Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs:20th May 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc.
Contents:
- Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs):
- Hotter Oceans and Supercyclones:
- Malaysian palm oil :
- India and the US under the Vaccine Action Programme (VAP) :
- Malicious Software Cerberus:
- Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR):
- Nepal-India border dispute:
- ‘Solar minimum’ :
- India has been elected to the World Health Organisation (WHO)’s Executive Board:
- Other important current affairs.
1. Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs):

Days after changing the definition of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), the government has decided to further revise the criteria for medium units by enhancing the investment and turnover limits to up to ₹50 crores and ₹200 crores respectively.
- As per the revised definition, any firm with investment up to ₹1 crore and turnover under ₹5 crore will be classified as “micro”.
- A company with investment up to ₹10 crore and turnover up to ₹50 crores will be classified as “small” and a firm with investment up to ₹20 crore and turnover under ₹100 crore will be classified as “medium”.
- The previous criteria for classifying enterprises in the “medium” category were investment up to ₹10 crore and turnover of up to ₹5 crores.
2.Hotter Oceans and Supercyclones:

The supercyclone ‘Amphan’ is likely to make landfall between the Sagar islands of West Bengal and the Hatiya islands of Bangladesh.
- Cyclone Amphan (pronounced as UM-PUN) is a tropical cyclone formed over Bay of Bengal that has turned into a “super cyclonic storm (maximum wind speed is 120 knots)”.
- The higher than normal temperatures in the Bay of Bengal (BoB) with the countrywide lockdown due to the Covid-19 pandemic have played a role in turning a storm into a super cyclone.
- The super cyclone Amphan is the strongest storm to have formed in the BoB since the super cyclone of 1999 that ravaged Paradip in Odisha.
‘Cyclones’ as a Regular Phenomenon
- The cyclones gain their energy from the heat and moisture generated from warm ocean surfaces.
- The BoB has a higher Sea Surface Temperature (SST) compared to the Arabian Sea. Some of the reasons for the higher SST of Bob are:
- Slow Flowing Winds: It keeps temperatures relatively high i.e. around 28 degrees around the year.
- Higher Rainfall: It provides required humidity for cyclone formation.
- Constant Inflow of Fresh Water: The inflow from the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers makes it impossible for the warm water to mix with the cooler water below, making it ideal for a cyclonic depression.
- On the other hand, the Arabian Sea receives stronger winds that help dissipate the heat, and the lack of constant freshwater supply helps the warm water mix with the cool water, reducing the temperature.
- Additionally, the tropical cyclones in these seas are a typical feature of the summer months and play a role in aiding the arrival of the monsoon.
Unusual Higher Temperature in BoB:
- In 2020, the BoB has observed record summer temperatures due to global warming from fossil fuel emissions that has been heating up oceans.
- The cyclone Fani in 2019 was also fuelled by high temperatures in the BoB.
- For the first two weeks of May, there were maximum surface temperatures of 32-34°C consecutively.
- These are record temperatures driven by climate change observed until now.
- Such unusual warming around India is no longer restricted to just the BoB but also the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It makes storm prediction less reliable as well as disrupting monsoon patterns.
3. Malaysian palm oil :

Indian buyers have resumed purchases of Malaysian palm oil after a four-month gap following a diplomatic row, with buying spurred by a fall in domestic inventories and discounted prices.
- The renewed purchases come amid improving trade relations between the two countries after the formation of a new government in Kuala Lumpur, with Malaysia signing a deal last week to buy a record 100,000 tonnes of Indian rice.
- Leading Indian importers last week contracted up to 200,000 tonnes of crude palm oil from Malaysia, the world’s No.2 producer after Indonesia, to be shipped in June and July.
- A restart to buying by India, the world’s biggest edible oil importer, could further support Malaysian palm oil prices.
- India buys more than 9 million tonnes of palm oil a year, accounting for nearly two-thirds of its total edible oil imports, and took a record 4.4 million tonnes of Malaysian palm oil in 2019.
4. India and the US under the Vaccine Action Programme (VAP) :

India and the US under the Vaccine Action Programme (VAP) are planning to collaborate on the development and testing of vaccine candidates and diagnostics for Covid-19.
- The U.S has already announced a donation of 200 ventilators to India. The ventilators, which will be paid for by the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), are part of the $5.9 million in funding announced till date for India.
- The U.S. Centres for Disease Control and Prevention has said it would separately fund the Government of India $3.6 million to support prevention, preparedness, and response activities in India, in collaboration with and concurrence from the GoI.
