Today’s Current Affairs: 12th May 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Raika tribe:

The Raika’s knowledge of pasture cycles, animal health and biodiversity has long supported the health of Rajasthan’s arid ecology.
- The Raika tribe is an indigenous pastoralist community primarily inhabiting the arid and semi-arid regions of Rajasthan, notably around Kumbhalgarh in Rajsamand district.
- Also known as Rabaris, they have a distinct socio-cultural relationship with camels.
- The Raikas have historically been the principal breeders of Rajasthan’s indigenous camel breeds, especially the Marwari camel, known for its strength, endurance, and desert adaptability.
- For the Raikas, camel herding is not just a livelihood but a cultural identity, woven into rituals, oral traditions, and seasonal migrations.
- The Raikas possess traditional knowledge of pasture cycles, animal health, and biodiversity, which has historically sustained the fragile ecology of Rajasthan’s arid landscapes.
- Their age-old migratory grazing routes allowed camels to feed on medicinal desert shrubs, enhancing both animal health and ecosystem balance.
Asteroid YR4:

On April 2, 2025, NASA announced that asteroid 2024 YR4 has a 3.8% probability of colliding with the Moon on December 22, 2032.
- YR4 is a Near-Earth Asteroid (NEA) discovered in December 2024 using the ATLAS telescope in Chile.
- Its orbit brings it within 1.3 times the Earth-Sun distance, making it a Near-Earth Object (NEO).
- Initially, YR4 triggered the highest-ever NASA asteroid impact alert in February 2025.
- New infrared data from the James Webb Space Telescope estimates its size at ~65 metres, comparable to a 10-storey building, which is below the 140-meter threshold for classification as a “Potentially Hazardous Asteroid”.
- Earlier, YR4 had a 1% chance of hitting Earth, but the latest trajectory analysis shows a negligible risk to Earth.
- Asteroids, also known as minor planets, are rocky remnants from the early solar system, dating back 6 billion years.
- They exhibit irregular shapes, though a few are nearly spherical, and some host small companion moons or even exist as binary or triple systems.
Indian Grey Wolf : In News

Indian Grey Wolves, apex predators and ecological regulators of grasslands, are facing rapid population decline due to rising threats from feral (free-ranging) dogs.
- The Indian Grey Wolf is a subspecies of the Grey Wolf found in the Indian subcontinent and Southwest Asia.
- The Indian grey wolf is protected under:
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern, but considered locally endangered in India due to sharp population decline.
- CITES: Appendix I, indicating species threatened with extinction.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Listed in Schedule I, providing the highest degree of protection in India.
- Maharashtra Forest Rules, 2014 allow the removal or elimination of trespassing animals (dogs) from reserve forests if they threaten wildlife.
- However, Forest officials hesitate to cull dogs due to animal rights concerns, considering vaccination as an alternative, though logistically difficult.
- The case highlights the complex human-animal-domestic dog interface, a rising concern in India’s open and agro-ecosystem habitats.
- It is a key example of emerging zoonotic threats (e.g., canine distemper virus) and genetic dilution through hybridisation.
PL-15 Missile:

Amid the ongoing escalating tensions between India and Pakistan, a fully intact Chinese-made PL-15 long-range air-to-air missile has been recovered in Punjab’s Hoshiarpur.
- The PL-15, known as “Thunderbolt-15,” is a long-range, beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM).
- It was developed by China’s 607 Institute and manufactured by the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation (CASIC).
- It can engage enemy aircraft at distances well beyond visual range.
- It features a dual-pulse solid-propellant rocket motor, allowing it to reach speeds exceeding Mach 5.
- The domestic Chinese version boasts a range of 200–300 km, while the export variant, the PL-15E, has a declared maximum range of 145 km, though operational factors may reduce this to 100–120 km depending on the launch platform.
- The missile is equipped with a high-explosive fragmentation warhead weighing 20–25 kg, optimized to destroy maneuvering aerial targets.
- The PL-15 employs a sophisticated guidance system, combining inertial navigation, Beidou satellite updates, a two-way datalink for mid-course corrections, and a terminal active radar seeker using advanced AESA (Active Electronically Scanned Array) technology.
- This suite provides high accuracy, resistance to electronic jamming, and the ability to engage targets in contested environments.
Crohn’s Disease:
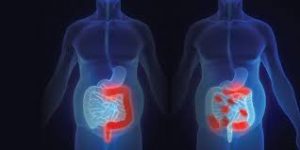
A former employee of Elon Musk’s SpaceX is suing the company for allegedly firing him over frequent restroom use caused by a chronic medical condition.
- Crohn’s Disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes swelling and irritation of the tissues, called inflammation, in the digestive tract.
- Inflammation caused by Crohn’s disease can affect different areas of the digestive tract in different people.
- It most commonly affects the end of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine.
- The inflammation often spreads into the deeper layers of the bowel.
- Crohn’s disease can be both painful and debilitating. Sometimes, it may lead to serious or life-threatening complications.
- Symptoms of Crohn’s disease vary from person to person and may include diarrhea, cramping, and pain in abdomen, and weight loss.
- There’s no known cure for Crohn’s disease, but therapies can greatly reduce its symptoms and even bring about long-term remission and healing of inflammation.
- With treatment, many people with Crohn’s disease can function well.
Anamalai Tiger Reserve:

The pre-monsoon (summer) estimation of tigers and other animals started in the Pollachi and Tiruppur divisions of the Anamalai Tiger Reserve (ATR) recently.
- It is located at an altitude of 1400 m in the Anamalai Hills of Pollachi and Coimbatore District of Tamil Nadu.
- It is located on the southern side of the South Western Ghat landscape.
- It covers 1,479.87 sq. km., including 958.59 sq.km. of core area.
- It is surrounded by Parambikulum Tiger Reserve on the East, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary and Eravikulum National Park on the South Western side.
- The reserve is also surrounded by Nenmara, Vazhachal, Malayattur and Marayur reserved forests of Kerala.
- The Kariyan shola, Grass hills and Manjampatti of Anamalai Tiger Reserve has been identified as a world heritage site by UNESCO.
- It is home to several indigenous tribal communities such as the Kadars, Muduvars, Malasars, Malai malasars, Eravalars and Pulayars.
- It ranges from wild wet evergreen forests and semi-evergreen forests to moist deciduous and dry deciduous forests.
- Some part of the reserve boundary also includes the shola forests in the Anamalai Hills and rarer Montane Grasslands, Savannahs and Marshy Grasslands.
- Around 2500 species of angiosperms are found in the Anamalai Tiger Reserve, with several species of Balsam, Crotalaria, Orchids, and Kurinchi.
- The reserve is rich in wild relatives of cultivated species like mango, jackfruit, wild plantain, ginger (Zingiber officinale), turmeric, pepper (Piper longum), cardamom, etc.
- The important wild animals of the reserve include: Tiger, Asiatic elephant, Sambar, Spotted deer, Barking deer, Jackal, Leopard, Jungle cat, etc.
First-Ever Pangenome Of Asian Rice:

Scientists have created the first-ever pangenome of Asian rice (Oryza sativa L.) by compiling genetic data from 144 varieties of both wild and cultivated rice strains.
Key Findings:
- Researchers used high-fidelity sequencing (PacBio HiFi) and advanced computational tools to assemble 87 billion base pairs of novel genetic sequences, which were absent from the earlier reference genome of Oryza sativa ssp. japonica.
- A total of 69,531 genes were identified, out of which:
- 28,907 are core genes common to all varieties,
- 13,728 are specific to wild rice, and
- About 20% of all genes were unique to wild rice species, offering potential for future improvements in rice breeding.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) recently developed two genome-edited rice varieties – Samba Mahsuri and MTU 1010 – that show promise for higher yield and drought resistance, though they are not yet released for cultivation.
- A pangenome includes not only the core genes shared by all varieties but also the unique genes found in individual strains, offering a comprehensive map of genetic diversity in Asian rice.
- This project is comparable to the Human Genome Project (2003) in its goal to map genome-wide variations, but it is focused on rice, which is a staple food for nearly two-thirds of the world population.
- India, a major rice producer, recorded a record production of 220 million tonnes in 2024-25 over 51,000 hectares, with an average yield of 4.2 tonnes/hectare.
- The new pangenome database enables the development of advanced rice cultivars with enhanced traits, such as disease tolerance and resilience to climate shocks.
RNA Exosomopathies:

Researchers at Emory University and the University of Texas Health Science Centre have shown that mutations causing brain defects in humans also produce similar effects in budding yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), a simpler eukaryotic organism.
- These mutations affect a cellular complex called the RNA exosome, which plays a critical role in RNA processing, surveillance, and degradation.
- This reveals the potential to use yeast as a model organism for studying human neurological disorders, particularly those related to RNA exosome dysfunction.
- RNA exosomopathies are disorders caused by mutations in genes coding for RNA exosome components.
- These disorders primarily lead to brain maldevelopment, affecting structures like the pons and cerebellum.
- A key example is Pontocerebellar Hypoplasia Type 1 (PCH1), which results in severe motor, cognitive, and developmental impairments in infants.
- The RNA exosome is a multi-protein complex discovered in yeast in 1997.
- It is responsible for: Processing, surveillance, and degradation of different types of RNA molecules, Maturation of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) – essential for building ribosomes, Elimination of faulty messenger RNA (mRNA) and regulation of non-coding RNAs (ncRNA).
Magnetars:

Researchers have found observational evidence that magnetar flares can produce heavy elements like gold through a process known as r-process nucleosynthesis. Until now, gold was believed to form predominantly in neutron star mergers.
- Magnetars are a type of neutron star characterised by exceptionally strong magnetic fields, estimated to be a thousand times stronger than typical neutron stars. Occasionally, they emit intense bursts of energy in the form of flares.
- The discovery was based on data from a giant flare emitted by a magnetar in 2004, during which unusual gamma-ray emissions were recorded almost a day after the initial flare by NASA’s Compton Gamma Ray Observatory.
- The delayed emission was not consistent with standard flare afterglows. Instead, it displayed signatures of radioactive decay from neutron-rich isotopes, suggesting the presence of r-process nucleosynthesis.
- The r-process or rapid neutron-capture process is a series of nuclear reactions where atomic nuclei rapidly capture neutrons, forming heavy elements like gold, platinum, and uranium. It requires extreme energy environments and neutron-rich matter.
- Researchers estimated that approximately 9 septillion kg of r-process material was ejected at nearly light speed during the flare. This material likely underwent rapid neutron capture, resulting in the synthesis of heavy elements.
- This discovery suggests that magnetars could have contributed to the universe’s heavy element inventory much earlier than neutron star collisions, offering insights into the chemical evolution of galaxies.
Niveshak Shivir Initiative:
IEPFA and SEBI jointly convened a strategic meeting, to launch the “Niveshak Shivir” initiative to help investors reclaim unclaimed dividends and shares.A nationwide investor assistance and outreach program to help investors reclaim unclaimed dividends and shares with ease.Launched by: Investor Education and Protection Fund Authority (IEPFA) under the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, in collaboration with SEBI.
Vruthi Campaign:
Kerala launched the ‘Vruthi’ campaign in October 2024 to combat the rising waste crisis through mass public participation and decentralized solutions.The recent ‘Clean Kerala Conclave 2025’ showcased innovative practices and collective achievements in waste.Vruthi’ means cleanliness of body and mind.It is a statewide behavioural change campaign for garbage-free Kerala. Part of the ‘Malinya Muktham Nava Keralam’ mission.
Taliban Suspends Chess in Afghanistan Over Sharia Law Concerns:
The Taliban regime in Afghanistan has officially suspended the sport of chess, citing concerns over its compatibility with Islamic law. The move, announced on May 12, 2025, reflects the Taliban’s ongoing imposition of stricter regulations on recreational and cultural activities since regaining power in August 2021. The ban is temporary, pending review by religious authorities, but has already impacted everyday life in Kabul and beyond.
Deepika Kumari Clinches Bronze at Archery World Cup Stage 2:
India’s top archer, Deepika Kumari, secured a bronze medal at the Archery World Cup Stage 2 held in Shanghai on May 11, 2025. After a tough semifinal loss to world No. 1 Lim Sihyeon, Deepika displayed remarkable resilience and composure to defeat Korea’s Kang Chae Young 7-3 in the bronze medal playoff. This victory brought India’s medal tally at the event to six, further establishing the country’s prowess in archery.
8th UN Global Road Safety Week 2025:
The 8th United Nations Global Road Safety Week is being observed from 12 to 18 May 2025, with the theme #MakeWalkingSafe and #MakeCyclingSafe. This global campaign aims to encourage safer urban infrastructure for pedestrians and cyclists and calls upon governments and communities to implement proven measures to reduce road traffic injuries and fatalities.




