Today’s Current Affairs: 5th September 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Acanthamoeba : New Study
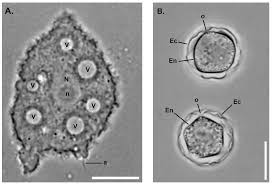
It is revealed that Acanthamoeba is more widespread in Kerala’s waterbodies than thought earlier.
- Acanthamoeba is a free-living ameba, a kind of one-celled organism that lives in water, soil, and dust.
- It can also be found in swimming pools, hot tubs, drinking water systems, humidifiers, and in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems.
- It can cause serious infections of the brain, skin, eyes, and sinuses.
- It can infect parts of the body through cuts or skin wounds or from being inhaled into the lungs or nostrils. It can get into the eyes through contact lens use.
- Types of infections caused by Acanthamoeba
- Granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE), which affects the brain and is almost always fatal
- Cutaneous acanthamoebiasis, a skin infection
- Acanthamoeba rhinosinusitis, an infection of the nasal cavity and sinuses
- Acanthamoeba keratitis: It is an eye infection that typically occurs in healthy people and can cause permanent vision loss.
Sudan : Landslide

A landslide buried a remote mountain village in the Darfur region of Sudan.
- Sudan is the third largest country in Northeast Africa
- South Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Egypt, Libya, Chad and Central African Republic.
- It borders the Sahara on the north and extends southward to the forests of West Africa and the Congo River basin.
- It also has a significant coastline along the Red Sea.
- It is mainly composed of vast plains and plateaus that are drained by the Nile River and its tributaries.
- Much of Sudan consists of deserts and arid grasslands with little in the way of vegetation. Massive plains and plateaus cover most of the nation.
- Highest point: Jabal Marrah
- Natural Resources: Petroleum; small reserves of iron ore, copper, chromium ore, zinc, tungsten, mica, silver, gold; hydropower
- Capital City: Khartoum, which is located roughly in the centre of the country, at the junction of the Blue Nile and White Nile rivers.
Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary: In News

Odisha’s Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is all set to be declared India’s newest tiger reserve.
- Debrigarh Wildlife Sanctuary is situated in the Bargarh district of Odisha.
- It is located near Hirakud Dam (the longest dam in India and the longest earthen dam in the world) on the Mahanadi River.
- It was declared a wildlife sanctuary in 1985.
- It finds a special mention because of noted freedom fighter Veer Surendra Sai.
- During his rebellion against the British, his base at Barapathara was located within the sanctuary.
- Most of the plant sanctuary is covered with mixed and dry deciduous forest.
- Major trees found here are Sal, Asana, Bija, Aanla, Dhaura, etc.
- Indian leopards, sloth bears, chousingha (four-horned antelope), sambar deer, gaurs (Indian bison), wild boars, and Indian wild dogs etc.
- It is one of the most flocked wintering grounds of migratory birds that visit the sanctuary from far off places.
- Some of the most prominent among them are the crested serpent eagle, Flower Peckers, red vented bulbul, tree pie, drongo and white eye oriental.
Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups:

The Ministry of Tribal Affairs requested the Registrar General and Census Commissioner of India (RGI) to consider enumerating Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) separately in the upcoming Census.
- PVTGs are a sub-category of Scheduled Tribes (STs) and are more vulnerable among the tribal groups in India.
- The criteria for identifying Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups are:
- A declining or stagnant population,
- Geographical isolation,
- Use of pre-agrarian practices (such as hunting and gathering),
- Economic backwardness and relatively low literacy
- This category was created based on the recommendations of the Dhebar Commission (1960-61) — led by former Member of Parliament U N Dhebar.
- At present there are 75 tribal groups considered as PVTGs and they are currently spread across 18 states and the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- As per the recent survey, there were an estimated 47.5 lakh PVTGs across India.
- Madhya Pradesh had the highest estimated population of PVTGs, followed by Maharashtra with an estimated population of 6.7 lakh, and Andhra Pradesh.
- PVTGs depend on various livelihoods such as food gathering, Non Timber Forest Produce (NTFP), hunting, livestock rearing, shifting cultivation and artisan works.
Immigration and Foreigners Act, 2025:

The Immigration and Foreigners Act, 2025 came into effect on 1st September 2025, consolidating India’s immigration laws, imposing stricter penalties for forged documents, and strengthening reporting and monitoring of foreigners.
- It repeals four outdated laws: the Passport (Entry into India) Act, 1920, the Registration of Foreigners Act, 1939, the Foreigners Act, 1946, and the Immigration (Carriers’ Liability) Act, 2000.
- Key Provisions of the Immigration and Foreigners Act, 2025:
- Tougher Penalties for Forged Travel Documents: 2–7 years imprisonment and a fine of Rs 1–10 lakh for using or supplying forged passports, visas, or other travel documents.
- Up to 5 years imprisonment or Rs 5 lakh fine for foreigners entering restricted areas without valid authorization.
- Mandatory Reporting of Foreigners’ Details: Hotels, universities, educational institutions, hospitals, and nursing homes must report information about foreign nationals staying or visiting.
- International airlines and shipping companies are required to share advance passenger and crew data before arrival.
- Government Control Over Premises: Central government empowered to regulate or shut down premises frequently visited by foreigners if deemed necessary for security reasons.
- Bureau of Immigration: It grants statutory backing to the Bureau of Immigration (established in 1971 under the Intelligence Bureau) to identify, detain, and deport illegal foreigners.
100 years of the Self-Respect Movement launched in Tamil Nadu in 1925:

This year (2025) marks 100 years of the Self-Respect Movement launched in Tamil Nadu in 1925 by Periyar E.V. Ramasamy.
- Self-Respect Movement is a radical social reform movement against caste oppression, patriarchy, and religious orthodoxy.
- Emphasised rationalism, equality, and dignity of individuals over ritualism and hierarchy.
- Launched in 1925, Tamil Nadu, through the Tamil weekly Kudi Arasu (Republic).
- Leaders:
- E.V. Ramasamy (Periyar) – founder and chief ideologue.
- Influenced by earlier reformers like Iyothee Thass, Jyotirao Phule, and B.R. Ambedkar.
- Supported initially by the Justice Party, later evolved into the Dravidar Kazhagam.
- Aim is To eradicate caste hierarchy and Brahmanical dominance, Promote self-respect, social equality, and gender justice, Shift focus of reform from elite non-Brahmins to the common masses.
WHO’s World Mental Health Report:

The World Health Organisation (WHO) has released two key reports World Mental Health Today and Mental Health Atlas 2024, the reports reveal that over a billion people globally live with mental health conditions and that suicide accounts for 1 in 100 deaths.
Key Findings of WHO’s Reports on World Mental Health:
- 13.6% of the world’s population currently has a mental disorder (age-standardized prevalence). Prevalence has risen faster than global population growth between 2011–2021.
- Anxiety and depressive disorders together account for over two-thirds of all cases.
- Anxiety disorders usually start earlier (childhood/adolescence), while depression becomes more common after 40 years and peaks between 50–69 years.
- Young adults (20–29 years) have seen the highest rise (1.8%) in the prevalence of mental disorders since 2011.
- Globally, males have higher rates of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorders, and intellectual disabilities.
- Females have higher rates of anxiety, depressive, and eating disorders.
- 1 in every 100 deaths globally is due to suicide. Suicide is the leading cause of death among young people worldwide.
- At the current pace, suicide mortality is projected to decline by only 12% by 2030, which falls far short of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) target of a one-third reduction.
Corporatisation of the Ordnance Factory Board:
India’s ordnance factories have posted record export orders of ₹3,500 crore in FY25, the highest ever since corporatisation.In October 2021, the government reorganised 41 Ordnance Factory Board units into seven Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs) Financial turnaround: from ₹2,844 crore cumulative loss (2019-20) → ₹625 crore profit (2022-23 & 2024-25). Exports surged from ₹81 crore in 2019-20 → ₹3,500 crore in 2024-25. MIL emerged as the top performer; three DPSUs (MIL, AVNL, IOL) granted Miniratna Category-I status.
Indian Navy’s First Training Squadron ( INS Tir, INS Shardul, and ICGS Sarathi) arrived at Port Victoria, Seychelles:
The Indian Navy’s First Training Squadron ( INS Tir, INS Shardul, and ICGS Sarathi) arrived at Port Victoria, Seychelles during a long-range training mission in the South West Indian Ocean Region. The deployment part of India’s MAHASAGAR vision (Mutual and Holistic Advancement for Security and Growth Across Regions). The Seychelles is an island nation located northeast of Madagascar off the east coast of continental Africa. It is the smallest nation in Africa in both land area and population. It is an archipelago of 155 islands located in the western Indian Ocean. Mahe, the largest and most diverse island in the archipelago. The islands of Seychelles are situated on the Mascarene Plateau, an extensive submarine plateau in the Indian Ocean.
Cabinet clears ₹1,500 cr scheme to promote critical mineral recycling:
The Union Cabinet has approved a ₹1,500 crore scheme under the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) to promote recycling of e-waste, lithium-ion batteries, and catalytic converters for recovery of critical minerals.It is a government incentive scheme worth ₹1,500 crore to promote recycling of e-waste and battery waste for recovery of critical minerals. It will serve as a near-term solution until mining and exploration projects begin to yield results. Launched under: National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM). Ministry: Ministry of Mines.
UPI Limit Increased to ₹10 Lakh for Select Transactions:
Starting September 15, 2025, the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) will implement revised UPI transaction limits for specific high-value payment categories. The per-transaction limit has been increased to ₹5 lakh, and the 24-hour aggregate limit raised to ₹10 lakh for several services, including insurance, capital markets, government tax payments, and credit card payments—a significant step in expanding UPI’s role in India’s digital financial ecosystem.
Centre Notifies Unified Pension Scheme Rules Under NPS:
The Central Government of India has formally notified the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) rules under the National Pension System (NPS), marking a key milestone in the evolution of public sector pension reforms. The newly issued Central Civil Services (Implementation of the Unified Pension Scheme under the NPS) Rules, 2025, were announced on September 4, 2025, and aim to regulate various service-related pension matters for central government employees opting for the UPS.
Nepal Bans 26 Unregistered Social Media Platforms:
The Government of Nepal has banned 26 unregistered social media platforms, including Facebook, WhatsApp, Instagram, YouTube, and X (formerly Twitter). The decision, announced by Minister of Communications and Information Technology Prithvi Subba Gurung on September 4, 2025, is aimed at enforcing digital accountability and ensuring regulatory compliance under Nepal’s Directive for Regulation of Social Media Use, 2080.
Royal Bhutan Buddhist Temple Inaugurated in Rajgir, Bihar:
The Royal Bhutan Buddhist Temple was formally inaugurated in Rajgir, Bihar, on September 4, 2025. This significant cultural and spiritual event was led by Bhutan’s Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay and India’s Union Minister for Minority Affairs, Kiren Rijiju, along with officials and religious leaders from both countries. The temple symbolizes the deep-rooted spiritual bond between India and Bhutan and reinforces Rajgir’s status as a sacred Buddhist destination.
UIDAI Records 221 Crore Aadhaar Authentications in August 2025:
The Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) recorded an impressive 221 crore Aadhaar authentication transactions in August 2025, signaling India’s accelerated shift toward digital governance and secure identity verification. This record-breaking number highlights the central role Aadhaar continues to play in facilitating welfare schemes, enhancing e-governance, and simplifying public and private service access across the country.
Piyush Goyal Assumes Charge as Mines Secretary:
Shri Piyush Goyal, a 1994-batch IAS officer of the Nagaland cadre, has officially assumed charge as the Secretary of the Ministry of Mines as of September 4, 2025. His appointment follows the transfer of Shri V.L. Kantha Rao, who is now serving as Secretary in the Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation.
DPIIT and ICICI Bank Join Hands to Boost Startups:
The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with ICICI Bank to extend targeted support to DPIIT-recognised startups across India. The partnership, formalized on September 4, 2025, is hosted under the Startup India initiative and is designed to offer startups a structured engagement programme involving accelerator access, mentorship, pilot opportunities, and ecosystem integration.
Anand V. Patil to Receive Prof. V.K. Gokak Award in Bengaluru:
Anand V. Patil, renowned for his contributions to children’s literature, will be conferred with the Prof. V.K. Gokak Award in Bengaluru on September 7, 2025. The award, named after one of India’s most influential literary figures, Prof. Vinayaka Krishna Gokak, honours individuals who have made significant contributions to Indian literature, particularly in Kannada.




