GPS Spoofing:
GPS interference on passenger aircraft, including ‘spoofing’ with false signals, are on the rise over conflict zones globally, including on India’s borders with Pakistan, a report from the OPSGROUP said recently.
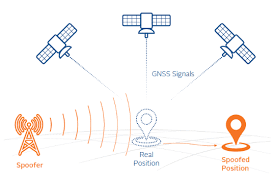
- GPS spoofing, also known as GPS simulation, refers to the practice of manipulating or tricking a GPS receiver by broadcasting false GPS signals.
- Essentially, it misleads the GPS receiver into believing it is located somewhere it is not, resulting in the device providing inaccurate location data.
- This form of cyberattack undermines the reliability of GPS data, which is vital for a variety of applications, from navigation to time synchronization and more.
- It exploits the inherent vulnerabilities in the GPS infrastructure – the weak signal strength of GPS satellites.
- The Global Positioning System (GPS) functions by sending signals from satellites to GPS receivers on Earth.
- These receivers then calculate their position based on the time it takes for these signals to arrive.
- However, due to the weak signal strength of the GPS satellites, these signals can be easily overwhelmed by fake signals, resulting in inaccurate location data on the receiving device.
- Typically, a GPS spoofer begins by acquiring a basic understanding of the victim’s GPS setup, including the types of signals it uses and how they are processed.
- With that information, the attacker then sends counterfeit GPS signals that mimic the real ones.
- These fake signals are stronger, causing the receiver to recognize them as authentic signals.
- As a result, the victim’s GPS receiver ends up processing these counterfeit signals, leading to erroneous location information.