About Vaccine Action Programme (VAP):
- The VAP is an Indo-US bilateral program, which supports a broad spectrum of activities relating to new and improved vaccines.
- Focus: The program was designed to encompass laboratory-based research, evaluation of candidate vaccines, testing for clinical development, vaccine quality control, delivery of vaccines, and so on.
- The program is under implementation since July 1987 under the Gandhi-Reagan Science & Technology Agreement.
- Major projects were initiated under VAP in the areas of rotaviral diarrhea, dengue, viral hepatitis, acute respiratory infections, tuberculosis, malaria, typhoid, E. coli, leishmaniasis, pneumococcal, HIV/AIDS, etc.
5.Malicious Software Cerberus:

Recently, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has sent alerts to all the States, Union Territories, and the central agencies on malicious software (Cerberus) threat that is taking advantage of the Covid-19 pandemic.
- The cyber alert related to Cerberus has been sent on the basis of inputs received from the Interpol.
- Cerberus: It is a Banking Trojan. It is primarily used to steal financial data, such as credit card numbers.
- Trojan:
- A trojan is a type of malicious code or software to damage, disrupt, steal, or inflict harmful action on data or network.
- The Trojan can also use overlay attacks to trick victims into providing personal information and can capture two-factor authentication details.
- An overlay attack happens when an attacker places a window over a legitimate application on the device. When the target application is running, the overlay opens messages or data input forms identical to the real ones.
- Victims enter information (E.g. login credentials or bank card numbers), believing that they are dealing with the original program.
- Banking Trojan is a malicious program used in an attempt to obtain confidential information about customers and clients using online banking and payment systems.
- It takes advantage of the Covid-19 pandemic and sends SMS to lure a user to download the link containing the malicious software.
- It deploys its malicious application usually spread via phishing campaigns to trick users into installing it on their smartphones.
- Phishing: The email or text message carrying a link appears to come from a trusted source like a bank.
- The link takes to a fake website and once details like login name and passwords are entered, the login credentials reach the hacker.
6.Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR):

Recently, a new prey and predator estimation in Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve (TATR) in Maharashtra found the presence of 115 tigers and 151 leopards.
- The estimation was done as part of the long-term monitoring of tigers, co-predators, and prey species in TATR inside the core and buffer areas of the reserve.
- The tiger reserves are constituted on a core/buffer strategy.
- The Project Tiger aims to foster an exclusive tiger agenda in the core areas of tiger reserves, with an inclusive people-oriented agenda in the buffer.
- The core areas have the legal status of a national park or a sanctuary, whereas the buffer or peripheral areas are a mix of forest and non-forest land, managed as a multiple-use area.
- The tiger numbers appear to be up but the population density shows a decline
- Population Density represents the number of animals residing in per unit area.
Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve
- It is located in Chandrapur district in Maharashtra.
- It is Maharashtra’s oldest and largest national park.
- It is one of India’s 50 “Project Tiger” reserves.
7.Nepal-India border dispute:
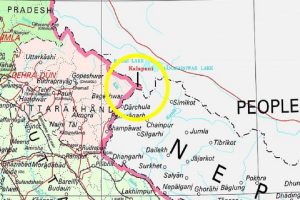
The Nepal government has decided it will release a new, updated political map which will include the disputed areas of Lipulekh, Kalapani, and Limpiyadhura as part of Nepali territory.
- This comes after the Indian defense ministry recently inaugurated a link road to the China border that passes through Lipulekh. The Kalapani territory is an area under the Indian administration as part of the Pithoragarh district in the Uttarakhand state.
- Following the road inauguration, the Nepal government released a press note stating that the eastern area from Mahakali River belongs to Nepal as per the Sugauli Treaty, 1816.
- But the Indian government said that it had constructed the road in its own territory.
- A few days later, the Indian Army chief General M.M. Naravane accused Nepal of acting ‘at the behest of someone else,’ a thinly veiled reference to China.
8.’Solar minimum’ :
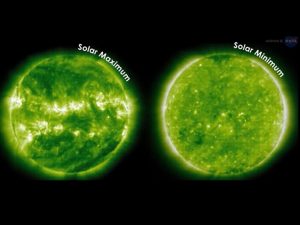
The sun is said to have gone into a state called the ‘solar minimum’ and is about to enter the deepest period of ‘sunshine recession’ as sunspots are virtually not visibly at all. Some reports suggest that it has been almost 100 days this year when the sun has shown zero sunspots.
- Sun has a cycle that lasts on average 11 years, and right now we are at the peak of that cycle.
