Today’s Current Affairs: 15th January 2026 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Konda Reddi Tribe:

At least 38 thatched houses belonging to members of the Konda Reddi tribe have been gutted in a fire mishap reportedly due to a short circuit at Sarlanka village in Prathipadu Mandal in Kakinada district, Andhra Pradesh, recently.
- Konda Reddis is a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group (PVTG) inhabiting the banks situated on either side of the Godavari River in the hilly and forest tracts of the East and West Godavari and Khammam districts of Andhra Pradesh.
- Their mother tongue is Telugu in its purest and chaste form and a unique accent.
- The primary religion practiced by the Konda Reddi is Folk Hinduism, characterized by local traditions and cults of local deities worshiped at the community level.
- Their main festivals are Ugadi, Akshade, and Dussehra.
- The family is patriarchal and patrilocal. Monogamy is a rule, but polygamous families are also found.
- Marriage by negotiations, by love and elopement, by service, by capture, and by exchange are socially accepted ways of acquiring mates.
- They have their own institution of social control called ‘Kula Panchayat’.
- Each village has a traditional headman called ‘Pedda Kapu’.
- The office of the headman is hereditary, and the headman is also the Pujari (priest) of the village deities.
- They are primarily shifting cultivators and largely depend on the flora and fauna of forest for their livelihood.
- They eat a variety of tubers, roots, leaves, wild fruits,
- They collect and sell non-timber forest produce like tamarind, adda leaves, myrobolan, broomsticks etc., to supplement their meagre income.
- They largely cultivate jowar, which is their staple food.
- The Konda Reddi tribe’s way of life largely revolves around the cow, which is a source of sustenance for them.
- These tribal people are aggressive in the cultivation of commercial crops such as cashew, niger, chilli, and cotton under the Podu cultivation method.
- The tribe has adopted a unique circular-shaped architecture for housing. The houses, built with circular mud walls and thatched roofs, resemble the Bhunga architecture of Gujarat’s Kachchh region.
Gharial : Survey

Despite significant existential threats, a comprehensive survey across the Ganga River basin recently revealed a population of 3,037 gharials (Gavialis gangeticus), the critically endangered fish-eating crocodile, inhabiting 13 of the surveyed rivers
- Gharial is a freshwater crocodile belonging to the Crocodylia Order and Crocodylidae Family.
- Scientific Name: Gavialis gangeticus
- The name ‘gharial’ comes from the Hindi word ghara, meaning pot or vessel, referring to the bulbous snout tip of adult males, which resembles an inverted pot.
- Its range spanned the rivers of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Their major population occurs in three tributaries of the Ganga River: the Chambal and Girwa Rivers in India and the Rapti-Naryani River in Nepal.
- The Gharial reserves of India are located in three States: Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- It is one of the largest crocodilian
- They have thick skin covered with smooth epidermal scales that do not overlap.
- It is also the most aquatic of all crocodilians, for it never moves far from the water. Individuals typically only leave the water to bask and nest on sandbanks.
- They mate during November–January and lay eggs March–May.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red List: Critically endangered.
Asola-Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary:

The Delhi government recently said that over 6,500 monkeys rescued by civic bodies from residential and commercial areas across the city have been shifted to Asola-Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary in the last five years.
- Asola-Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary, on the Southern Delhi Ridge of the Aravalli hill range on the Delhi-Haryana border, lies in Southern Delhi as well as the northern parts of Faridabad and Gurugram districts of Haryana state.
- It is part of the Northern Aravalli Leopard Wildlife Corridor.
- In Delhi, Sanctuary passes through historical sites such as Chattarpur Temple, Tughlakabad, Surajkund, Anangpur Dam, and Adilabad Ruins.
- The semi-arid forest vegetation of the Aravali region provides homes to certain plant species.
- It includes dhak (flame of the forest), babool (Acacia), khejri, and various shrubs and grasses that are well-adapted to dry conditions.
- It is home to a wide variety of animals, including the Indian leopard, jackal, Indian blue bull, sambar deer, wild boar, and mongoose.
- It is also a birdwatcher’s paradise, with various birds spotted here, including the Indian peafowl, crested serpent-eagle, and Indian roller.
- Reptiles such as the monitor lizard, Indian cobra, and Russell’s viper can also be found here.
Molecular Cloud:

Astronomers studied the L328 molecular cloud, located around 700 light years away, to map the magnetic fields at multiple scales.
- It is an interstellar cloud of gas and dust in which molecules can form, the most common of which is Hydrogen (H2).
- These are characterized by their low temperatures (below 40 K, colder than liquid nitrogen) and relatively high densities.
- The size of these clouds can be from a few light years up to 600 light years. Their total mass can reach several million solar masses.
- Molecular clouds with dimensions of more than about 15 light years are also called giant molecular clouds.
- The complex interplay between three key forces, namely gravity, magnetic fields, and turbulence, determines how these clouds collapse to form stars.
- The central regions of these clouds are completely hidden from view by dust.
- They are the raw material of stars and planets. These clouds do not last for a very long time.
- After the new stars are born, their solar winds blow away the remaining gas and dust.
- Molecular clouds are so important because they are the raw material of stars and planets.
- It is thought to be the birthplace of stars and planetary systems through processes of contraction, condensation, and accretion.
Export Preparedness Index 2024:

NITI Aayog released the Export Preparedness Index (EPI) 2024.
Under EPI 2024, the following States and UTs have emerged as leading performers in their respective categories:
- Leading Performers
- Large States: Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh
- Small States, North Eastern States & Union Territories: Uttarakhand, Jammu and Kashmir, Nagaland, Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Goa.
Export Preparedness Index 2024:
- It is a comprehensive assessment of export readiness across India’s States and Union Territories (UTs).
- It recognises the diversity of subnational economic structures and their critical role in advancing India’s global trade ambitions.
- The first edition of the EPI was published in August 2020 and this is the 4th edition.
- It is structured around four pillars, further disaggregated into 13 sub-pillars and 70 indicators. Four Pillars are:
- Export Infrastructure (20% Weightage)
- Business Ecosystem (40% Weightage)
- Policy and Governance (20% Weightage)
- Export Performance (20% Weightage)
Menkes Disease:
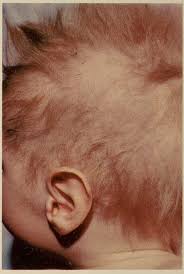
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently approved the Zycubo (copper histidinate) as the first treatment for Menkes disease in pediatric patients.
- It is a genetic disorder that affects body’s ability to process copper.
- It is caused by a mutation of the ATP7A gene located on the X chromosome. This ATP7A gene affects how the body transports copper and maintains copper levels.
- While the body only uses a small amount of copper, even this tiny amount is required for many functions.
- Copper helps with metabolism, brain functioning, blood vessel and blood cell formation, wound healing, and the immune system.
- Copper also helps to convert iron into a usable form in the body.
- It is naturally available in many foods and dietary supplements.
- Menkes Disease usually causes low copper levels in blood plasma, the liver, and the brain.
- The condition also reduces the activities of copper-dependent enzymes in the body.
- Copper may accumulate in other tissues, such as the kidney.
- Because the condition prevents the body from using copper correctly, Menkes disease can lead to serious damage to the brain and nervous system and can harm a child’s development.
- It occurs mostly in male infants and is characterized by coarse, kinky hair (leading to its nickname of “kinky hair disease”), as well as failure to grow and thrive.
- Symptoms include seizures, slow growth, floppy muscles, and kinky (crinkly) hair.
- There isn’t a cure for Menkes disease, but early treatment with copper can help reduce symptoms and prolong life.
- Treatment includes copper replacement injections (also known as a copper histidine compound) to increase the development of copper in your child’s body.
- Without treatment, most Menkes disease patients do not survive past age 3.
Valley of Flowers National Park:

With forest fire raging in the Valley of Flowers, a UNESCO heritage site, for the last five days, the Uttarakhand Disaster Management Department has sought the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) help to douse the inferno.
- It is located in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand.
- It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and forms one of the two core zones (the other being the Nanda Devi National Park) of the Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve.
- The gentle landscape of the Valley of Flowers National Park complements the rugged mountain wilderness of Nanda Devi National Park.
- Together they encompass a unique transition zone between the Zanskar and Great Himalayan ranges.
- It is famed for its vibrant alpine meadows, rich biodiversity, and breathtaking scenic beauty.
- It has snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas as a backdrop.
- It remains covered with a thick blanket of snow during the winter
- Exotic flowers (over 600 species) like orchids, poppies, primulas, marigolds, daisies, and anemones are an eye-catching spectacle.
- The valley also abounds in medicinal plants and herbs.
- Sub-alpine forests birch and rhododendron cover parts of the park’s area.
- It is home to such rare and amazing wildlife species like the gray langur, the flying squirrel, the Himalayan weasel, black bear, the red fox, the lime butterfly, and the snow leopard.
Zanskar River:

The much-awaited Chadar trek on the frozen Zanskar River in Ladakh has been deferred due to inadequate ice formation, disappointing trekkers eager to participate in the adventure sport.
- Zanskar River is a major left-bank tributary of the Indus River, flowing entirely within the union territory of Ladakh in northern India.
- It drains the remote Zanskar Valley in the northwestern Himalayas.
- The Zanskar River starts high in the Himalayas.
- The Zanskar River has two main branches; one is Doda, with main source near Pansi-La Pass, and the other branch is formed by the Kargyag River (source near Shingo La) and the Tsarap River (source near Baralacha La).
- The river meanders northwestwards and finally meets the Indus River near Nimmu of the Ladakh region.
- It is famous for its incredible Zanskar Gorge, which is a super deep canyon it has carved over many years.
- The entire catchment area of the Zanskar River has been formed by the action of glaciers.
- Its valley is U-shaped, and a number of hanging valleys open into it.
- The Zanskar River offers immense opportunities for expeditions to adventure lovers.
- In the summer season, tourists can embark on river rafting trips, especially in the stretches between Chilling and Nimmu.
- Winter brings a unique and thrilling experience of walking along the frozen river of Zanskar, which is often called ‘Chadar Trek’.
Advisory Board on Disarmament Matters:

Indian diplomat has been nominated by the UN Secretary General as chair of Advisory Board on Disarmament Matters for 2026-27.
- It was established in 1978.
- Functions of Advisory Board on Disarmament Matters:
- To advise the Secretary-General on matters within the area of arms limitation and disarmament
- To serve as the Board of Trustees of the United Nations Institute for Disarmament Research (UNIDIR)
- To advise the Secretary-General on the implementation of the United Nations Disarmament Information Programme
- The Secretary-General chooses the members of the Board from all regions of the world for their knowledge and experience in the field of disarmament and international security.
- There are fifteen members of the Board. The Director of UNIDIR is an ex officio member.
- The Advisory Board holds two sessions a year, alternating between New York and Geneva.
- Board adopts its agenda based on requests from the Secretary-General for advice on specific disarmament issues and upon its own recommendations of items to be considered.
- The chairman of the Board rotates by region on a yearly basis.
- Headquarter: New York
Urban Cooperative Banks : In News

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) proposed resuming the issuance of licenses for Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) after nearly two decades.
- Urban Cooperative Banks are not formally defined but refer to primary cooperative banks located in urban and semi-urban areas
- The first formal co-operative legislation in India came with the Co-operative Credit Societies Act of 1904 (During Lord Curzon’s tenure) and also enacted the more comprehensive Co-operative Societies Act of 1912.
- The first urban cooperative credit society,(Anyonya Sahakari Mandali) was established in 1889 in Baroda.
- It Provide services like housing finance, personal loans, MSME credit, and deposits to small borrowers, traders, and small-scale industries.
- They are registered as cooperative societies under the provisions of, either the State Cooperative Societies Act of the State concerned or the Multi State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002.
- The Reserve Bank regulates and supervises the banking functions of UCBs under the provisions of Banking regulation Act, 1949.
- Banking related functions (viz. licensing, area of operations, interest rates etc.) are to be governed by RBI.
- Registration, management, audit and liquidation, etc. are governed by State Governments as per the provisions of respective State Acts.
- The Reserve Bank has been vested powers to issues licence to UCBs under Section 22 and 23 Banking Regulation Act, 1949 to carry on banking business and to open new places of business(branches, extension counters, etc.) respectively.
PANKHUDI Portal:

The Ministry of Women and Child Development has launched PANKHUDI portal aimed at strengthening collaboration and transparency in initiatives for women and child development.
- PANKHUDI is an integrated, single-window digital portal launched to facilitate Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) and partnership initiatives for women and child development.
- Inspired by the vision of technology-driven governance and Jan Bhagidari, PANKHUDI acts as a bridge between the government, citizens, and institutions to promote transparency, participation, and trust.
- It brings together individuals, NRIs, NGOs, CSR contributors, corporate entities, and government agencies on a common digital interface to streamline voluntary and institutional contributions.
- The portal covers key thematic areas such as nutrition, health, Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE), child welfare, protection and rehabilitation, and women’s safety and empowerment.
- Through the portal , contributors can register, identify initiatives, submit proposals, and track approvals and project progress, enhancing coordination, monitoring, and accountability.
- To ensure financial transparency and traceability, all contributions are accepted only through non-cash modes.
- PANKHUDI strengthens the implementation of flagship schemes including Mission Saksham Anganwadi & Poshan 2.0, Mission Vatsalya, and Mission Shakti through structured workflows.
Shaksgam Valley Dispute:

India rejected China’s infrastructure activities in the Shaksgam Valley, termed projects under the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) as illegal and invalid, and asserted that the valley is an inseparable part of India.
- The Shaksgam Valley (Trans-Karakoram Tract) is a high-altitude, sparsely populated region in the eastern Karakoram mountain range.
- It lies north of the Siachen Glacier, a part of the Hunza-Gilgit region of Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (POK), and borders China’s Xinjiang province to the north.
- Prior to 1947, the region was part of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir; after the 1947–48 Indo-Pak conflict, Pakistan occupied parts of it and, under the 1963 Sino-Pakistan Boundary Agreement, ceded the Shaksgam Valley to China.
- India rejects the 1963 agreement as illegal, asserting that Pakistan lacked authority to transfer territory belonging to Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
- It is currently administered by China as part of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, where China has developed infrastructure, including roads linked to CPEC.
- CPEC aims to connect Gwadar Port (Pakistan) with Kashgar (Xinjiang, China), giving China an alternative energy route bypassing the Malacca Strait.
- Its proximity to the Siachen Glacier allows oversight of Pakistani positions, while access to the Karakoram Pass enables monitoring of Chinese military movements.
Iranian conundrum:
Iran is witnessing fresh nationwide unrest that began with bazaar shutdowns on 28 December 2025 amid a sharp rial collapse (market rate reported around ~1.45 million rials/USD).The “Iranian conundrum” refers to Iran’s recurring cycle of economic distress + political legitimacy stress + external pressure, where short-term control measures contain unrest, but structural causes (sanctions, inflation, governance constraints, factional power centres) keep reproducing crises.Tehran’s commercial districts saw merchant/shop closures protesting currency instability and rising costs.
Karuna Abhiyan:
Gujarat Chief Minister reviewed rescue operations under Karuna Abhiyan-2026 during the Uttarayan festival after a surge in bird injuries caused by kite strings, highlighting the state’s large-scale wildlife protection drive.Karuna Abhiyan is a state-wide wildlife rescue and rehabilitation campaign launched by Gujarat in 2017 to protect birds and animals injured during festivals, especially kite-flying during Uttarayan.More than 700 veterinarians, 8,600+ volunteers and 1,000+ centres operate across Gujarat during the high-risk festival period. Includes specialised Water Bird Units, mobile veterinary clinics, animal ambulances and branch clinics.WhatsApp (8320002000), Forest emergency (1926) and Animal Husbandry helpline (1962) enable instant reporting and district-wise centre access.Karuna Abhiyan is India’s first state-driven festival-linked wildlife protection campaign, having rescued over 1.12 lakh animals and birds since 2017.It has become a national benchmark for humane wildlife governance, integrating technology, volunteers and public institutions to protect biodiversity during mass cultural events.
Responsible Nations Index:
The World Intellectual Foundation (WIF) will launch the Responsible Nations Index (RNI), in collaboration with JNU, IIM Mumbai and Dr Ambedkar International Centre.The Responsible Nations Index is a global ranking framework that evaluates how responsibly countries govern their societies, protect the environment, and contribute to global stability.Aim is to shift global benchmarking from pure economic or power-based rankings to a values-based assessment of how nations uphold human dignity, sustainability and international responsibility.
BRICS India 2026 Logo:
India has officially launched the BRICS India 2026 logo and website as it prepares to assume the Chairship of BRICS in 2026.The BRICS India 2026 logo is the official visual identity of India’s BRICS Chairship, representing the country’s vision, values and priorities for leading the grouping in 2026.
2026 Host country: India, Chairship period: Calendar year 2026, Milestone year: 20th anniversary of BRICS (2006–2026).The logo is inspired by India’s national flower – the Lotus, symbolising: Resilience and renewal,Unity in diversity,Spiritual and cultural harmony.At its core, the logo conveys “togetherness for global welfare”, aligning with India’s vision of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam (One Earth, One Family).
M.S. Sahoo Committee:
The Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) has set up an expert committee under M.S. Sahoo to design a framework for assured pension payouts under the National Pension Scheme (NPS).The M.S. Sahoo Committee is a 15-member expert group constituted to design a regulatory and operational framework for providing assured, predictable pension income under the National Pension Scheme (NPS).Constituted by: Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA)Chairperson: M.S. Sahoo, former Chairperson of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI)Aim is to create a robust system of assured pension payouts under NPS that reduces market-linked risks and ensures stable and predictable post-retirement income for subscribers.
Jharkhand Megaliths:
Jharkhand has initiated a push to secure a UNESCO World Heritage Tag for its extensive megalithic landscapes, with Jharkhand CM highlighting them internationally at Davos and the UK.Megaliths are large stone structures such as menhirs (standing stones), dolmens (table-like tombs), burial slabs, cairns and stone circles.They were built for burials, ancestor memory, rituals, boundary marking, and in some cases tracking the sun’s movement.Jharkhand’s megaliths connect strongly with Adivasi life, especially Munda, Ho, Oraon and Asur traditions. Unlike many megalith sites that are only “old ruins”, Jharkhand has layered landscapes—old stones + new stones added over generations.




