Today Current Affairs: 14th May 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Foreign Exchange Reserves:

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) added another 16.58 tonnes of gold to the country’s foreign exchange reserves in the last six months, bringing the country’s gold holdings to more than 700 tonnes (around 760.42).
- Gold was acquired by the RBI at a time when Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) left India, and forex reserves dropped by USD44.73 billion from USD 642.45 billion in September 2021 to USD 597.72 billion on April 29, 2022.
- Now, India is the ninth-largest holder of gold reserves.
Foreign Portfolio Investors:
- Foreign portfolio investment (FPI) consists of securities and other financial assets passively held by foreign investors.
- It does not provide the investor with direct ownership of financial assets and is relatively liquid depending on the volatility of the market.
- Examples of FPIs include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange traded funds, American Depositary Receipts (ADRs), and Global Depositary Receipts (GDRs).
- FPI is part of a country’s capital account and is shown on its Balance of Payments (BOP).
- The BOP measures the amount of money flowing from one country to other countries over one monetary year.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) brought new FPI Regulations, 2019, replacing the erstwhile FPI Regulations of 2014.
- FPI is often referred to as “hot money” because of its tendency to flee at the first signs of trouble in an economy. FPI is more liquid, volatile and therefore riskier than FDI.
Foreign Exchange Reserves:
- Foreign exchange reserves are assets held on reserve by a central bank in foreign currencies, which can include bonds, treasury bills and other government securities.
- It needs to be noted that most foreign exchange reserves are held in US dollars.
- India’s Forex Reserve include:
- Foreign Currency Assets
- Gold reserves
- Special Drawing Rights
- Reserve Tranche Position with the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
Shallow And Deep Ecologism:
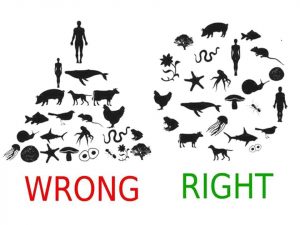
As India continues to grapple with the unrelenting heat waves, it becomes relevant to unpack two strands of environmental philosophy that reinvent the relationship between nature and humans — Shallow and Deep Ecologism.
- The concepts emerged in the 1970s, when Norwegian philosopher Arne Næss sought to look beyond the popular pollution and conservation movements of his milieu to address environmental degradation.
- In his study of ecological concerns, Næss is more preoccupied with the role of the individual in nature. He believes that owing to increased anthropocentrism, humans have cut themselves off from nature, viewing nature and themselves as competing entities and establishing a master-slave dynamic.
- By placing humans at the heart of the environmental crisis, Næss outlines the difference between the two styles of ecologism.
Shallow Ecologism:
- Shallow ecology refers to the philosophical or political position that environmental preservation should only be practiced to the extent that it meets human interests.
- It is more like a powerful and fashionable fight against pollution and resource depletion rather than a radical change.
- Exponents of this philosophy believe in continuing our present lifestyle, but with specific tweaks aimed at minimising the damage to the environment.
- Also referred to as weak ecologism, it may include the use of vehicles that cause less pollution or air conditioners that do not release chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
- This branch of ecologism primarily serves to maintain the lifestyle of those dwelling in developed countries.
Deep Ecologism:
- Deep ecologism believes that humans should radically change their relationship with nature.
- Its proponents reject shallow ecologism for prioritizing humans above other forms of life, and subsequently preserving the environmentally destructive way of life in modern societies.
- It maintains that by sustaining this lifestyle, shallow ecologism further widens the inequalities between countries.
- For instance, despite constituting only 5% of the world’s population, the U.S. accounts for 17% of the world’s energy consumption and is the second largest consumer of electricity after China.
- Similarly, while low and middle-income countries have recorded lower cumulative and per capita carbon dioxide emissions over the past two centuries, it is the wealthier countries which are most responsible for a majority of carbon emissions.
BHARAT TAP Initiative:

The Minister for Housing and Urban Affairs launched the BHARAT TAP initiative at the ‘Plumbex India’ exhibition. This exhibition is aimed at products and services related to the plumbing, water, and sanitation industry.
- At the exhibition, NAREDCO (National Real Estate Development Council) MAHI’s ‘Nirmal Jal Prayas’ initiative was also launched.
BHARAT TAP Initiative:
- It is a concept to use low flow tap and fixtures.
- It will provide low-flow, sanitary-ware at scale, and thereby reduce water consumption at the source considerably.
- It is estimated to save approximately 40% of water. This will in turn result in water saving and energy saving due to less water and energy will be required for pumping, transporting, and purification.
- This initiative will also be accepted quickly in the country and will lead to a renewed focus on water conservation efforts.
NAREDCO MAHI:
- It seeks to help solve the global water crisis, removing the financial barriers that stand between people in need and access to safe water and sanitation at home.
- Nirmal Jal Prayas’ initiative will look into mapping ground water as it is very important to save underground water and will work to save 500 crore litres of water per year.
- The women wing of NAREDCO, was set up in 2021 with an aim to empower women entrepreneurs and encourage the participation of women in the real estate sector and allied fields.
- It strives to create an environment where women in the real estate sector can come together to share experiences, harnesses their skills, draw on their resources, influence, grow and bring about lasting change.
- Such an initiative in water conservation will be of immense importance to save water.
Goa Civil Code:

Goa chief minister Pramod Sawant recently said that the Goa civil code can be a model that other states can emulate. This statement comes amid the ongoing discussions for having a Uniform Civil Code for India.
What is Goa Civil Code?
- In 1867, Portugal enacted a Portuguese civil code and in 1869 it was extended to Portugal’s overseas provinces (that included Goa). It is considered a Uniform Civil Code.
- While when it comes to marriage and adoption, there is not complete uniformity, generally the Goa Civil Code is far more gender-just than other laws in the country.
- The law also doesn’t recognise bigamy or polygamy, including for Muslims but grants an exception to a Hindu man to marry once again if his wife doesn’t conceive a child by the age of 21 or a male child by the age of 30.
- The law provides for:
- Compulsory registration of marriages before a civil authority, ensuring that the wife is an equal inheritor and is entitled to half of the “common assets” including those inherited by her husband in the case of a divorce.
- The parents must compulsorily share at least half of the property with their children including daughters.
- The Portuguese Civil Code in Goa continued in India by virtue of Section 5(1) of the Goa, Daman and Diu Administration Act, 1962, through which the Indian Government ruled that “all laws in force in Goa, Daman and Diu or any part thereof shall continue to be in force therein until amended or repealed by a competent legislature or other competent authority.”
- Because of this, the Portuguese civil code continues to be in force in Goa.
Great Indian Bustards : Important Points

The Supreme Court of India had directed the governments of Rajasthan and Gujarat to ensure installation of bird-diverters on power lines before July 20, 2022.
- The move is aimed at protecting the Great Indian Bustard (GIB), the state bird of Rajasthan, and the lesser floricans in the area.
Great Indian Bustards (GIB):
- IUCN status: critically endangered.
- Listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection)Act, 1972 and in the CMS Convention and in Appendix I of CITES.
- Identified as one of the species for the recovery programme under the Integrated Development of Wildlife Habitats of the Ministry of Environment and Forests.
- Project Great Indian Bustard — state of Rajasthan — identifying and fencing off bustard breeding grounds in existing protected areas as well as provide secure breeding enclosures in areas outside protected areas.
- Protected areas: Desert National Park Sanctuary — Rajasthan, Rollapadu Wildlife Sanctuary – Andhra Pradesh and Karera Wildlife Sanctuary– Madhya Pradesh.
- Habitats in India: Only two districts in Rajasthan — Jaisalmer and Barmer — have a breeding GIB population in the wild.
- The bird can also be found in very small numbers in Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.
Cyclone Karim:

Cyclone Asani, active now in the Bay of Bengal, has a twin — cyclone Karim — in the southern hemisphere.
- Karim has been classified as a category II hurricane, with a wind speed of 112 kilometres per hour (kmph).
- “Asani remains a Severe Cyclonic Storm over the Bay of Bengal, with wind speeds of 100-110 kmph gusting to 120 kmph,” the Weather Channel said.
- Both were formed in the Indian Ocean region.
- Both cyclones originated in the same longitude and now drifting apart.
- Cyclone Karim has created a path in the open seas west of Australia.
- The name Karim was given by the South African country Seychelles.
Second Global Summit On Covid-19:

The Second Global Summit on COVID-19 was recently held virtually.
- The summit was co-hosted by the United States, Belize, Germany, Indonesia, and Senegal.
- Theme of the Second Global COVID Summit: Preventing Pandemic Fatigue and Prioritizing Preparedness.
- Objectives of the Second Global Summit on COVID-19:
- To accelerate efforts to increase global vaccine coverage.
- To enhance access to tests and treatments.
- To protect the health workers.
- To ensure health security for future health crises.
- India said it will continue efforts to extend the coverage of COVID-19 booster doses to eligible populations and strive towards complete vaccination coverage for India’s adult population.
- India highlighted the increased funding allocated for the health sector in the recent budget and said that it will increase the number of integrated public health labs, as well as bio-safety labs.
- India also said that it is committed to supplying vaccines to neighboring countries and will share COVID-19 genomic data.
Sagittarius A* (SgrA*) : Black Hole at Centre of Milky Way

Scientists from the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) facility revealed the first image of the black hole at the centre of the Milky Way.
- The image of Sagittarius A* (SgrA*) gave further support to the idea that the compact object at the centre of our galaxy is indeed a black hole, strengthening Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
- In 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope facility, a collaboration of over 300 researchers, made history by releasing the first-ever image of a black hole, M87* — the black hole at the centre of a galaxy Messier 87, which is a supergiant elliptic galaxy.
- The ring-shaped image of SgrA*, which looked a lot similar to the one of M87*, occupied 52 microarcseconds in the field of view, which is as big a span of our view as a doughnut on the moon.
- The whole exercise was possible because of the enormous power of the Event Horizon Telescope, an ensemble of several telescopes around the world, which together were like a giant eye on the earth with a sight that is 3 million times sharper than the human eye.
- Sagittarius A* is 27,000 light years from us.
Macolin Convention:

The 12th meeting of Interpol’s Match-Fixing Task Force (IMFTF), in which the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) was one of the participants, concluded with a call for harmonised global efforts to curb competition manipulation.
- The participants discussed the emerging uses of technology, big data and social media given that criminal syndicates were increasingly operating across betting and sports markets.
- They also acknowledged that match-fixers are still very much relying on tried and true methods of manipulation, such as targeting the entourage of athletes and grooming young players, pointing to a continued need for education.
- The members deliberated on various mechanisms to improve intelligence sharing “such as the establishment of national platforms, as outlined in the Macolin Convention, that centralise and analyse information on irregular and suspicious trends”.
- The Council of Europe Convention on the Manipulation of Sports Competitions, known as the Macolin Convention, is a multilateral treaty aimed at checking match-fixing.
- It came into force on September 1, 2019.
Utkarsh Samaroh : Gujrat

Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually addressed ‘Utkarsh Samaroh’ held at Bharuch in Gujarat.
- The programme has organized to mark the celebration of 100 percent saturation of four key schemes of the state government in the district.
- These will help in providing timely financial assistance to those in need.
- Bharuch district administration has carried out ‘Utkarsh Initiative’ drive to ensure complete coverage of schemes providing assistance to widows, elderly and destitute citizens.
- A total of 12,854 beneficiaries were identified across the four schemes, which include Ganga Swaroopa Aarthik Sahay Yojana, Indira Gandhi Vrudh Sahay Yojana, Niradhar Vrudh Aarthik Sahay Yojana and Rashtriy Kutumb Sahay Yojana.
- During the drive from January to March this year, taluka-wise Whatsapp helpline numbers were announced to collect information about those who were not receiving benefits of the scheme.
- Utkarsh camps were organized in all villages and wards of municipality areas of the district, to collect the necessary documents for on the spot approval.
- Incentives were also given to Utkarsh assistants to further facilitate the drive.
New Chief Election Commissioner : Rajiv Kumar

The President of India has appointed Rajiv Kumar as the Chief Election Commissioner in the Election Commission of India.
- Rajiv Kumar will assume the charge of office of the Chief Election Commissioner with effect from 15th of May.
- Sushil Chandra will demit the Office of the Chief Election Commissioner on 14th of this month.
- The power to appoint the CEC and the ECs lies with the President of India under Article 324(2) of the Constitution, which states that “the President shall fix the number of ECs in a manner he sees fit, subject to the provisions of any law made by Parliament”.
- Thus, Article 324(2) left it open for the Parliament to legislate on the issue.
- But, in the absence of any Parliamentary law governing the appointment issue, the ECs are appointed by the government of the day, without pursuing any consultation process. There is no concept of collegium and no involvement of the opposition.