- Every 11 years or so, sunspots fade away, bringing a period of relative calm. This is called the solar minimum. And it’s a regular part of the sunspot cycle.
- While intense activity such as sunspots and solar flares subside during solar minimum, that doesn’t mean the sun becomes dull. Solar activity simply changes form.
- For instance, during solar minimum, we can see the development of long-lived coronal holes.
- This may cause health risks to astronauts traveling through space as “the sun’s magnetic field weakens and provides less shielding from these cosmic rays.
9. India has been elected to the World Health Organisation (WHO)’s Executive Board:
xfd
Recently, India has been elected to the World Health Organisation (WHO)’s Executive Board. It will also be holding a Chairmanship of the Executive Board for the next year (from May 2020- May 2021)
- Currently, the chairmanship of the WHO Executive Board is being held by Japan.
- The proposal to appoint India’s nominee to the executive board was signed by the 194-nation at the 73rd World Health Assembly between 18-19 May 2020.
- In 2019, WHO’s South-East Asia group had unanimously decided that India would be elected to the executive board for a three-year-term beginning from May, 2020.
- WHO Member States are grouped into 6 WHO regions namely, African Region, Region of the Americas, South-East Asia Region, European Region, Eastern Mediterranean Region, and Western Pacific Region.
- India has been elected along with 10 other countries including Botswana, Colombia, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Madagascar, Oman, Republic of Korea, Russia, and the United Kingdom.
- WHO Executive Board
- Composition: The Executive Board is composed of 34 individuals technically qualified in the field of health, each one designated by a member state elected to do so by the World Health Assembly.
- Member States are elected for three-year terms.
- Chairman: The chairman’s post is held by rotation for one year among regional groups.
It is not a full-time assignment and the chairman is just required to chair the Executive Board’s meetings. - Meeting: The Board meets at least twice a year.
- Functions: The main functions of the Executive Board are to give effect to the decisions and policies of the World Health Assembly, to advise it and generally to facilitate its work.
- World Health Assembly
- The World Health Assembly is the decision-making body of WHO.
- It is attended by delegations from all WHO Member States and focuses on a specific health agenda prepared by the Executive Board.
Other important current affairs:
1. Union Human Resource Development (HRD) Minister launched a new mobile app called the ‘National Test Abhyas’.
- The AI-powered mobile App has been developed by National Testing Agency (NTA) to enable candidates to take mock tests for upcoming exams such as JEE Main, NEET under the NTA’s purview.
- The app has been launched to facilitate candidates’ access to high-quality mock tests in their homes since there was a demand for making up the loss to students due to closure of educational institutions and NTA’s Test-Practice Centers (TPCs) due to the continuing lockdown.
2. The Center for International Climate and Environmental Research (CICERO) has evaluated Covid-19’s effect on carbon emissions.
- It has predicted that emissions will fall between 4.2 and 7.5% last year, as against a rise of 1% which was earlier predicted for 2020 before the pandemic outbreak.
- Earlier, the International Energy Agency (IEA) released Global Energy Review: 2020 with details on the effects of the pandemic on global energy demand and carbon emissions.
- In India, the nationwide lockdown led to minimal air pollution and improved air quality.
Data Analysis:- Carbon emissions were 5% lower than during the same time in 2019.
- The decline was noticed in coal emissions (8%), oil emissions (4.5%), and natural gas emissions (2.3%) as well.
- Emissions declined the most in regions that were impacted the highest by the disease.
- For example, there was an 8% decline in emissions in China and Europe and a 9% decline in the USA.
- Countries in full lockdown are seeing an average decline of 25% in energy demand per week, while in those with a partial lockdown, the fall in energy demand is about 18% per week.
3. Union Housing and Urban Affairs Ministry has announced the results of the garbage-free star rating for the cities.
- A total of 141 cities have been rated — six of them 5-star, 65 of three-star, 70 one-star.
- Around 6 cities were given a 5-star rating. This includes Ambikapur, Surat, Rajkot, Mysuru, Indore, and Navi Mumbai.
- Karnal, New Delhi, Tirupati, Vijayawada, Chandigarh, Bhilai Nagar, Ahmedabad are among ‘three-star garbage-free ratings while Delhi Cantonment, Vadodara, Rohtak are among one-star garbage-free cities.
- The star rating protocol was launched by the central government in January 2018 to institutionalize a mechanism for cities to achieve garbage free status leading to a higher degree of cleanliness.
- The protocol includes components such as the cleanliness of drains & water bodies, plastic waste management, managing construction & demolition waste which are critical drivers for achieving garbage-free cities.
- It is one of the various initiatives which intends to make Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U) as a successful project.
