Today’s Current Affairs:7th October 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
PM-SETU Scheme:

During the Kaushal Deekshant Samaroh which is being held at Vigyan Bhawan in New Delhi, the Prime Minister launched the Pradhan Mantri Skilling and Employability Transformation through Upgraded ITIs- PM – SETU.Pradhan Mantri Skilling and Employability Transformation through Upgraded ITIs (PM-SETU) scheme is a centrally sponsored scheme with an investment of Rs 60,000 crore.
- The scheme aims to transform 1,000 Government ITIs across India into modern, industry-aligned training institutions.
- PM-SETU will follow a hub-and-spoke model, with 200 hub ITIs linked to 800 spoke ITIs.
- Each hub will be equipped with advanced infrastructure, innovation and incubation centres, production units, training of trainer facilities, and placement services, while the spokes will extend access and outreach.
- The scheme will:
- Introduce new, demand-driven courses and revamp existing ones in collaboration with industry;
- Set up Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) with credible Anchor Industry Partners to manage clusters and ensure outcome-based training;
- Create pathways for long-term diplomas, short-term courses, and executive programs;
- Strengthen 5 National Skill Training Institutes in – Bhubaneswar (Odisha), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Hyderabad (Telangana), Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh), Ludhiana (Punjab), as Centres of Excellence with global partnerships.
- The initiative is backed by global co-financing from the World Bank and Asian Development Bank, with the first phase focusing on Patna and Darbhanga ITIs.
Tikhir Tribe:

The Tikhir Tribal Council (TTC) recently submitted a representation to the Nagaland Director General of Police, urging the inclusion of aspirants from Tikhir tribe residing in Noklak district in the now-declared Nagaland Police constable recruitment.
- The Tikhir tribe is one of the indigenous Naga tribes found in the northeastern India.
- According to the 2011 census, the population of the Tikhir people in Nagaland was 7,537.
- Some live across the border in Myanmar.
- They are listed as a Scheduled Tribe, in the official Census of India.
- They speak a language called Naga Yimchungru, which is part of the Tibeto-Burman language family, like most Naga languages.
- At one time, the Tikhir were headhunters and a man’s prestige depended upon the number of enemies he had killed.
- Tikhirs are an agricultural community whose livelihood depends on agricultural cultivation.
- Since the Tikhir are a small tribe in Nagaland, some of the larger tribes harass them.
- With the coming of the Christian missionaries to Nagaland, most Tikhirs converted to Christianity.
- Many of the Tikhir practice elements of folk religion with their Christianity.
- “Tsonglaknyi” , the main Tikhir Festival, is observed from 9th to 12th Oct. every year. It is basically a festival of the sanctification of Shield.
Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary : Six Days Of Daily Bird Walks

Delhi’s Forest and Wildlife Department recently announced six days of daily bird walks at Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary as part of Wildlife Week celebration.
- Asola-Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary covering 32.71 sq.km. area on the Southern Delhi Ridge of Aravalli hill range on Delhi-Haryana border lies in Southern Delhi as well as northern parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts of Haryana state.
- The sanctuary is part of the Southern Ridge and has biodiversity significance as it merges with the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
- It is an important part of the North Aravalli Leopard Wildlife Corridor, which starts from Sariska National Park in Rajasthan, passes through various districts of Haryana, and finally meets the Delhi Ridge.
- As per Champion & Seth (1968), the vegetation falls under the Northern Tropical Thorn Forests
- The native plants exhibit xerophytic adaptations such as thorny appendages, wax-coated, succulent, and tomentose leaves.
- The sanctuary’s flora includes trees like the Neem, Peepal, and Jamun.
- The sanctuary is also known for its huge collection of medicinal plantations.
- The sanctuary is also home to mammals like the Nilgai, Indian Porcupine, Indian Hare, and Indian Grey Mongoose.
- The sanctuary has over 200 species of birds, including the Indian Peafowl, Red Junglefowl, and the Indian Grey Hornbill.
Ortolan Bunting:

The rare European bird, the Ortolan Bunting, with just a single recorded sighting in Bengal, was spotted at Baruipur, situated in the southern periphery of the city, recently.
- Ortolan Bunting is a small Palearctic migrant songbird.
- Scientific Name: Emberiza hortulana
- The bird is found in most of Europe, with populations found as far west as Mongolia and as far north as the Arctic Circle.
- Its habitat consists of open, cultivated, or uncultivated areas with sparse woody vegetation, up to an altitude of 2500 metres locally.
- It absolutely avoids forested areas, including during migration.
- The oceanic climate is not suitable for it.
- The males have a greenish-gray head along with a yellow throat, swooping mustache, and ring around the eye.
- Its belly is brown and its back and rump are brown and streaked.
- The females and juveniles are smaller, have spots on the belly, and are duller overall.
- Like most buntings, the ortolan has a conical beak that’s good for cracking seeds.
- Conservations Status: IUCN Red List: Least Concerned
Phosphine:
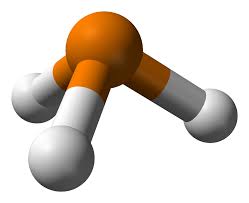
Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope have detected phosphine (PH3) in the atmosphere of brown dwarf Wolf 1130C.
- Phosphine is a chemical compound made of one phosphorus atom and three hydrogen atoms.
- Phosphine on Earth is developed naturally by bacteria that live in very low-oxygen environments.
- To produce phosphine, Earth bacteria take up phosphate from minerals or biological material and add hydrogen.
- It is also found in the atmospheres of Jupiter and Saturn.
- It is also called hydrogen
- Properties of Phosphine
- It is a colourless, flammable, extremely toxic gas with a disagreeable garlic like odour.
- It is slightly soluble in water.
- It is formed by the action of a strong base or hot water on white phosphorus or by the reaction of water with calcium phosphide (Ca3P2).
- It is structurally similar to ammonia (NH3), but phosphine is a much poorer solvent than ammonia and is much less soluble in water.
- It is used in semiconductor and plastics industries, in the production of a flame retardant, and as a pesticide in stored grain.
Chlorophytum vanapushpam:

Researchers during a field exploration in Idukki district’s Vagamon hills have identified a new species of the genus Chlorophytum and named the new species as Chlorophytum vanapushpam.
- It is a perennial herb belonging to the genus Chlorophytum (family Asparagaceae).
- It is a close relative of the safed musli.
- It has been found in the rocky hills of Vagamon and Neymakkad – parts of the Western Ghats regions of Idukki district – at elevations between 700 m and 2124 m.
- The species name vanapushpam is a composite of ‘Vanam’ and ‘Pushpam,’ the Malayalam for forest and flower respectively.
- Features of Chlorophytum vanapushpam:
- It has white flowers in small clusters and slender leaves and grows up to 90 cm in height.
- But unlike its more famous cousin Chlorophytum borivilianum, Chlorophytum vanapushpam lacks tubers.
- Its seeds are about 4 to 5 mm across. Flowering and fruiting occurs from September to December.
- The Western Ghats region is thought to be a centre of origin of the genus Chlorophytum.
- A total of 18 species have been identified here so far, with many of them exhibiting medicinal properties.
- One of these is the Chlorophytum borivilianum, more familiar to Indians as the ‘safed musli,’ a herb widely used in traditional medical preparations and also popular as a leaf vegetable.
Exercise KONKAN-25:

Exercise KONKAN-25 commenced on 05 Oct 2025, off the western coast of India.
- It is a bilateral naval exercise between the Indian Navy and Royal Navy of UK.
- The exercise will be conducted in two phases.
- The harbour phase of the Exercise will include professional interactions between naval personnel, cross deck visits, sports fixtures, and cultural engagements.
- The sea phase will encompass complex maritime operational drills focusing on anti-air, anti-surface, and anti-submarine exercises, flying operations and other seamanship evolutions.
- Both participating nations will deploy frontline assets, including aircraft carriers, destroyers, frigates, submarines, and integral and shore based air assets.
- The Indian side will be represented by the carrier battle group of the indigenous aircraft carrier INS Vikrant in company with other surface, sub-surface and air combatants.
- This exercise is a reaffirmation of the shared commitment to ensuring secure, open and free seas and will exemplify the Comprehensive Strategic Partnership outlined in ‘India-UK Vision 2035’.
- Exercise Konkan 2025 will serve as a platform to consolidate strategic ties, enhance interoperability and contribute to regional maritime stability.
Blizzard:

A severe blizzard struck the eastern face of Mount Everest in Tibet, trapping nearly 1,000 trekkers in the remote Karma valley.
- A blizzard is a severe mid-latitude snowstorm characterized by strong winds (≥56 km/h), low temperatures, and near-zero visibility caused by blowing snow.
- It occurs when polar or continental cold air masses interact with moist maritime or tropical air, producing intense snowfall accompanied by violent winds.
It Develops:
- Cold, dense air from high latitudes or elevated terrain ensures snow formation instead of rain.
- Moist air masses, often from nearby oceans or large lakes, provide water vapour for condensation and precipitation.
- Warm, moist air is forced to rise over cold air (frontal uplift) or up mountain slopes (orographic uplift), forming snow-laden clouds.
- A steep pressure difference generates high wind speeds, driving snow horizontally and drastically reducing visibility.
Features:
- Wind Velocity: 80–100 km/h (often exceeding 120 km/h in severe cases).
- Temperature: Falls below freezing, intensifying wind chill effects.
- Visibility: Drops below 0.4 km for over three hours, leading to whiteout conditions.
- Duration: Can persist for several hours to days, often followed by cold wave conditions.
Variants:
- Ground Blizzard: Pre-existing snow lifted by strong winds.
- Nor’easter: Coastal blizzard type common along North Atlantic coasts.
Impact:
- Causes snow accumulation, avalanches, and temporary glacial expansion.
- Alters albedo and local energy balance, affecting regional climate feedbacks.
80th session of the United Nations General Assembly:

India’s External Affairs Minister addressed the 80th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in New York, highlighting the need for UN reform and India’s readiness to assume greater responsibilities in driving UN reforms.
- The UN often faces paralysis in decision-making due to conflicts, limited resources, and terrorism.
- The veto power held by the five permanent members (P5) allows a single nation to block resolutions, even if the majority supports them, as seen with Russia in Ukraine and the US on Israel-related resolutions.
- The UN Security Council reflects the geopolitical realities of 1945, not the 21st century.
- Rising powers like India, Brazil, Germany, and Japan lack permanent membership, while the Global South remains underrepresented, limiting the UN’s legitimacy.
- The UN has struggled to prevent or resolve large-scale conflicts due to internal divisions and weak peacekeeping mandates. Historical failures in Bosnia and Rwanda, and inaction in Syria, Sudan, and Myanmar highlight systemic shortcomings.
- Heavy reliance on a few major donors, especially the US, creates leverage for influencing UN policies and operations, compromising impartiality and global trust.
- The UN’s sprawling bureaucracy slows responses to crises and suffers from corruption, misuse of funds, and misconduct.
- The United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) reported 434 new investigations, including procurement fraud and sexual misconduct, undermining credibility.
- Some nations perceive the UN as a threat to sovereignty, arguing that resolutions on climate change, human rights, or immigration can override national interests.
- This criticism challenges the UN’s authority and global acceptance.
- The rise of organizations like the G20, BRICS, and African Union provides alternative, often more agile platforms for international cooperation, bypassing the UN and further highlighting the need for reform.
Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PMDDKY):

