Sickle Cell Disease:
A decade-long study by a Gurugram hospital has found success in curing Sickle Cell Disease among children through bone marrow (stem cell) transplantation, placing India among the leading nations in advanced paediatric transplant outcomes.
- It is a group of inherited blood cell disorders that affect hemoglobin, the protein that carries oxygen through the body.
- SCD can cause episodes of severe pain and lead to life-threatening complications.
- The most common and severe type of SCD is sickle cell anemia.
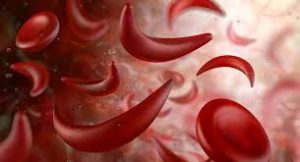
- Normally, RBCs are disc-shaped and flexible enough to move easily through the blood vessels.
- People with SCD have atypical hemoglobin molecules called hemoglobin S, which can distort RBCs into a sickle, or crescent shape.
- When RBCs sickle, they do not bend or move easily and can block blood flow to the rest of the body.
- SCD interferes with the delivery of oxygen to the tissues.
- The cause of SCD is a defective gene, called a sickle cell gene.
- A person will be born with SCD only if two genes are inherited—one from the mother and one from the father.
- Symptoms:
- Early stage: Extreme tiredness or fussiness from anemia, painfully swollen hands and feet, and jaundice.
- Later stage: Severe pain, anemia, organ damage, and infections.
- Treatments:
- A bone marrow transplant (stem cell transplant) can cure SCD.
- However, there are treatments that can help relieve symptoms, lessen complications, and prolong life.
- Gene therapy is also being explored as another potential cure.
- The UK recently became the first country to approve gene therapy treatment for SCD.




