exclave, the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, bypassing Armenia’s Syunik Province.
- Zangezur, which is currently part of southern Armenia, has been a disputed territory since World War I.
- On Azerbaijan’s side, the corridor would be integrated into the Horadiz-Agbend transport highway and railway network.
- On Turkey’s side, it would link into the Nakhchivan-Igdir-Kars railway and highway, providing a direct land route to Anatolia and beyond.
- It carries significant economic and strategic weight for the South Caucasus and beyond.
- The project aims to enhance Azerbaijan’s trade with Turkey and Europe by improving logistics infrastructure, reducing transportation costs, and significantly cutting travel time between Azerbaijan and Nakhchivan.
- The Zangezur Corridor plays a crucial role in increasing regional connectivity — not only throughout Caucasia, but also across greater Eurasia, joining Turkish, Russian, Central Asian, Iranian and Armenian territories and linking Europe to Asia.
Vitamin B9 (Folate) : New Study

According to a recent study by the All-India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), nearly 41 per cent of urban adolescents in government schools across northern India suffer from folate or vitamin B9 deficiency, which might be affecting their growth and development.
- Folate is the natural form of vitamin B9, water-soluble and naturally found in many foods.
- It is needed for red blood cell formation and for healthy cell growth and function, crucial for children in their developmental years.
- It is needed by cells to carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Foods containing Vitamin B9: Green leafy vegetables (like spinach and fenugreek), legumes (lentils, chickpeas), citrus fruits, nuts, whole grains and fortified cereals.
- Vitamin B9 is essential for supporting rapid growth phases in children.
- Folate is involved in the synthesis and repair of DNA and RNA, which are the building blocks of genetic material.
- It aids in the production of red blood cells and the development of the central nervous system during early childhood.
- In growing children, folate ensures proper brain function and emotional health.
- It is also crucial for tissue growth and cellular repair, processes that are continuous during childhood.
- If there isn’t enough folate, it can lead to anaemia, when the body lacks enough red blood cells.
DHRUVA (Digital Hub for Reference and Unique Virtual Address):

The Department of Posts has introduced a far-reaching digital policy titled DHRUVA—Digital Hub for Reference and Unique Virtual Address.
- Developed by the Department of Posts, DHRUVA sets the foundation for a nationwide Digital Address Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI).
- DHRUVA outlines a framework for creating a standardized, geo-coded and interoperable digital address system.
- It is designed to simplify address-related services and ensure secure, consent-based sharing of address information across public and private sectors.
- At the core of DHRUVA is the concept of Address-as-a-Service (AaaS)—a model that supports efficient, secure and user-controlled management of address data.
- The system aims to serve as a backbone for service delivery, governance and commercial interactions.
- Under this system, citizens, government bodies and businesses can engage in secure, consent-driven and real-time sharing of verified address information.
- The AaaS framework ensures:
- Interoperability across different address systems used by various sectors
- Standardization of address formats and geolocation tagging
- Consent-based sharing to empower user control and privacy
- Public-private integration for seamless adoption and innovation
- By recognizing digital addresses as core infrastructure, akin to Aadhaar and Unified Payments Interface (UPI),
- DHRUVA sets out to streamline everything from e-governance and online commerce to urban planning and emergency services.
- The policy also places emphasis on user-centric design, ensuring that citizens have meaningful control over how their address data is used and shared.
- Citizens will retain full control over their digital address identity, with options to manage access, update details, and share their verified address securely for various use cases.
- The DHRUVA platform will also feature multilingual support, mobile-first access, and integration with identity systems like Aadhaar, thereby improving usability and accessibility for all demographics.
- The DHRUVA policy builds upon the earlier launch of the Digital Postal Index Number (DIGIPIN)—the National Addressing Grid introduced by the Department of Posts.
- DIGIPIN is an open-source nationwide geo-coded addressing system developed by the Department of Posts in collaboration with IIT Hyderabad and NRSC, ISRO.
