Bluetongue Disease:
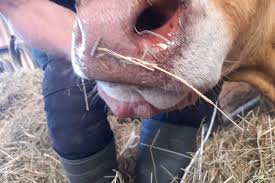
Bluetongue disease has been confirmed in all 12 Dutch provinces, according to official data released recently.
- Bluetongue Disease is an infectious, non-contagious, vector-borne viral disease that affects wild and domestic ruminants such as sheep, goats, cattle, buffaloes, deer, most species of African antelope and camels.
- The bluetongue virus is transmitted by biting midges (Culicoides spp.).
- It is not transmitted through contact with animals or wool, or consumption of milk.
- Infections range from mild to severe, depending on the species affected.
- Most infections in cattle are asymptomatic.
- Sheep are most likely to show symptoms.
- In infected sheep, bluetongue damages the blood vessels, resulting in hemorrhage (internal bleeding), lack of oxygen in the blood, and necrosis (death) of affected tissues.
- Infections are more obvious in young lambs, and the mortality rate can be high (up to 30 per cent).
- Vaccination is used as the most effective and practical measure to minimize losses related to the disease and to potentially interrupt the cycle from infected animal to vector along with insect control measures.




