Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
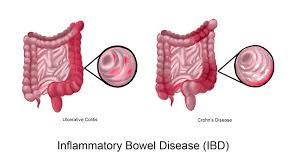
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) comprising primarily Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease has been on the rise globally.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is an umbrella term for chronic inflammatory conditions affecting the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
- Two main forms of IBD:
- Crohn’s disease: It can affect any part of the digestive tract, from mouth to anus. Inflammation can be patchy, meaning areas of healthy tissue can be interspersed with inflamed areas. It often affects the deeper layers of the bowel wall.
- Ulcerative colitis: Limited to the inner lining (mucosa) of the large intestine (colon) and rectum. The inflammation is continuous, affecting the entire colon in severe cases.
- Causes: The exact cause of IBD remains unknown, but research suggests a complex interplay of factors like genetics, immune system and environmental factors.
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain and cramping, diarrhea, often bloody, urgent need to have a bowel movement, weight loss and fatigue.
- Treatment: There is no cure for IBD, but treatments aim to manage symptoms and induce remission. These include medications, dietary modifications and surgeries.




