Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 17th September 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Contents:
- The Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda Bill 2020 :
- Serial interval.:
- Djibouti Code of Conduct (DCOC) :
- Banking Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2020:
- Solar Cycle 25:
- Environment Ministerial Meeting (EMM) of the G20 countries:
- Draft Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020:
- Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act::
- Other important current affairs
1.The Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda Bill 2020 :
The Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda Bill 2020 has been passed by Rajya Sabha. The Bill was earlier passed in Lok Sabha on 19th March 2020.
- This paves the way to establish a state-of-the-art Ayurvedic institution called the Institute of Teaching and Research in Ayurveda (ITRA) at Jamnagar, Gujarat, and to confer the status of Institution of National Importance (INI) to it.
- ITRA will be the first institution with INI status in the AYUSH sector.
- The ITRA is sought to be established by conglomerating the presently existing Ayurveda institutes at Gujarat Ayurved University campus Jamnagar.
- This is a cluster of highly reputed institutions, namely,
- Institute for Post Graduate Teaching and Research in Ayurveda,
- Shree GulabKunverba Ayurveda Mahavidyalaya, and
- Institute of Ayurvedic Pharmaceutical sciences,
- Maharshi Patanjali Institute for Yoga Naturopathy Education & Research (to be made part of the Department of Swasthvritta of the proposed ITRA).
2.Serial interval.:
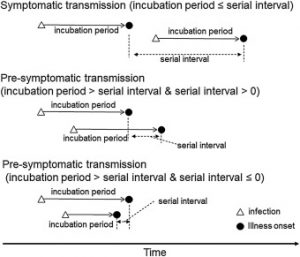
China, which has now gone over a month without any locally transmitted Covid-19 cases, was able to contain Covid-19 due to its ability to manage the serial interval.
- The serial interval is the duration between symptom onset of a primary case and symptom onset of secondary cases (contacts) generated by the primary case.
- In simple terms, the serial interval is the gap between the onset of Covid-19 symptoms in Person A and Person B, who is infected by Person A.
- The term was first used by British physician William Pickles, who had initially referred to it as transmission interval with reference to a hepatitis epidemic in the United Kingdom during 1942-45.
- Main Factors on which Serial Interval depends:
- Incubation period: The time between a person’s exposure to the virus and symptom onset.
- Reproduction rate or R naught: The number of people who will be infected by one infected person.
- The serial interval helps to gauge the effectiveness of infection control interventions besides indicating rising population immunity and forecast future incidence.
- Thus, the more quickly persons who contracted Covid-19 are identified and isolated, the shorter the serial interval becomes and cuts down opportunities for transmission of the virus.
3.Djibouti Code of Conduct (DCOC) :

India joined the Djibouti Code of Conduct (DCOC) as an observer as part of efforts aimed at enhancing maritime security in the Indian Ocean region.
Djibouti Code of Conduct:
- It is also known as the Code of Conduct concerning the Repression of Piracy and Armed Robbery against Ships in the Western Indian Ocean and the Gulf of Aden.
- It was adopted on 29th January 2009.
- It was established under the International Maritime Organization (IMO).
- Under the code, the signatories agreed to co-operate to the fullest possible extent in the repression of piracy and armed robbery against ships.
- Jeddah Amendment: An amendment to DCOC was made in 2017 to cover other illicit maritime activities, including human trafficking and illegal, unreported, and unregulated fishing, and to build national and regional capacity to address wider maritime security issues, as a basis for the sustainable development of the maritime sector.
- It has been signed by 20 countries including Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Madagascar, Maldives, Seychelles, Somalia, the United Republic of Tanzania, Yemen, Comoros, Egypt, Eritrea, Jordan, Mauritius, Mozambique, Oman, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Sudan, and the United Arab Emirates.
- The member states are located in areas adjoining the Red Sea, Gulf of Aden and the east coast of Africa and include island nations in the Indian Ocean.
- Observers: India, Japan, Norway, the UK and the USA.
4.Banking Regulation (Amendment) Bill, 2020:
Passed in Lok Sabha. The Bill replaces an ordinance to the same effect promulgated on June 26.
- The Bill proposes amendments to the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- With this new Bill, the central government aims to bring cooperative banks under the supervision of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
Key changes:
- Now, Provisions applicable to banking companies will also applicable to cooperative banks.
- This ensures that cooperative banks are equally subject to better governance and sound banking regulations through the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- With the amendments, RBI will be able to undertake a scheme of amalgamation of a bank without placing it under moratorium.
- It will help the central bank to develop a scheme to ensure the interest of the public, banking system, account holders in the bank, and banking company’s proper management, without disrupting any banking functionalities.
- The amendments also allow cooperative banks to raise money via public issues and private placements of equity or preference shares as well as unsecured debentures, with the central’s bank’s nod.
- The changes will not:
- Affect the existing powers of the state registrars of co-operative societies under state laws.
- Apply to Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) or co-operative societies whose primary object and principal business is long-term finance for agricultural development, and which do not use the words “bank”, “banker” or “banking”.
5.Solar Cycle 25,:

Scientists from NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) have announced their predictions about the new solar cycle, called Solar Cycle 25, which they believe has begun.
