Today Current Affairs: 16th July 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
World’s Greatest Places Of 2022:

Ahmedabad and Kerala have been named by TIME magazine among the 50 extraordinary destinations to explore in its list of the World’s Greatest Places of 2022.
- These are two major tourist destinations in India. Besides Ahmedabad and Kerala, other cities which made to the list of top 50 include Seoul, Buahan in Bali, the Great Barrier Reef in Australia, and many more.
- TIME described Kerala as ‘one of India’s most beautiful states.
- It described Ahmedabad as India’s first UNESCO World Heritage City, and a city which “boasts both ancient landmarks and contemporary innovations.
Dunagiri, a Project 17A Frigate:

Dunagiri, a Project 17A frigate, will be launched into the Hooghly river at Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited, Kolkata on 15 July 2022.
- Christened after a mountain range in the state of Uttarakhand, ‘Dunagiri’ is the fourth ship of P17A Frigates.
- These are follow-on of the P17 Frigates (Shivalik Class) with improved stealth features, advanced weapons and sensors and platform management systems.
- The first two ships of P17A Project, were launched in 2019 and 2020 at MDL and GRSE respectively.
- The third ship (Udaygiri) was launched at MDL on 17 May 2022 earlier this year.
- P17A ships have been designed in-house by Indian Navy’s Directorate of Naval Design (DND), which has successfully spear-headed design of numerous class of indigenous warships in the past.
Integrated Food Parks:

India will provide “appropriate land” for “food parks” across the country that will be built in collaboration with Israel, the United States and the United Arab Emirates.
- The plan for the “integrated food parks” was announced in a joint statement after the leaders of the I2U2 grouping — India, Israel, the UAE and the U.S. — held a summit recently.
- The leaders said they would bring in private capital for specific projects in the fields of water, energy, transportation, health, space and food security.
- S. and Israeli private sectors will be invited to lend their expertise and offer innovative solutions that contribute to the overall sustainability of the project.
- These investments will help maximise crop yields which, in turn, will help tackle food insecurity in South Asia and the Middle East. India will “facilitate farmers’ integration into the food parks.
- The food parks aimed at cutting down “food waste and spoilage” are a few of the collaborations that the four countries declared after the summit.
- The UAE will invest $2 billion in India to create the food parks.
Horticulture Production In 2021-22:

The total horticulture production in 2021-22 is estimated to be 341.63 million tonnes (MT), an increase of about 7.03 MT or 21% over the 2020-21 figure, according to the second advanced estimates of area and production of various horticultural crops released by the Union Agriculture Ministry.
- Last year, the total horticulture cultivation was on 27.48 million hectares and according to the second advanced estimates, in 2021-22, it could be 27.74 million hectares.
- The Centre said that while there could be an increase in the production of fruits, vegetables and honey, the cultivation of spices, flowers, medicinal plants and plantation crops could decrease over previous year.
- The fruit production is estimated at 107.1 MT compared to 102.48 MT in 2020-21.
- The production of vegetables is estimated to be 204.61 MT, compared to 200.45 MT in 2020-21.
- In the case of onion, the production is estimated to be 31.7 MT against 26.64 MT in 2020-21.
- Potato production is likely to be 53.58 MT, from 56.17 MT in 2020-21.
- Tomato yield is expected to be 20.34 MT, from 21.18 MT in 2020-21. Farmers of the three crops had agitated against the drop in prices last year.
Monkeypox In India:
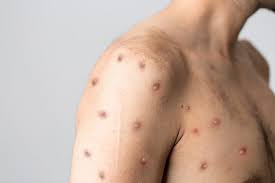
The first known lab-confirmed case of monkeypox in India has been reported in a 35-year-old man in Kerala, who reached the State capital three days ago from the UAE.
- Monkeypox initially presents like any tropical disease with fever, headache, joint ache and possible swelling of the lymph glands.
- The incubation period for the disease the time from exposure to the virus to the manifestation of symptoms ranges from five to 21 days.
- Rashes appear on the face, inside palms and the body one to four days after fever.
- The course of the disease could last two to four weeks, during which time the rashes progress into pustules, vesicular lesions and scabs.
- Transmission happens only through close contact and by touching or sharing the clothes or bedding used by the patient, because the lesions usually have a high viral load.
- Transmission also extends throughout the course of the illness, till the lesions heal.
National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2022:

The Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (IIT-M), is yet again the top higher educational institute in the country followed by the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, and IIT Bombay, according to the Ministry of Education’s National Institutional Ranking Framework (NIRF) 2022.
- Among the universities, IISc, Jawaharlal Nehru University, Jamia Millia Islamia, Jadavpur University and Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham were among the top five.
- And among the top five colleges in the country are Miranda House, Hindu College, Presidency College, Loyola College and Lady Shri Ram College for Women.
- The top five medical institutes are All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, Christian Medical College, Vellore, National Institute of Mental Health & Neuro Sciences, Bengaluru, and Banaras Hindu University.
- The top five management institutes are Indian Institute of Management (IIM) Ahmedabad, IIM Bengaluru, IIM Kolkata, IIT Delhi and IIM Kozhikode.
- This is the seventh consecutive edition of NIRF.
- It ranks colleges, universities and research institutions and also provides an overall ranking of all of them combined. Institutes are also ranked across seven subject domains, namely engineering, management, pharmacy, law, medical, architecture and dental.
- A total of 4,786 institutions were evaluated on five parameters — teaching, learning and resources (TLR); research and professional practice; graduation outcome; outreach; and inclusivity and perception.
Platform of Platforms (PoP) Under The National Agriculture Market (e-NAM):