The Centre has announced 100 Aspirational Agriculture Districts under the Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PMDDKY), aiming to boost farm productivity and rural prosperity.
- The PMDDKY announced in the Union Budget 2025 to make farming easier, modern, and more profitable.
- It is modeled after the NITI Aayog’s Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP), but focused exclusively on agriculture and allied sectors.
- PMDDKY has no separate budgetary allocation, it converges budgets of 36 existing schemes from 11 departments, including Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (cash transfers), Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (crop insurance), and Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojna (irrigation) with an annual outlay of Rs 24,000 crore from 2025-26 to 2030-31, totaling Rs 1.44 lakh crore.
- Around 40% is earmarked for subsidies, 30% for infrastructure, 20% for loans, and 10% for training and market support.
Key Objectives of the Scheme:
- Enhancing agricultural productivity and farmer income.
- Promoting crop diversification and sustainable farming practices.
- Expanding post-harvest storage and value addition.
- Support women, youth, and allied sectors (e.g., dairy, fisheries, poultry) to diversify income sources.
- Achieve self-sufficiency in foodgrains, pulses and oilseeds to reduce India’s dependence on imports.
- Strengthening irrigation infrastructure and improving access to both long-term and short-term agricultural credit.
District Selection Criteria:
- Districts with yields below national averages (e.g., wheat below 3.5 tonnes/hectare or rice below 2.7 tonnes/hectare).
- Districts with fewer than 1.55 crop cycles per year.
- Districts with limited penetration of bank loans or Kisan Credit Cards, often below 30% of farmers in a district.
- The selection will consider the share of Net Cropped Area and operational holdings in each state/union territory.
- A minimum of one district will be selected from each state to ensure balanced regional development.
- PMDDKY operates under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, each selected district will set up a District Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (DDKY) Samiti, chaired by the District Collector, to implement the District Agriculture Development Plan (DADP).
- Coordination will involve local administrations, agriculture departments, and 100 appointed Central Nodal Officers (mostly joint secretaries) to monitor scheme performance.
- PMDDKY is expected to directly benefit 1.7 crore farmers across India, integrating allied sectors like livestock, dairy, and fisheries.
Tribal Village Vision 2030:

On 2nd October 2025, tribal villages across India formally adopted the Tribal Village Vision 2030 Declaration through Special Gram Sabhas, outlining local development priorities aligned with Viksit Bharat@2047.
- The Government of India has also declared 15th November 2024 to 15th November 2025 as Janjatiya Gaurav Varsh.
- As part of this celebration, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs launched (on 17th September 2025) the Adi Karmayogi Abhiyan, envisaged as the world’s largest tribal grassroots leadership mission, reaching over 11.5 crore tribal citizens across 1 lakh villages & tolas in 30 States/UTs.
- Tribal Village Vision 2030 is a landmark grassroots initiative, under which special Gram Sabhas in tribal villages and hamlets adopted their own Vision 2030 Declarations.
- These declarations are community-crafted blueprints for development in areas like education, health, infrastructure, and livelihoods.
- Key features include:
- Community-Led Development: Transect Walks, Focused Group Discussions (FGDs), and Gap Analysis to identify local needs.
- Village-Level Goals: Education, health, livelihoods, financial inclusion, and infrastructure.
- Integration with Schemes: PM JANMAN, Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan 2.0, and other programmes.
- Institutional Mechanism: Adi Sewa Kendras as single-window citizen service centres; villagers contribute 1-hour weekly voluntary service.
- Tech-Enabled Governance: AI-powered Adi Vaani App for real-time communication in native languages.
India’s first cooperative multi-feed Compressed Biogas:

Union Home Minister and Minister of Cooperation inaugurated India’s first cooperative multi-feed Compressed Biogas (CBG) plant in Kopargaon, Maharashtra.
- The plant will produce 12 tons of CBG daily and 75 tons of potash from jaggery/molasses, reducing imports.
- Compressed Biogas (CBG) is a renewable fuel produced from biomass and organic waste (agricultural residue, cattle dung, sugarcane press mud, sewage) via anaerobic decomposition (breakdown of organic matter by bacteria in the absence of oxygen).
- Similar calorific value (amount of energy released on complete combustion) to CNG. CBG can replace CNG in automotive, industrial, and commercial sectors.
- CBG Benefits:
- Eco-Friendly: Cleaner alternative to fossil fuels, supporting India’s target of net zero emissions by 2070.
- Waste Management: Converts organic waste into fuel, reducing pollution and promoting a circular economy.
- Energy Security: Reduces oil imports and increases the share of natural gas in India’s energy mix (currently ~6%, targeted 15% by 2030).
What Is Schedule M Norms?

