Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 11th December 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- Aurora Borealis:
- Shakti Act:
- Karnataka’s new anti-cow slaughter bill:
- .Anthrax:
- Indian Muraingrasses (Genus Ischaemum)
- ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- New Parliament Building:
- Other important current affairs
1.Aurora Borealis:

The Northern Lights, also known as aurora borealis, are usually witnessed far up in the polar regions or the high latitude regions of Europe. But, today, they could be visible in parts of Illinois and Pennsylvania in the US.
- This is happening due to a solar flare, which emerged from a Sunspot.
- The flare is accompanied by a Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) a large bubble of radiation and particles emitted by the Sun that explodes into space at high speed. This causes the Northern Lights to be visible in more number of areas than usual.
- An Aurora is a display of light in the sky predominantly seen in the high latitude regions (Arctic and Antarctic). It is also known as a Polar light.
- There are two types- the aurora borealis and aurora australis – often called the northern lights and southern lights.
- They commonly occur at high northern and southern latitudes, less frequent at mid-latitudes, and seldom seen near the equator.
- Colors: While usually a milky greenish color, auroras can also show red, blue, violet, pink, and white. These colors appear in a variety of continuously changing shapes.
- Auroras are a spectacular sign that our planet is electrically connected to the Sun. These light shows are provoked by energy from the Sun and fueled by electrically charged particles trapped in Earth’s magnetic field.
- The typical aurora is caused by collisions between fast-moving electrons from space with the oxygen and nitrogen in Earth’s upper atmosphere.
- The electrons—which come from the Earth’s magnetosphere, the region of space controlled by Earth’s magnetic field —transfer their energy to the oxygen and nitrogen atoms and molecules, making them “excited”.
- As the gases return to their normal state, they emit photons, small bursts of energy in the form of light.
- When a large number of electrons come from the magnetosphere to bombard the atmosphere, the oxygen and nitrogen can emit enough light for the eye to detect, giving us beautiful auroral displays.
- They origin at altitudes of 100 to more than 400 km.
- The color of the aurora depends on which gas — oxygen or nitrogen — is being excited by the electrons, and on how excited it becomes.
- The color also depends upon how fast the electrons are moving, or how much energy they have at the time of their collisions.
- High energy electrons cause oxygen to emit green light (the most familiar color of the aurora), while low energy electrons cause red light. Nitrogen generally gives off a blue light.
- The blending of these colors can also lead to purples, pinks, and whites. The oxygen and nitrogen also emit ultraviolet light, which can be detected by special cameras on satellites.
- Auroras affect communication lines, radio lines, and power lines.
- It should also be noted here that Sun’s energy, in the form of the solar wind, is behind the whole process.
2.Shakti Act:

In a bid to curb crimes against women and children in Maharashtra, the state cabinet approved two draft bills that propose the death penalty for heinous cases of rape, acid attack, and child abuse.
- The two interconnected bills, which will be tabled in the winter session of the state legislature as part of the Shakti Act, are the Maharashtra Shakti Criminal Law (Maharashtra Amendment) Act 2020 and the Special Court and Machinery for Implementation of Maharashtra Shakti Criminal Law 2020.
- Drafted on the lines of the Disha Act framed by Andhra Pradesh, they seek to amend relevant sections of the Indian Penal Code (IPC), Criminal Procedural Code (CrPC) and Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act.
- The bills also have provisions to increase the quantum of punishment, including life term, cover new categories of crimes, and propose a mechanism for speedy trials.
- The media is not allowed to report the name of a rape victim. The proposed Acts will provide similar protection to victims of molestation and even acid attack.
- The draft bills propose to amend IPC Section 376 (rape) to increase the quantum of punishment to life term or death penalty in heinous cases where there’s adequate conclusive evidence or exemplary punishment is warranted.
3.Karnataka’s new anti-cow slaughter bill:

The government in Karnataka passed the Karnataka Prevention of Slaughter and Preservation of Cattle Bill (2020) in the Assembly.
- ‘Beef’ is defined as the flesh of cattle in any form.
- ‘Cattle’ is defined as “cow, the calf of a cow and bull, bullock, and he or she buffalo below the age of thirteen years”.
- ‘Gau Shalas’: Shelters established for the protection and preservation of cattle registered with the Department of Animal Husbandry and Fisheries.
- Police officers ranked sub-inspector and above or a competent authority will have the power to search premises and seize cattle and materials used or intended to use to commit the offense.
- Such seizures, if any, will then be reported before the Sub Divisional Magistrate without unreasonable delay.
Penalties:
- It is a cognizable offense, violators can attract three to seven years of imprisonment.
- While a penalty between Rs 50,000 and Rs 5 lakh can be levied for the first offence, second and subsequent offenses can attract penalties ranging between Rs 1 lakh and Rs 10 lakh.
4.Anthrax:
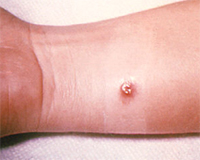
Anthrax was confirmed as the cause of the death of two female elephants a week ago in the Joypur rainforest in Assam. The two elephants died after ingesting anthrax spores that can remain buried underground for 25-30 years.
- Following this, the authorities have undertaken a drive to vaccinate livestock around this area.
- This is the second case of anthrax in the State after two Asiatic water buffaloes died in the Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary in October 2019.
- Anthrax is a disease caused by Bacillus anthracis, a spore-forming bacteria.
- Affects animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats more often than people.
- People can get anthrax from contact with infected animals, wool, meat, or hides.
- Spread: It does not spread directly from one infected animal or person to another; it is spread by spores. These spores can be transported by clothing or shoes.
Symptoms & Infection:
- Respiratory infection in humans initially presents with cold or flu-like symptoms for several days, followed by pneumonia and severe (and often fatal) respiratory collapse.
- Gastrointestinal (GI) infection in humans is most often caused by consuming anthrax-infected meat and is characterized by serious GI difficulty, vomiting of blood, severe diarrhea, acute inflammation of the intestinal tract, and loss of appetite.
- Cutaneous anthrax, also known as Hiding porter’s disease, is the cutaneous (on the skin) manifestation of anthrax infection in humans.
Anthrax has been used in biological warfare by agents and by terrorists to intentionally infect. It was spread in the US through the mail. It killed 5 people and made 22 sick.
In June last year, DRDO and JNU scientists developed a potent Anthrax vaccine.
- They Claim the new vaccines superior to existing ones as it can generate an immune response to anthrax toxin as well as spores.
5. Indian Muraingrasses (Genus Ischaemum) :

A new species of Indian Muraingrasses (Genus Ischaemum) known for their ecological and economic importance, such as fodder, have been spotted by scientists in Goa in the Western Ghats, one of the four global biodiversity hotspots of India.
- Agharkar Research Institute (ARI), Pune, an autonomous institute of the Department of Science & Technology, discovered a novel species named Ischaemumjanarthanamii from plateaus of Western Ghats of Goa.
- The species was named Ischaemumjanarthanamii in honour of Prof. M. K. Janarthanam, Professor of Botany, Goa University, for his contribution to the Indian grass taxonomy and documentation of the floristic diversity of Goa state.
- Ischaemumjanarthanamii grows on low altitude lateritic plateaus in the outskirts of Bhagwan Mahavir National Park, Goa.
- The species has adapted to survive harsh conditions, low nutrient availability, and blossoms every monsoon.
- Globally 85 species are known from Ischaemum, of which 61 species are exclusively found in India.
- The Western Ghats have 40 species with the highest concentration of the genus.
6.ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting Plus (ADMM-Plus):

Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh, attended the 14th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting Plus organized online at Hanoi, Vietnam on 10 December 2020 that marked the 10th anniversary of ADMM Plus.
Agreed five areas of practical cooperation under this mechanism are:
- Maritime security, counter-terrorism, humanitarian assistance, and disaster relief, peacekeeping operations and military medicine.
- In 2013, a new priority area of humanitarian mine action was agreed upon.
About ASEAN Defense Minister’s Meeting-Plus (ADMM-Plus):
- ADMM-Plus is the only official framework of Defense Minister’s meetings in the Asia-Pacific Region.
- It is a platform for ASEAN and its eight Dialogue Partners to strengthen security and defense cooperation for peace, stability, and development in the region.
- The ADMM-Plus comprises the ten ASEAN countries as well as Australia, China, Japan, India, the Republic of Korea, New Zealand, Russia, and the United States.
- Established in: 2010.
7.New Parliament Building:

Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of the New Parliament Building.
- The new parliament building will be the highlight of the ambitious ₹ 20,000 crore Central Vista project that PM Modi said will become “a symbol of a new and self-reliant India”.
- The four-story building will be triangular and its interiors will have three national symbols – the lotus, the peacock, and the banyan tree – as its themes.
- The triangular shape of the new parliament was a reference to “sacred geometries in various religions and cultures of India”.
- In the Lok Sabha chamber, the national bird (peacock) will be the theme. In the Rajya Sabha the national flower (lotus) and in the central lounge the national tree (banyan) will be the theme.
- The parliament building alone will cost an estimated ₹ 971 crore and will, the government hopes, be ready before India’s 75th Independence Day anniversary (in 2022). However, construction cannot yet begin as a legal challenge is pending in the Supreme Court.
- To be constructed by Tata Projects Ltd, the new parliament building will overlook the old – which was built nearly 100 years ago at a cost of ₹ 83 lakh and will be turned into a museum.
- The new Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha halls will have increased seating capacities (888 and 384 seats, respectively) in anticipation of an expanded Parliament; a 25-year-old freeze on increasing state-wise distribution of seats ends in 2026.
- In addition, seating in the Lok Sabha hall can be expanded to 1,272 to host joint sessions.
- Dholpur stone will be the primary construction material (as it was with the current building) and red granite may replace red sandstone in some interior sections.
- The building will be equipped with modern audio-visual communication systems. The new parliament will also be fully wheelchair- and disabled-access friendly.
Other important current affairs:
1.Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) designed 5.56×30 mm Protective Carbine has successfully undergone the final phase of User trials on 7th December 2020. This has paved the way for induction into the services.
- JVPC is a Gas Operated Semi Bull-pup automatic weapon having more than 700 rpm rate of fire.
- The effective range of the carbine is more than 100 m and weighs about 3.0 kg with key features like high reliability, low recoil, retractable Butt, ergonomic design, single hand firing capability, and multiple Picatinny rails, etc.
- These features make it a very potent weapon for Counter Insurgency /Counter-Terrorism operations by security agencies.
- The carbine has been designed as per the Indian Army’s GSQR, by Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE), a Pune based laboratory of DRDO.
- The Weapon is manufactured at Small Arms Factory, Kanpur while the Ammunition is manufactured at ammunition Factory, Kirkee Pune.
2.BSNL, in partnership with Skylotech India, announced a breakthrough in satellite-based NB-IoT (Narrow Band-Internet of Things).
- This new ‘Made in India’ Solution, which is indigenously developed by Skylo, will connect with BSNLs satellite- ground infrastructure and provide PAN-India coverage, including Indian seas.
- The coverage will be so vast that it will not leave any dark patch within the boundary of India.
- This is the world’s first satellite-based NB-IoT network.
- This new technology supports the Department of Telecom and NITI Aayog’s plan of bringing indigenous IoT connectivity to India’s core sectors.
- Examples of where this technology has already been tested successfully include, Indian Railways, fishing vessels, and enabling connected vehicles across India.
- A small, smart, incredibly rugged box, the Skylo ‘User Terminal’ interfaces with sensors and transmits data to the Skylo Network and into people’s hands.
3.HelpAge India presented UN Population Award for 2020:
- HelpAge India has been presented with the UN Population Award for 2020 (institutional category).
- For the first time in the history of the UN Population Award, the honor is being conferred on an Indian institution.
- The last time the Award came to an Indian was 28 years ago, back in 1992, when it was awarded to Mr. J.R.D. Tata as an individual laureate. HelpAge India has been working for ‘the cause and care of disadvantaged older persons to improve their quality of life’ for over four decades.
- Established by the United Nations General Assembly in 1981, the United Nations Population Award recognizes contributions in the fields of population and reproductive health.
- Better Than Cash Alliance:
- It is a partnership of governments, companies, and international organizations that accelerates the transition from cash to digital payments in order to reduce poverty and drive inclusive growth, and to advance the Sustainable Development Goals.
- The United Nations Capital Development Fund serves as the secretariat.
- India became a member of the Better Than Cash Alliance in 2015.




