Glioblastoma:
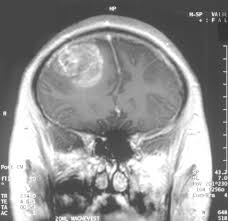
Glioblastoma is a type of cancer that starts as a growth of cells in the brain or spinal cord.
- Like all cancers, glioblastoma is caused by DNA mutations that result in uncontrolled cell growth. The underlying causes for these genetic cell mutations are largely unknown.
- Glioblastoma forms from cells called astrocytes that support nerve cells.
- Astrocytes help give your brain the nutrients it needs.
- Glioblastoma tumors make their own blood supply, which helps them grow. It’s easy for them to invade normal brain tissue.
- It grows quickly and can invade and destroy healthy tissue.
- It can happen at any age. However, it tends to happen more often in older adults.
- It accounts for almost half of all cancerous brain tumors in adults.
- Glioblastoma symptoms may include headaches that keep getting worse, nausea and vomiting, blurred or double vision, trouble speaking, altered sense of touch, and seizures.
- There also may be trouble with balance, coordination, and moving parts of the face or body.
- There’s no cure for glioblastoma. Treatments might slow cancer growth and reduce symptoms.
- The main treatments for glioblastomas are surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.




