Candida tropicalis:
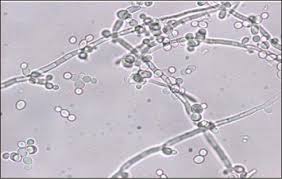
‘Candida tropicalis’, an important fungal pathogen in India and in many other parts of the world, has been found using chromosome alterations to resist common antifungal drugs such as fluconazole and voriconazole.
- Candida tropicalis is a species of yeast (fungus) that is part of the Candida genus.
- It is a human pathogen associated with high mortality rates.
- It is one of the fungal species that has been obtained from seawater, sea sediments, mudflats, marine fish intestine, mangrove plants, marine algae, and shrimps.
- Therefore, they are widely distributed in the tropical and subtropical marine environments.
- It is also dominantly found in the human gut, fruit surfaces, a variety of foods, and soil.
- It is a common systemic fungus, affecting persons with immune-compromised and immune-suppressed systems.
- It is known to be pathogenic in neutropenic hosts and disseminating through the bloodstream to peripheral organs.
- A neutropenic host refers to a person with neutropenia, a condition characterized by an abnormally low count of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell essential for fighting off infections, especially bacterial and fungal infections.
- It is also known to cause infections when the normal microbiota in the human host has been compromised by intake of antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics or when the sugar levels are high in the system.
- It causes infections on human skin, in the gastrointestinal tract, and also in the female genitourinary tract.
- Its infections are associated with a mortality rate of 55-60%.
- The most common mode of transmission is the nosocomial transmission between health-care workers and patients.
- Treatment: Antifungal drugs are typically utilized to treat C. tropicalis infections.




