Phoenicia:
Archaeologists excavating near ruins on the island of Sardinia discovered an Iron Age scarab amulet that originated from ancient Phoenicia.
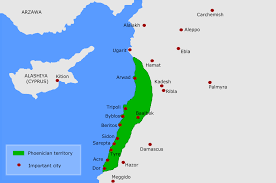
- Phoenicia was an ancient region at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea.
- It covered the land where the present day Lebanon is located.
- The Phoenicians lived on the seacoast and were skilled shipbuilders and navigators.
- Their trade routes reached as far as Spain and the British Isles.
- The Phoenicians traded wood, linen, dyes, and wine.
- They also carved wood and ivory and worked with metals and glass.
- The art of glassblowing was probably invented in Phoenicia.
- The Phoenician alphabet was the source of the Greek alphabet and of the Latin alphabet, which most people use today.
- They built the cities of Sidon, Tyre, and Berot (modern Beirut).
- The Phoenicians set up colonies all around the Mediterranean. Carthage, in North Africa, was a very successful colony.
- Decline:
- Over the centuries a number of foreign powers controlled all or parts of Phoenicia. They included Egypt, Assyria, Babylonia, and Persia.
- The Macedonians, led by Alexander the Great, conquered Phoenicia in 332 BCE.
- In 64 BCE Phoenicia became a part of the Roman Empire.




