New Pathway To Regulate Nitrate Absorption In Plants:
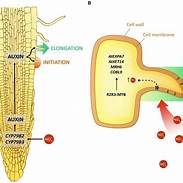
Researchers led by those from the National Centre of Biological Sciences, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bengaluru (NCBS-TIFR), have found a new pathway that regulates nitrate absorption in plants.
- The gene MADS27, which regulates nitrate absorption, root development and stress tolerance, is activated by the micro-RNA, miR444, therefore offers a way to control these properties of the plant.
- The researchers studied this mechanism in both rice (monocot) and tobacco (dicot) plants.
- The research is published in Journal of Experimental Botany.
- Nitrogen is one of the most important macronutrients needed for development of a plant.
- It is a part of chlorophyll, amino acids and nucleic acids, among others.
- It is mostly sourced from the soil where it is mainly absorbed in the form of nitrates and ammonium by the roots.
- Nitrates also play a role in controlling genome-wide gene expression that in turn regulates root system architecture, flowering time, leaf development, etc.
- Thus, while a lot of action takes place in the roots to absorb and convert nitrogen into useful nitrates, the absorbed nitrates in turn regulate plant development apart from being useful as a macronutrient.