- It divides India into approximately 4m x 4m grids and assigns each grid a unique 10-character alphanumeric code based on latitude and longitude coordinates.
- The DIGIPIN system is publicly accessible and supports improvements in emergency response, logistics efficiency and citizen service delivery.
Thrombectomy:
The Technology Development Board (TDB), under the Centre’s Department of Science and Technology (DST), recently announced financial support for the development of India’s first indigenous thrombectomy device for stroke care.
- A thrombectomy is a surgical or interventional treatment to remove blood clots in an artery or vein to help restore blood flow through your blood vessel.
- A blood clot, also known as a thrombus, can obstruct blood flow, leading to tissue damage or even death.
- Some of the most common places for blood clots to occur are your legs, arms, intestines, brain, lungs and heart.
- Thrombectomies are performed to restore blood flow and prevent serious consequences.
- Sometimes a thrombectomy must be performed within a matter of hours to prevent life- or limb-threatening complications from occurring.
- There are two large categories of thrombectomies:
- Surgical (open) Thrombectomy: During a surgical thrombectomy, your surgeon makes an incision to get to your blocked blood vessel, cuts open your blood vessel, removes the blood clot using a balloon and then repairs the blood vessel.
- Percutaneous (minimally invasive) Thrombectomy: During a mechanical thrombectomy, your surgeon introduces special devices through catheters that can either macerate or suction out clots from within your blood vessel.
- When there’s a residual clot left, your surgeon will infuse the area with local clot-dissolving medicines.
RBI Annual Report 2024-25:

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) released its Annual Report 2024-25, providing a comprehensive overview of the country’s monetary policy, financial stability, regulatory initiatives, and key economic developments.
RBI Annual Report 2024-25:
- Global growth slowed to 3.3% in 2024, below the historical average of 3.7% (2000-19). Growth in 2025 expected at 2.8% and 3.0% in 2026 amid geopolitical tensions, trade protectionism, and elevated public debt.
- Global inflation moderated to 5.7% in 2024 from 6.6% in 2023, but services inflation remained sticky in major advanced economies.
- India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth moderated to 6.5% in 2024-25, yet it remained the fastest-growing major economy globally.
- Agricultural Gross Value Added (GVA) grew by 4.6% (up from 2.7% in previous year), driven by record foodgrain production and favourable weather.
- Industrial sector growth slowed to 4.3% and the services sector remained strong with a 7.5% growth and accounted for 64.1% of GVA.
- As of March, 2025, the RBI’s balance sheet grew by 8.2% year-on-year.
- Its income rose by 22.77% (driven by a ~33% surge in forex transaction gains and higher returns from investments), while expenditure increased by 7.76%.
- This led to a record surplus of Rs 2.68 lakh crore, up 27.37% from Rs 2.11 lakh crore in the previous year.
- On the assets side, gold rose by 52.09%, domestic investments by 14.32%, and foreign investments by 1.70%.
- Liabilities expanded due to higher notes issued, revaluation accounts, and other liabilities.
- As of March, 2025, foreign assets (including gold and loans) made up 74.27% of total assets, with domestic assets at 25.73%. Gold holdings rose by 57.48 metric tonnes to 879.58 metric tonnes.
- Headline inflation moderated to 4.6% in 2024-25 from 5.4% in 2023-24.
- Core inflation stood at 3.5%, with food inflation falling to 2.9% by March 2025.
- Fuel prices saw deflation of 2.5% due to softer global energy prices.
- The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) maintained the repo rate at 6.50% through much of 2024-25 but shifted the stance from “withdrawal of accommodation” to “neutral” in October 2024.
- The cash reserve ratio (CRR) was reduced to 4% in December 2024 to ease liquidity pressures.
- Merchandise exports grew marginally by 0.1%, while imports rose by 6.2%, widening the trade deficit to USD 282.8 billion.
- Current Account Deficit (CAD) remained manageable at 1.3% of GDP. Foreign exchange reserves stood at USD 668.3 billion, covering 11 months of merchandise imports.
