What Is Wind Shear?
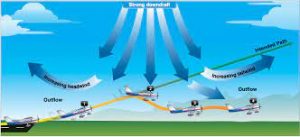
The concept of wind shear has gained increased attention due to its crucial role in determining whether a storm intensifies into a destructive hurricane.
- Wind shear is a meteorological phenomenon that refers to a sudden change in wind speed and/or wind direction over a relatively small distance.
- It is mainly of 2 types:
- Vertical Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly with increasing altitude.
Common examples include low-level jet streams and wind shear associated with thunderstorms. - Horizontal Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly over a horizontal distance.
- In this case, the wind might be blowing from the west at one spot, but then suddenly switch to blowing from the north just a bit further on.
- Common examples include frontal systems and sea breezes
- Vertical Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly with increasing altitude.