The Union Health Ministry has directed strict enforcement of the revised Schedule M norms under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940.
- The move follows reports of child deaths linked to a cough syrup adulterated with diethylene glycol (DEG), highlighting serious lapses in manufacturing quality.
- Schedule M is a section of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940, prescribing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for pharmaceutical products in India.
- It defines the minimum requirements for facilities, equipment, quality systems, documentation, and personnel to ensure safe, effective, and consistent drug production.
Features of Revised Schedule M:
- Mandatory adoption of a structured quality and risk management framework across all manufacturing stages.
- Identification and mitigation of product risks through scientific and evidence-based evaluation.
- ALCOA+ Principles: All records must be Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, Accurate, Complete, Consistent, Enduring, and Available.
- Compulsory reporting and tracking of adverse drug events to ensure post-market surveillance.
- Lifecycle-based validation (Design, Installation, Operation, Performance Qualification).
- Complete raw material traceability with supplier audits and digital monitoring systems.
- Requirement for computerised storage systems, controlled environments, and regular self-inspections.
Diethylene Glycol (DEG):
- Diethylene Glycol (DEG) is a colorless, odorless, syrupy organic chemical compound (formula: C₄H₁₀O₃).
- It is a synthetic industrial solvent, belonging to the glycol family, and is not approved for pharmaceutical or food use.
- Chemically, DEG is a by-product of ethylene oxide hydrolysis, often used where water-miscible, low-volatility liquids are required.
Southeast Asia’s First Coral Larvae Cryobank:
The Philippines has launched Southeast Asia’s first coral larvae cryobank, a pioneering initiative to freeze and preserve coral “seeds” to protect marine biodiversity and revive damaged reefs.It is a scientific facility that freezes and stores coral larvae at ultra-low temperatures to preserve their genetic material for future use in reef restoration or research.It Functions as a “genetic seed vault” for corals, helping safeguard biodiversity that could be lost due to climate change and coral bleaching. The project is part of a regional network under the Coral Research & Development Accelerator Platform.
Participating countries include the Philippines, Taiwan, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Process:
- The free-swimming reproductive stage are collected during spawning events.
- The larvae are exposed to cryoprotective solutions that prevent ice crystal formation during freezing.
- Using a rapid freezing technique, larvae are plunged into liquid nitrogen at –196°C, turning them into a glass-like state without crystallisation.
- When needed, laser-based rapid warming thaws the samples within seconds, preventing cell damage.
- Revived larvae are rehydrated in seawater, monitored for movement and settling, then transferred to controlled tanks for coral regrowth.
IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025:
India will unveil its first-ever Red List of Endangered Species at the IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025 in Abu Dhabi, UAE.The IUCN World Conservation Congress (WCC) is a quadrennial (every 4 year) global summit organised by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
It brings together governments, civil society, scientists, indigenous groups, and private sector leaders to decide global priorities for nature conservation, climate action, and sustainable development. It is regarded as the world’s largest and most influential conservation policy forum. Host Country: United Arab Emirates.
Themes of IUCN Congress 2025:
- Scaling Up Resilient Conservation Action – Expanding effective ecosystem restoration and species protection efforts.
- Reducing Climate Overshoot Risks – Accelerating climate mitigation to prevent irreversible ecological tipping points.
- Delivering on Equity – Ensuring inclusive, just, and community-driven conservation.
- Transitioning to Nature-Positive Economies and Societies – Promoting sustainable production, circular economy, and green finance.
- Disruptive Innovation and Leadership for Conservation – Harnessing technology, AI, and youth leadership for conservation breakthroughs.