- Net household savings increased to 5.1% of Gross National Disposable Income (GNDI) (measures the income available to the nation for final consumption and gross saving) in FY24.
- Bank credit growth outpaced deposit growth, improving credit-to-deposit ratio slightly.
- Gross Non-Performing Assets (NPA) ratio and Net NPA ratio declined further. Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) showed improved credit growth and lower GNPA ratios.
- Digital payments volume grew by 34.8%, value by 17.9% in 2024-25.
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) accounted for 48.5% of global real-time payments by volume.
- The RBI’s Financial Inclusion Index rose from 60.1 in 2023 to 64.2 in 2024, reflecting deeper usage of financial services.
- RBI introduced ‘bank.in’ domain to enhance digital banking security, and expanded the Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) pilot to 17 banks and 60 lakh users.
- RBI launched the FinTech Repository and EmTech Repository to track tech adoption by FinTechs and regulated entities. Managed by RBI Innovation Hub, these platforms capture data on technologies like Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence, aiding policy and industry insights.
- Gross Fiscal Deficit (GFD) of the central government reduced to 4.7% of GDP in 2024-25 from 5.5% in 2023-24.
- Capital expenditure grew by 5.2%; revenue expenditure grew by 5.8%. States’ consolidated fiscal deficit is likely to remain within 3.2% of GDP.
- India projected to sustain GDP growth at 6.5% with risks balanced.
- Inflation expected at 4.0%, with easing supply pressures but upward risks from global uncertainties.
- The central government aims to reduce the fiscal deficit to 4.4% of GDP in 2025-26 and target a declining public debt-to-GDP ratio reaching 50% by 2031.
Primates in Peril : Report

A recent report titled Primates in Peril highlights the increasing risks faced by 25 primate species from across the globe.
- Out of 25 primates, 6 species belong to Africa, 4 species from Madagascar, 9 species from Asia, and 6 species from South America (Neotropics)
- Most Endangered Primates: The Cross River Gorilla and Tapanuli Orangutan are highlighted as critically endangered in the report.
- Cross River gorillas are scattered in at least 11 groups in Cameroon and Nigeria, while the Tapanuli orangutan, the most endangered great ape, has fewer than 800 individuals.
- Both are listed as Critically Endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
- Primate Species from India: Phayre’s Langur and the Western Hoolock Gibbon, found in Northeast India and Bangladesh, were evaluated based on risks faced by them, but ultimately excluded from the final list.
- Phayre’s Langur: This primate, known for its distinct ‘spectacled’ appearance, is primarily found in eastern Bangladesh and northeastern India, including Assam, Mizoram, and Tripura.
- Western Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock hoolock): It is a tailless ape found in the tropical forests of India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar, with black males having a white stripe above their eyes while females are light colored (beige, brown, grey).
Valley of Flowers National Park : Reopened
The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand’s Chamoli district reopened to tourists for this year. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and forms one of the two core zones (the other being the Nanda Devi National Park) of the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve. The valley is believed to have been discovered in 1931, when three British mountaineers – led by Frank S Smythe – lost their way and chanced upon this spectacular valley. The Valley of Flowers is located within the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, spread over an area of 87 sq.km.
Samoa on their Independence Day:
India’s External Affairs Minister recently extended greetings to the Government and people of Samoa on their Independence Day–observed on 1 June every year.It is a Polynesian island nation located in the central South Pacific Ocean.
Samoa sits about halfway between New Zealand and Hawaii. It is made up of an archipelago of nine islands, four of which are inhabited. It covers an area of 2,842 sq.km. The two largest islands are Savai’i and Upolu. About three-quarters of the population lives on the island of Upolu. The country originated from volcanic activity. It is mountainous, with many lakes and rivers. The islands are ringed by coral reefs and shallow lagoons. Its capital and main commercial centre is Apia, on the island of Upolu. Samoa gained its independence from New Zealand in 1962. It is the first Pacific island country to achieve independence.