4. The Ministry of Finance is not in favor of granting Goods and Services Tax (GST) exemption, as has been demanded by various sections of the industry.
- Providing GST exemption will have seriously adverse implications on state finances, also businesses would suffer and consumers would be hit by the price rise.
- The exemption would block Input Tax Credit (ITC) as manufacturers will pay GST on inputs but cannot claim ITC because the final product is tax-free. Thus, it will increase the cost of manufacturing, which will lead to an increase in the cost of products.
- The GST exemption will also increase the compliance burden for manufacturers who would be required to maintain separate accounts for inputs and goods used for the production of the item.
- Further, the GST exemption provides an incentive for imports, which do not have input taxes as compared to domestic supplies.
- This makes imported goods cheaper than locally produced goods.
- In the past when the GST exemption on sanitary napkins was allowed, it had led to similar hardship for domestic manufacturers of sanitary napkins.
5. The government has notified the cut in Employee’s Provident Fund (EPF) contribution to 10% for May, June, July.
- The Centre has notified the reduction in statutory rate of contributions from 12 per cent to 10 per cent for wage month period from May to July 2020 for all class of establishments covered under the Employees Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952.
- Reduction in rate of EPF contributions from 12 per cent to 10 percent of basic wages and Dearness allowances is intended to benefit both 4.3 Crore employees.
- As a result of the reduction in the statutory rate of contributions, the employee will have a higher take-home pay.
6. The Indian Railways has operationalized its first 12,000 hp electric locomotive manufactured locally by French rolling stock manufacturer Alstom. The loco is named WAG12 with Number 60027.
- The locomotive made its maiden commercial run between Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Station to Shivpur.
- India became the sixth country in the world to join the club of countries producing high horsepower locomotive indigenously.
- It has been manufactured at the Madhepura Electric Locomotive Pvt. Ltd. (MELPL), in Bihar, which is a joint venture between the French major and the Indian railways holding an equity share of 74% and 26% respectively.
- The joint venture remains the largest Foreign Direct Investment in the railway sector.
- The entry of WAG 12B (e-loco) into the Indian Railways fleet will allow faster and safer movement of heavier freight trains capable to haul around 6000 tonnes at a top speed of 120 mph.
- It is the first time, high horsepower locomotive has been operationalized on a broad gauge track in the world.
7. The United Nations Relief and Works Agency (UNRWA), has applauded India’s financial support to keep its basic services operating, under the Covid-19 crisis.
- The Government of India provided USD 2 million to the UNRWA in support of its core programs and services, including education and health.
- India had increased its annual contribution to the UNRWA from USD 1.25 million in 2016 to USD 5 million in 2019.
- It pledged another USD 5 million for 2020 which opens its way to become a member of the agency’s advisory commission.
- It is also preparing medical supplies for the Palestinians.
8. Rajiv Gandhi Nyay Yojana will be launched by the Chhattisgarh government to ensure “minimum income availability” to farmers of the state through direct bank transfer.
- The scheme will formally be launched in the state on May 21, the death anniversary of former prime minister Rajiv Gandhi.
- Based on registered area and area under cultivation during Kharif crop season 2019, Rs 10,000 per acre will be deposited in the bank accounts of farmers as agriculture assistance grants for sowing crops such as paddy, maize, and sugarcane.
- At least 19 lakh farmers will benefit from the scheme, for which the state government had allocated Rs 5,756 crore in the budget 2020-21.
- Similarly, for sugarcane crop, payment of FRP amount of Rs 261 per quintal and incentive and input support, amounting to Rs 93.75 per quintal, i.e. maximum Rs 355 per quintal, will be made depending on the quantity of sugarcane purchased by the cooperative mill in the crushing year 2019-20.
- Under this, 34,637 farmers of the state will get Rs 73 crore 55 lakh in four installments and the first installment of this amount, Rs 18,43 crore will be transferred on May 21.
- The government is also going to provide incentive money (outstanding bonus) at the rate of Rs 50 per quintal based on the quantity of sugarcane purchased through cooperative sugar factories in the year 2018-19.
9. World Bee Day 2020 is being celebrated on May 20 under the theme “Save the Bees.”
- To raise awareness of the importance of Bees and other pollinators, such as butterflies, bats, and hummingbirds, the threats they face and their contribution to sustainable development, the UN-designated 20 May as World Bee Day.
- 20 May coincides with the birthday of Anton Janša, who in the 18th century pioneered modern beekeeping techniques in his native Slovenia and praised the bees for their ability to work so hard, while needing so little attention.
10.