NATPOLREX-X 2025:
Conducted by the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) from October 5–6, 2025, off the coast of Chennai, Tamil Nadu. Participants: Central ministries, coastal state governments, major ports, oil-handling agencies, maritime organisations, and over 40 foreign observers from 32 countries. Aim is To assess and enhance India’s national capability to respond to marine oil spills and test inter-agency coordination under the National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOSDCP).
Features:
- Deployment of ships and aircraft equipped with pollution-control technology.
- Demonstration of India’s multi-tiered pollution response strategy.
- Focus on sustainable maritime practices and environmental protection.
Namchik Namphuk Coal Block:
Arunachal Pradesh launched its first commercial coal mine at the Namchik-Namphuk coal block in Changlang district.The Namchik-Namphuk coal block is Arunachal Pradesh’s first commercial coal mining project and part of India’s broader push to develop domestic energy resources under Atmanirbhar Bharat.Situated in Changlang district, southeastern Arunachal Pradesh, within the Upper Assam coal belt region.It Holds an estimated 1.5 crore tonnes of coal reserves, sufficient for long-term production.
Rajasthan’s First Namo Biodiversity Park:
Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav inaugurates Rajasthan’s first Namo Biodiversity Park in Alwar, promoting greenery, clean air, and environmental awareness.The inauguration was marked by a symbolic tree plantation ceremony and attended by Shri Sanjay Sharma, Cabinet Minister, Government of Rajasthan. The park represents a milestone in the state’s commitment to biodiversity preservation, climate resilience, and community participation in environmental conservation.The Namo Biodiversity Park—developed as a “green lung” for the Alwar region—aims to improve local air quality, enhance urban green cover, and restore ecological balance. According to the Ministry, the park has been envisioned not merely as a recreational zone but as a model of urban ecological development, promoting coexistence between humans and nature.
Nobel Prize 2025 in Medicine:
The 2025 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to Mary E. Brunkow, Fred Ramsdell, and Shimon Sakaguchi for their pioneering discoveries on peripheral immune tolerance a fundamental mechanism that keeps the human immune system from attacking its own tissues. Their work has not only transformed our understanding of how the immune system is regulated but also opened up new avenues for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, cancer, and transplant rejection.
Multiple landslides In Darjeeling And Kalimpong:
Heavy rainfall triggered multiple landslides in Darjeeling and Kalimpong, killing at least 14 people and destroying vital infrastructure including the Dudhia bridge and Teesta Bazaar link road.A landslide is the downward movement of rock, debris, or soil along a slope under gravity. It occurs when the shear stress exceeds the shear strength of slope materials, often due to heavy rainfall, earthquakes, deforestation, or human activity. These events disrupt slope stability and can destroy roads, settlements, and infrastructure, especially in hilly terrains.Nearly 13% of India’s land area (0.42 million sq. km) is landslide-prone, as per the Geological Survey of India (GSI). High-risk zones include the Himalayas, Northeastern hills, Western Ghats, Nilgiris, and Eastern Ghats. The Northeast alone accounts for 42% of the total hazard zone due to fragile geology, steep gradients, heavy monsoons, and unregulated construction. India’s tectonic activity and population pressure amplify the frequency and intensity of slope failures.
BWF World Junior Championships 2025:
The BWF World Junior Championships return to India, marking a major milestone for Indian badminton. The tournament, featuring the world’s best young shuttlers, is being held in Guwahati, Assam, from October 6 to 19, 2025. This is the second time India is hosting the event the first being in Pune in 2008 and it reaffirms the country’s growing role as a global badminton hub. The 2025 BWF World Junior Championships are divided into two parts.
- Suhandinata Cup (Mixed Team Event) : Scheduled in the first week (October 6–11), Features 36 national teams competing for team supremacy
- Eye-Level Cup (Individual Events) : Takes place from October 13–19, Includes singles, doubles, and