Key findings:
- The solar minimum for Solar Cycle 25 occurred in December 2019.
Scientists predict a solar maximum (middle of the solar cycle) will be reached by July 2025. - This solar cycle will be as strong as the last solar cycle, which was a “below-average cycle” but not without risks.
Solar cycle:
- The Sun is a huge ball of electrically-charged hot gas. This charged gas moves, generating a powerful magnetic field. This magnetic field goes through a cycle, called the solar cycle.
- Every 11 years or so, the Sun’s magnetic field completely flips. This means that the Sun’s north and south poles switch places. Then it takes about another 11 years for the Sun’s north and south poles to flip back again.
- So far, astronomers have documented 24 such cycles, the last one ended in 2019.
6.Environment Ministerial Meeting (EMM) of the G20 countries:
The G20 Environment Ministers Meeting (EMM) has taken place under the Presidency of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
- Global initiatives to reduce Land Degradation and Coral Reef Programme and two documents on climate change, related to managing emissions and climate change adaptations under the G20 in 2020, have been launched.
- G20 EMM, 2019 saw an agreement on adopting a new implementation framework for actions to tackle the issue of marine plastic waste on a global scale.
Global Initiative on Reducing Land Degradation:
- It aims to strengthen the implementation of existing frameworks to prevent, halt, and reverse land degradation within G20 member states.
- The Scientific Conceptual Framework for Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN), developed by the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), provides a scientific foundation for understanding, implementing, and monitoring land degradation.
- Globally, it aims to take into account possible implications on the achievement of Sustainable Development Goals (SDG-13: Climate Action, SDG-14: Life below Water, SDG-15: Life on Land) and adhere to the principle of doing no harm.
Global Coral Reef Research and Development Accelerator Platform:
- It is an innovative action-oriented initiative aimed at creating a global research and development program to advance research, innovation, and capacity building in all facets of coral reef conservation, restoration and adaptation.
- It will strengthen ongoing efforts and commitments made to enhance coral reefs conservation and stop their further degradation.
- Limiting global average temperature and pursuing efforts to limit the temperature increase, in line with the Paris Agreement, provides the only chance for the survival of coral reefs globally.
India’s Stand:
- India intends to take measures to enhance coral reef conservation under the National Coastal Mission Programme.
- The proposed mission under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) will address the impact of climate change on coastal and marine ecosystems.
- It will include all phases of the Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) Project.
- India has also put efforts towards achieving land degradation neutrality and towards the attainment of global goals of climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- The Indian government sees schemes such as the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, Soil Health Card Scheme, and Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana as tools to tackle the problem of land degradation.
- India is committed to working with G20 nations for a better world and is taking adequate action to meet the Paris Agreement and its climate commitments.
- It was emphasized that equity, common but differentiated responsibilities, finance, and technology partnerships are the key pillars to tackle the problem of climate change.
7.Draft Electricity (Rights of Consumers) Rules, 2020::
Union Power Ministry has drafted Rules providing for the Rights of Electricity Consumers for the First Time.
The main features are:
- Reliability of service: State Electricity Regulatory Commissions to fix the average number and duration of outages per consumer per year for DISCOMs. (A power outage is the loss of the electrical power network supply to an end-user.)
- Timely and simplified procedure for connection: Only two documents for connection up to load of 10 kw and no estimation of demand charges for loads up to 150 kw to expedite giving connection.
- The time period to provide new connection: Not more than 7 days in metro cities, 15 days in other municipal areas, and 30 days in rural areas, to provide new connection and modify existing connections.
- 2 to 5% rebate on serving bills with a delay of sixty days or more.
- Push to online payment: Option to pay bills in cash, cheque, debit cards, net banking etc but bills of Rs. 1000 or more to be paid online.
- Prosumers: Recognition to the emerging category of consumers known as “Prosumers”.They will have the right to produce electricity for self-use and inject excess in the grid using the same point of the connection up to limits prescribed by the SERC.
- Consumer Grievance Redressal Forum with 2-3 representatives of consumers at various levels starting from Sub-division for ease of consumer grievance redressal.
8.Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act::
According to the latest data released by the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), a total of 3,005 cases were registered in the country under the anti-terror law Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) in 2016, 2017, and 2018, and 3,974 people were arrested under the Act
The Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act:
- Passed in 1967, the law aims at effective prevention of unlawful activities associations in India.
- The Act assigns absolute power to the central government, by way of which if the Centre deems an activity as unlawful then it may, by way of an Official Gazette, declare it so.
- It has the death penalty and life imprisonment as the highest punishments.
- Under UAPA, both Indian and foreign nationals can be charged. It will be applicable to the offenders in the same manner, even if the crime is committed on foreign land, outside India.
- Under the UAPA, the investigating agency can file a charge sheet in a maximum of 180 days after the arrests and the duration can be extended further after intimating the court.
Amendments and changes:
- The 2004 amendment, added “terrorist act” to the list of offenses to ban organizations for terrorist activities, under which 34 outfits were banned. Till 2004, “unlawful” activities referred to actions related to secession and cession of territory.
