Today’s Current Affairs: 14th April 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Neutrino Mass and the KATRIN Experiment:

Latest update from the KATRIN experiment (April 2025) has brought significant advancement in particle physics.
- In its latest analysis, KATRIN has reduced the upper limit of the neutrino mass to less than 0.45 electron volts (eV).
- This is a significant improvement over its earlier result and represents a nearly 50% reduction in the previously estimated maximum value.
- The data is based on the precise measurement of energies from 36 million electrons produced in tritium decay.
- Neutrinos are electrically neutral subatomic particles that are produced in processes like radioactive decay and nuclear reactions, including those occurring in the sun and stars.
- They are one of the fundamental particles in the Standard Model of particle physics, but their mass remains unknown.
- Unlike other fundamental particles, neutrinos are extremely lightweight, with masses less than a millionth that of an electron.
- KATRIN stands for Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino experiment, and it is located in Karlsruhe, Germany.
- Its primary aim is to precisely measure the mass of the electron antineutrino, a type of neutrino produced in beta decay.
- The experiment focuses on studying the decay of tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen, which emits both an electron and an electron antineutrino.
- The energy of the emitted electron is affected by the mass of the neutrino — hence, measuring electron energies helps infer the upper limit of the neutrino’s mass.
ENSO (El Niño Southern Oscillation):
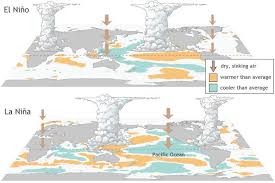
The recent La Niña event in the tropical Pacific Ocean has officially ended, with the climate system now transitioning to ENSO-neutral conditions as confirmed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
- ENSO (El Niño Southern Oscillation): ENSO is a significant climate phenomenon that involves changes in sea-surface temperatures (SST) in the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean.
- It affects various global weather patterns, including wind behavior, atmospheric pressure, and rainfall distribution.
- El Niño: Warmer-than-usual sea surface temperatures, associated with unusual global warming patterns.
- La Niña: Cooler-than-usual sea surface temperatures, often linked with colder atmospheric patterns and stronger trade winds.
- ENSO-Neutral: Neither El Niño nor La Niña dominates the climate system, making forecasts less certain, but often acting as a transitional phase between the two extreme conditions.
- ENSO-Neutral Phase is typically seen as a transition period between El Niño and La Niña.
- In March 2025, NOAA scientists observed that SST anomalies in the Niño-3.4 region had reached -0.01°C, much warmer than the La Niña threshold of -0.5°C.
- The cool waters that had characterized La Niña in previous months have now faded.
The Beijing India Report 2024:

The Beijing India Report 2024, submitted on the 30th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995), highlighted progress on gender equality and exposed gaps in addressing the gender-climate nexus.
- Beijing Declaration & Platform for Action (1995) was a landmark global framework adopted at the Fourth World Conference on Women by the United Nations.
- It identified 12 critical areas for action, including poverty, education, health, violence against women, and decision-making.
- The Declaration emphasized women’s rights as human rights and promoted legal and social reforms to achieve gender equality.
- India, as a signatory, has enacted several laws including the Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act (2005) and the POSH Act (2013) for workplace safety. However, their implementation remains inconsistent, revealing a gap between legislation and lived reality.
- India is a signatory to several international frameworks that mandate gender equity and climate justice, including:
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948),
- ICCPR (1966),
- CEDAW (1979),
- UN Convention Against Corruption (2003),
- Agenda 2030 for Sustainable Development, and
- Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action (1995).
Modernization of Command Area Development and Water Management (M-CADWM) Scheme:

The Union Cabinet recently approved the ‘Modernisation of Command Area Development and Water Management (M-CADWM)’ as a sub-scheme of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
- Modernization of Command Area Development and Water Management (M-CADWM) Scheme is a sub-scheme of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY).
- This initiative, with an initial outlay of ₹1,600 crore, is set to run from 2025-2026 and is designed to significantly enhance the irrigation infrastructure in India.
- The key goal of the M-CADWM is to modernise the irrigation water supply network, ensuring that irrigation water reaches the designated farming clusters from existing canals or other water sources.
- This will help farmers with small land-holdings, by improving water-use efficiency through the use of advanced technologies such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- These technologies will assist in better water accounting and management, directly contributing to increased Water Use Efficiency (WUE) at the farm level.
- A key feature of the M-CADWM scheme is the implementation of underground pressurised, piped irrigation systems, extending up to 1 hectare per farm.
- This infrastructure will be developed to enhance micro-irrigation practices, enabling farmers to use water more effectively and ultimately increasing agricultural production and productivity.
- In addition to modernising the irrigation systems, the scheme aims to build sustainable farming practices.
Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB) ‘Gaurav’:

Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) successfully conducted the Release Trials of Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB) ‘Gaurav’ recently.
- “Gaurav” is a 1,000-kg class glide bomb designed and developed indigenously by the DRDO.
- Unlike conventional bombs that fall vertically after release, glide bombs are equipped with fins or wings that allow them to glide forward through the air toward their target.
- Importantly, a glide bomb does not have an engine. Instead, it relies on the momentum from being dropped from a high-flying aircraft and uses aerodynamic surfaces to cover long distances.
- This enables the launching aircraft to stay away from the enemy’s radar and air defence systems, thereby reducing risk to pilots while still achieving accurate strikes.
- Developed by DRDO’s Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in Hyderabad, the Gaurav project involved active collaboration with Indian private sector partners such as Adani Defence Systems & Technologies, Bharat Forge, and several Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs).
- With a diameter of 0.6 metre, it is four metre long and has a wingspan of 3.4 metre.
- It is an air-launched glide bomb capable of striking targets at long distances.
- When launched from high altitudes—typically over 40,000 feet—the Gaurav can glide to a range of over 100 kilometres.
- It is equipped with a dual guidance system that combines an Inertial Navigation System (INS) with satellite-based GPS.
Mount Spurr:

Mini-earthquakes occured in Alaska’s Mount Spurr recently, sparking fears among scientists that the towering 11,000-foot volcano may be on the verge of a major eruption.
- It is an ice- and snow-covered active stratovolcano complex located in the north-central Cook Inlet region about 100 kilometers west of Anchorage, Alaska, United States.
- The volcano sits at the south edge of a break in the Alaska Range.
- It is composed mostly of andesite.
- It consists of a breached stratovolcano, a lava dome at the summit of Mount Spurr, and Crater Peak vent, a small stratocone on the south flank of Mount Spurr volcano.
- The mountain is 3,000 meter high and is topped with a 5 by 6 km caldera.
- The mountain suffered a crater collapse around 10,000 years ago that created Chakachamna Lake.
- There is an active icefield in the caldera and multiple glaciers.
- The volcano last erupted in 1992, that resulted in heavy ashfall and affected air travel in the region.
Blue Washing:

The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) has recently introduced a new category of industries called the ‘Blue Category’, which falls under Essential Environmental Services (EES).
- ‘Blue Washing’ refers to the practice of portraying polluting industries as environmentally friendly by categorising them under less polluting or cleaner industry labels.
- This term is now used to describe the reclassification of highly polluting Waste-to-Energy (WTE) incineration industries by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) into the new ‘Blue Category’.
- The ‘Blue Category’ is introduced as part of a subset of EES activities like composting, biogas plants, sewage treatment, and material recovery facilities.
- Waste-to-Energy (WTE) incineration, previously under the ‘Red Category’ with a Pollution Index (PI) of 6, is now reclassified as a ‘Blue Category’ industry.
- WTE incineration burns mixed municipal solid waste (MSW) to produce heat and electricity.
- It generates energy through turbine-driven steam, similar to coal plants, but emits more CO₂
Sunbird : Nuclear Fusion-Powered Rocket

Sunbird is a nuclear fusion-powered rocket being developed by Pulsar Fusion, a British startup, to revolutionise interplanetary travel.
- Sunbird could potentially reach speeds of up to 805,000 km/h, which is faster than the Parker Solar Probe (692,000 km/h), currently the fastest human-made object.
- This technology could enable missions to Pluto in just 4 years and cut travel time to Mars by nearly half.
- It aims to revolutionize interplanetary travel by drastically reducing travel time to distant planets like Mars and Pluto.
- An orbital demonstration is scheduled for 2027, marking a major milestone in space propulsion technology.
- Nuclear fusion replicates the energy generation process of stars, fusing atoms to release energy.
- Unlike fission, fusion is cleaner and offers higher energy output with lower radioactive waste.
BM-04 Missile:

India unveiled the BM-04 missile at a defense exhibition in Hyderabad last month. This next-generation short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) reflects India’s focus on enhancing its conventional counterforce capabilities.
- The BM-04 is India’s latest short-range ballistic missile (SRBM) developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Unveiled at the Vigyan Vaibhav 2025 defense exhibition in Hyderabad, it represents a significant advancement in India’s missile technology.
- The BM-04 is 10.2 meters long, 1.2 meters in diameter and weighs 11,500 kg.
- The missile has a two-stage solid-fuel propulsion system; it can engage targets located at a maximum distance of up to 1,500 km, with a 500 kg conventional warhead, and has a 30-meter circular error probability (CEP).
- It can be deployed using a six-wheel indigenous transport erector launcher (TEL).
- Like the existing missiles in the Indian arsenal, the BM-04 is canisterized, which allows the warheads to be mated with the delivery systems in advance, thus reducing the time required to fire the projectile.
- The BM-04 incorporates a Common Hypersonic Glide Body (C-HGB), enabling it to maneuver during flight and evade enemy missile defenses.
- This design allows for unpredictable flight paths, enhancing its survivability against anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) systems.
- BM-04 missiles can be regularly upgraded with new warheads, sensors, and propulsion systems as the threat matrix evolves.
- This will make the BM-04 a robust and reliable system that can withstand future threats.
Legionnaires’ Disease:
Health authorities in New South Wales (NSW) have issued a public alert following a spike in Legionnaires’ disease cases in Sydney, prompting concerns over possible contaminated air conditioning systems.
- Legionnaires’ disease is a severe form of pneumonia caused by Legionella bacteria commonly found in freshwater environments like lakes or streams but can also thrive in man-made water systems.
- Legionella most commonly causes one of two lung diseases:
- Legionnaires’ disease is a type of severe pneumonia
- Pontiac fever is mild respiratory disease
- The symptoms of Legionnaires’ disease are similar to those of other types of pneumonia and typically include cough, fever, headaches, muscle aches, and shortness of breath. In some cases, individuals may also experience confusion, diarrhea, or nausea.
- The most common form of transmission of Legionella is inhalation of contaminated aerosols from contaminated water. It is not contagious, meaning it is not spread from person-to-person.
- Treatments exist, but there is no vaccine currently available for Legionnaires’ disease. Patients with Legionnaires’ disease always require antibiotic treatment following diagnosis.
Thar Desert : Annual increase in greening
According to a new study, the Thar Desert in India has experienced a 38% annual increase in greening over the past two decades, driven by significant monsoon rainfall and agricultural expansion.It is an arid region of rolling sand hills on the Indian subcontinent. It spans an area of 200,000 sq kms across northwestern India (Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana) and southeastern Pakistan (Sindh and Punjab provinces).It is bordered by the Indus River plain to the west, the Punjab Plain to the north and northeast, the Aravalli Range to the southeast, and the Rann of Kachchh to the south.The desert experiences a subtropical desert climate, characterized by persistent high pressure and subsidence.
City Key of Honour Award to Indian President:
The President of India received the ‘City Key of Honour’ of Lisbon (Portugal), acknowledging the strong ties and goodwill between India and Portugal.It is the highest honour accorded by the city of Lisbon, given by the Mayor to recognise contributions to society or ties with Portugal.2025 marks the 50th anniversary of India-Portugal diplomatic relations.
WMO Retired Hurricane Names for 2024:
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has retired four hurricane names Beryl, Helene, Milton, and John from its Atlantic and East Pacific storm lists due to the devastation they caused in 2024, making their reuse inappropriate due to the associated trauma and sensitivity. Beryl became the earliest Category-5 hurricane (Winds exceeding 157 miles per hour) on record, severely impacting the Caribbean.Helene and Milton caused catastrophic damage in the United States, while John led to deadly flooding in Mexico.
Hybrid Paddy Seeds : Banned
Punjab government has banned the sale of hybrid paddy seeds ahead of the 2025 Kharif season.The decision follows rice millers’ refusal to accept hybrid rice due to low milling efficiency and broken grain output.Hybrid paddy is a crossbred rice variety developed from two different parent lines to increase yield, water efficiency, and early maturity.These varieties are non-Basmati and cultivated for commercial high-yield farming.
Thorium-based Small Modular Reactor:
Maharashtra signed an MoU with Russia’s ROSATOM to jointly develop a thorium-based Small Modular Reactor (SMR) — a first-of-its-kind initiative by an Indian state in nuclear energy.A Small Modular Reactor (SMR) is a compact, scalable nuclear reactor designed for safe, efficient, and flexible power generation.Thorium-based SMRs utilise Thorium-232, a fertile material, to generate Uranium-233 fuel through transmutation.Institutions Involved: MAHAGENCO (Maharashtra State Power Generation Company Ltd) and ROSATOM (Russia’s State Atomic Energy Corporation).
Golden Tiger : Sighted
A rare golden tiger, also known as a golden tabby tiger, was recently sighted and photographed in Kaziranga National Park, AssamGolden tiger or “golden tabby” is a rare colour variant of the Bengal tiger, not a separate subspecies.
Location: Only four are known in the wild, all found in Kaziranga National Park, Assam.Caused by a mutation in the wideband gene that extends reddish-yellow pigment production (pheomelanin).Both parents must carry the mutated gene for the golden color to appear.Color is harmless, but inbreeding may cause genetic weaknesses.
Razorpay Launches Turbo UPI Plugin to Revolutionize Digital Payments:
Fintech major Razorpay has unveiled its Turbo UPI plugin, in partnership with NPCI BHIM Services Limited (NBSL) and Axis Bank, leveraging the BHIM Vega platform. This advanced UPI solution eliminates the need for external redirection during transactions, enabling users to complete payments within the app itself. The innovation is designed to reduce payment failures, increase speed, improve reliability, and provide a seamless user experience setting a new benchmark for digital payments in India.
Meghalaya Into Global Fame with GI Tag for Ryndia & Khasi Handloom:
The Government of India has officially granted Geographical Indication (GI) tags to two traditional textile products from Meghalaya Ryndia silk and Khasi handloom. This recognition not only boosts the cultural identity of the region but also provides legal protection and improved marketability to its indigenous crafts.
Mauritius Becomes First African Country to Sign ISA’s Country Partnership Framework:
Mauritius has marked a historic milestone by becoming the first African nation and the fourth globally to sign the Country Partnership Framework (CPF) with the International Solar Alliance (ISA). This strategic agreement aims to strengthen cooperation between ISA and Mauritius on clean energy initiatives, particularly solar energy, in line with the nation’s sustainable development and energy security goals. The CPF will serve as a blueprint for long-term solar energy collaboration, focusing on innovative and scalable technologies
UK Set to Host the 2035 FIFA Women’s World Cup:
The United Kingdom is poised to host the 2035 FIFA Women’s World Cup, emerging as the only “valid” bidder for the prestigious event, as confirmed by FIFA President Gianni Infantino. With a joint bid submitted by England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland, the home nations are set to bring the tournament to Europe for the first time since the 2023 edition. This historic opportunity follows successful events like the UEFA Women’s Euro 2022 and aligns with the growing momentum of women’s football in the region.
Amrit Bharat Station Scheme : stations being redeveloped
The Railway Minister recently announced that 104 of the 1,300 stations being redeveloped under the Amrit Bharat Station scheme are complete. Scheme is an ongoing Indian Railways mission launched in February 2023.It aims to enhance and modernize railway stations throughout the Indian Railways network.The scheme currently intends to upgrade and modernize a total of 1,300 stations across the Indian Railway system.It envisages the development of stations on a continuous basis with a long-term approach.
Sea Lions : Showing Aggressiveness
An algal bloom along the California coast has resulted in a neurotoxin release, which is causing sea lions to become aggressive, leading to attacks on beachgoers and surfers.Sea lions, typically non-aggressive marine mammals, have shown violent and erratic behaviour, attributed to exposure to a neurotoxin called domoic acid.Domoic acid is secreted by the toxic diatom algae Pseudo-nitzschia, which blooms excessively under nutrient-rich conditions in the ocean.Once released, this neurotoxin enters the marine food chain, affecting not just small fish, but also larger predators like sea lions that consume these fish.
ADB Projected India Economy Grow By 6.7% in FY2025:
India’s economy continues to demonstrate resilient growth despite global uncertainties. According to the Asian Development Outlook (ADO) April 2025, the Indian GDP is projected to grow by 6.7% in FY2025, driven by higher domestic demand, rising rural incomes, and moderating inflation. The Asian Development Bank (ADB) expects the growth momentum to continue into FY2026, with a forecasted GDP growth of 6.8%, supported by favorable fiscal and monetary policies. However, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has slightly revised its own projection down to 6.5%, citing global trade challenges and policy uncertainties.




