Volume Weighted Average Price:
To make trading easier for institutional investors and market participants, SEBI recently made it mandatory to issue a Common Contract Note with a single volume weighted average price.
- The Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) is, as the name suggests, is the average price of a stock weighted by the total trading volume.
- The VWAP is used to calculate the average price of a stock over a period of time.
- It helps compare the current price of the stock to a benchmark, making it easier for investors to decide when to enter and exit the market.
- Also, the VWAP can assist investors in determining their approach towards a stock (active or passive) and make the right trade at the right time.
- The VWAP is calculated for each day.
- It starts when the markets open and ends when the markets close for the day. Since it is done every day, the calculation uses intraday data.
- The formula for calculating VWAP is as follows:
- VWAP = Typical Price*Volume / Cumulative Volume
- Here, the numerator indicates the total value of all the trades for any specific period, and the denominator indicates the total trading volume for the same duration.
- The typical price is the average of the high price, the low price, and the closing price of the stock for that day.
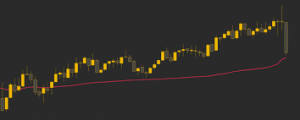
- The VWAP ratio is then presented on a chart as a line.
- It has been likened to a moving average, in that when the price is above the VWAP line, the market is seen as in an uptrend, and when the price is below the VWAP, the market is in a downtrend.