Bayraktar TB2:
Turkey’s much-hyped Bayraktar TB2 drones have suffered a devastating reputational blow after Pakistan’s Turkish-origin drone fleet failed spectacularly during Operation Sindoor. Bayraktar TB2 is a Turkish-made Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) tactical unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed for intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance (ISR) and precision strike missions.
It is Turkey’s first domestically developed armed UAV. It is an effective, low-cost platform that can be produced with commercial, off-the-shelf parts, which drives down cost and makes maintenance affordable for many countries.
Perito Moreno Glacier : Crumbling
The most famous glacier, the Perito Moreno glacier, which has a surface area of 250 sq km is crumbling.It is also called the ‘White Giant’, is located near the city of El Calafate in the Argentine province of Santa Cruz.It lies in the Andes Mountains in South America.It comes under the Los Glaciares National Park — a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It was formed during the last Ice Age, which occurred approximately 18,000 years ago. Estimates suggest that the glacier is 30 km long and has a towering height of 60 m above the water level. Due to its enormous size, it is a major source of freshwater for Argentina. The Perito Moreno glacier is now part of the long list of glaciers around the globe which are disappearing faster than ever due to rising temperatures. Since at least 1917, the glacier has witnessed numerous large-scale ice calving events due to its forward movement.
Padma Awards 2025:
The President of India presented Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan and Padma Shri Awards for the year 2025 to 139 distinguished persons whose names were announced on the eve of the 76th Republic day 2025. Instituted in 1954, the Padma Awards are among India’s highest civilian honours, announced annually on Republic Day (26th January). Their objective is to honour excellence in various fields involving public service.
Categories:
- The Awards are given in 3 categories:
- Padma Vibhushan: For exceptional and distinguished service
- Padma Bhushan: For distinguished service of high order
- Padma Shri: For distinguished service.
International Air Transport Association (IATA):
Prime Minister of India will address the 81st Annual General Meeting (AGM) of the International Air Transport Association (IATA) in New Delhi.This is the first time in 42 years that India is hosting the IATA AGM, highlighting India’s growing role in global aviation.IATA is a global trade association representing the airline industry, working to simplify and standardize air travel regulations and promote safe, efficient air transport.Founded in April 1945 in Havana, Cuba, as a successor to the 1919 International Air Traffic Association. Headquarters: Main office in Montreal, Canada, with executive offices in Geneva, Switzerland.
RBI New Draft Rules for Gold Loans:
The Reserve Bank of India released new draft rules for gold loans to address rising defaults and standardize lending practices.The RBI’s draft guidelines aim to regulate and harmonize gold loan practices across banks and NBFCs, enhance borrower protection, and reduce the risk of asset loss due to over-leveraging.Loans only allowed against gold jewellery and bank-issued coins. Loan-to-Value (LTV) Cap ratio capped at 75% of gold’s assessed value. For bullet repayment loans, interest must be included in LTV, reducing the loan disbursed.Primary gold like bars, ingots, bullion cannot be used as collateral.Fresh loans allowed only after full repayment of principal and interest. Lenders must return gold within 7 working days or pay ₹5,000/day compensation.Consumption loans must follow stricter tenure norms (max 12 months). Business-purpose loans must be evaluated based on cash flow, not collateral value.
Jharkhand Has Proposed Its First-Ever Tiger Safari:
Jharkhand has proposed its first-ever tiger safari in the fringe area of Palamau Tiger Reserve (PTR), aimed at boosting tourism and wildlife education.A tiger safari is a tourism model involving naturalistic enclosures to house tigers — mainly rescued, conflict-prone, or orphaned — allowing guaranteed sightings unlike traditional wild safaris. First proposed in NTCA Guidelines 2012, further refined in 2016 and later by Supreme Court directives in 2024.Palamu Tiger Reserve is one of the original nine Project Tiger reserves in India, and the only tiger reserve in Jharkhand, notified in 1974.




