Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis:
Due to continued rain in Kerala, the health department has issued caution on amoebic meningoencephalitis.
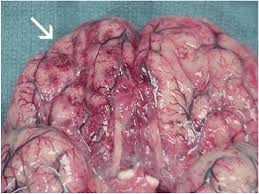
- Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a rare, usually fatal, infection of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- It is caused by a type of free-living amoeba (a microscopic, single-celled organism) called Naegleria fowleri.
- Naegleria fowleri occurs in shallow surface waters and incorrectly maintained swimming pools, hot tubs, and spas, particularly in warm climates.
- The amebas can enter the brain through the nose when people swim in contaminated warm, fresh water.
- The amoeba then invades the brain and meninges through the nose.
- Symptoms, which include fever, headache, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, typically appear within five days of infection and progress rapidly.
- In the later stages, one can suffer from a stiff neck, seizures, hallucinations, and even coma.
- There are no standard treatments for the treatment of PAM.
- Combination therapy using medicines to treat parasites offers the most promise.
- PAM differs from granulomatous amebic encephalitis, which is another very rare, usually fatal infection of the central nervous system caused by different free-living amebas, Acanthamoeba species or Balamuthia mandrillaris.