- As per amendments of 2019:
- The Act empowers the Director-General of the National Investigation Agency (NIA) to grant approval of seizure or attachment of property when the case is investigated by the said agency.
- The Act empowers the officers of the NIA, of the rank of Inspector or above, to investigate cases of terrorism in addition to those conducted by the DSP or ACP or above rank officer in the state.
Other important current affairs:
1.The World Patient Safety Day 2020 is being observed on 17 September under the theme “Health Worker Safety: A Priority for Patient Safety.”
- The 72nd World Health Assembly adopted resolution WHA 72.6 ‘Global action on patient safety’ on 25 May 2019.
- The resolution recognizes patient safety as a global health priority and endorses the establishment of World Patient Safety Day to be observed annually on 17 September.
- World Patient Safety Day calls for global solidarity and concerted action by all countries and international partners to improve patient safety.
2.The Prime Minister Narendra Modi shall dedicate to the nation the historic Kosi Rail Mahasetu (mega bridge) to the Nation on the 18th of September 2020.
- The Kosi Rail Mahasetu is 1.9 KM long.
- In 1887, a meter gauge link was built in between Nirmali and Bhaptiahi (Saraigarh).
- During the heavy flood and severe Indo Nepal earthquake in 1934, the rail link was washed away, and thereafter due to the meandering nature of river Kosi, no attempt was made to restore this Rail link for long period.
- The Kosi Mega Bridge line project was sanctioned by the Government of India during 2003-04.
- The dedication of the Kosi Rail Mahasetu is a watershed moment in the history of Bihar and the entire region connecting to the North East. This bridge is of strategic importance along the India-Nepal border.
3.The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) governor has called for a balanced loan restructuring scheme to tackle the Covid-19 related stress.
- The financial stability of the banking sector needs to be kept in mind while providing loan restructuring along with depositors’ interest.
- There are crores of depositors (small depositors, middle-class people, retired persons) who depend on deposit income while borrowers are only in lakhs.
- The loan restructuring includes altering the terms of existing loans, usually to make them more favorable to the borrower. For example, the lender may restructure a loan to receive a lower interest rate or monthly payment.
- Restructured loans are most common if the borrower states that he/she can no longer afford payments under the old terms.
- The governor does not want a repeat of the Non-Performing Asset (NPA) surge that happened after 2014 with loan restructuring.
- The economic measures taken by the RBI in the wake of the global financial crisis of 2008-09, led to a surge in bad loans from 2014-15.
- The idea behind loan restructuring was to protect viable businesses that are facing genuine cash flow problems.
- The revival of business will ensure NPA levels are kept low and also ensure quick economic recovery.
- However, the governor cautioned that the economic recovery would be gradual, as the upticks in some sectors appear to be leveling off as efforts towards reopening of the economy are confronted with rising infections.
4.The Russia Direct Investment Fund (RDIF), which is piloting Russia’s Sputnik V vaccine, has partnered with the Hyderabad-based Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories to supply 100 million doses of the vaccine.
- Sputnik V: The Russian vaccine has been named after the first artificial Earth satellite, Sputnik-I launched by the Soviet Union.
- It is the first Covid-19 vaccine to be approved by any government for common people.
- The Russian vaccine has outrun other Covid-19 vaccines like Oxford-Astra Zeneca, Moderna and Pfizer which are still in trials.
- India’s Covaxin has been approved for human clinical trials.
- Another Indian vaccine ZyCoV-D has entered phase I/II of clinical trials.
- It has been developed by Moscow’s Gamaleya National Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology in collaboration with Russia’s defense ministry.
- India has also partnered with the USA for the development of the Covid-19 vaccine.
5.Indian scientists from the Zoological Survey of India, Pune have reported a first-of-its-kind discovery of morphological phenotypic plasticity (MPP) in the Kalinga cricket frog.
- Kalinga Cricket Frog:
- Scientific Name: Fejervarya kalinga.
- It is a recently identified species that were documented in 2018.
- It was thought to be endemic only to the higher-elevation hill ranges of the Eastern Ghats in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- Cricket frogs are indicators of a healthy ecosystem and live in wide habitat ranges in agricultural fields, streams, swamps, and wetlands.
- Latest Findings:
- It has been reported from the central Western Ghats, with the evidence of considerable MPP.
- Its physical characteristics are entirely different from the other known Fejervaraya/Minervarya species from the Western Ghats.
- It was the only genetic analysis that helped prove that physically different-looking frogs from eastern and western ghats were the same.
- Morphological Phenotypic Plasticity:
- Phenotypic plasticity is the ability of an organism to change in response to stimuli or inputs from the environment.
6.National Hispanic Heritage Month began in the USA. The annual event is marked every year from 15th September to 15th October.
- The Hispanic Heritage Month honors the history, culture, and contributions of American citizens whose ancestors hailed from Spain, Mexico, the Caribbean, and Central, and South America.
- The observation was started in 1968 by President Lyndon Johnson as Hispanic Heritage Week.
- It was extended to an entire month in 1988 by President Ronald Reagan, the year it was enacted into law.