The Union Minister of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare launched the Platform of Platforms (PoP) under the National Agriculture Market (e-NAM) on the side-lines of the State Agriculture and Horticulture Ministers’ Conference in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
Platform of Platforms (PoP):
- e-NAM integrates the platform of Service Providers as “Platform of Platforms” which includes:
- Composite Service Providers (Service Providers who provide holistic services for trading of agricultural produce including quality analysis, trading, payment systems and logistics)
- Logistics Service Provider, Quality Assurance Service Provider, Cleaning, Grading, Sorting & Packaging Service Provider, Warehousing Facility Service Provider, Agricultural Input Service Provider, Technology Enabled Finance & Insurance Service Provider
- Information Dissemination Portal (Advisory Services, crop forecasting, weather updates, capacity building for farmers etc.)
- Other platforms (e-commerce, international agri-business platforms, barter, private market platforms etc.).
e-NAM Portal:
- National Agriculture Market (eNAM) is a pan-India electronic trading portal which networks the existing APMC mandis to create a unified national market for agricultural commodities.
- Small Farmers Agribusiness Consortium (SFAC) is the lead agency for implementing eNAM under the aegis of Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Government of India.
- Vision:
- To promote uniformity in agriculture marketing by streamlining of procedures across the integrated markets, removing information asymmetry between buyers and sellers and promoting real time price discovery based on actual demand and supply.
- Mission:
- Integration of APMCs across the country through a common online market platform to facilitate pan-India trade in agriculture commodities, providing better price discovery through transparent auction process based on quality of produce along with timely online payment.
Mission Shakti:

The Ministry of Women and Child Development has issued detailed guidelines for the ‘Mission Shakti’ scheme.
- The norms of ‘Mission Shakti’ will be applicable with effect from 1st April 2022.
- Mission Shakti’ was launched during the 15th Finance Commission period 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- Mission Shakti is an integrated women empowerment programme is launched as an umbrella scheme for the safety, security and empowerment of women for implementation.
- Components:
- Sambal:
- It is for Safety and Security of Women.
- It consists of schemes of One Stop Centre (OSC), Women Helpline (WHL), Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP), with a new component of Nari Adalats – women’s collectives to promote and facilitate alternative dispute resolution and gender justice in society and within families.
- Samarthya:
- It is for Empowerment of Women.
- It consists of erstwhile schemes of Ujjwala, Swadhar Greh and Working Women Hostel have been included with modifications.
- In addition, the existing schemes of National Creche Scheme for children of working mothers and Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana (PMMVY) under umbrella Integrated Child Development Services ICDS have now been included in Samarthya.
- A new component of Gap Funding for Economic Empowerment has also been added in the Samarthya Scheme.
- Sambal:
India Stack Knowledge Exchange 2022:

As a part of the Digital India week celebrations, a three day dedicated event titled ‘India Stack Knowledge Exchange’ programme was organised.
- India Stack refers to ambitious project of creating a unified software platform to bring India’s population into the digital age.
India Stack Knowledge Exchange Programme (ISKE):
- The idea behind ISKE 2022 was to get the real practitioners – the IT champions – to speak of the implementation of ground-breaking projects, the challenges faced and the road ahead for these projects.
- ISKE 2022 was also visualised to present to the global community, India Stack solutions and goods, and welcomed any nation to adopt and customize them for their own use.
Changes In Forest Conservation Rules (FCA) 1980:

The Forest Conservation Rules deal with the implementation of the Forest Conservation Act (FCA), 1980.
- They prescribe the procedure to be followed for forest land to be diverted for non-forestry uses such as road construction, highway development, railway lines, and mining.
- Aim of FCA: The broad aims of the Forest Conservation Act are
- To protect forests and wildlife
- Dissuade State governments’ attempts to divert forest land for commercial projects
- Increase the area under forests.
Rules :
- States to ask central government permission: For forest land beyond five hectares, approval for diverting land must be given by the Central government. This is via a specially constituted committee, called the Forest Advisory Committee (FAC).
- It scrutinises the project and ensures that- the felling of trees and denuding of the local landscape — will be minimal and the said piece of land doesn’t cause damage to wildlife habitat.
- States to ensure rights under FRA 2006: Once the FAC is convinced and approves (or rejects a proposal), it is forwarded to the concerned State government where the land is located, which then has to ensure that provisions of the Forest Right Act, 2006, a separate Act that protects the rights of forest dwellers and tribals over their land, are complied with.
- Compensation: The FAC approval also means that the future users of the land must provide compensatory land for afforestation as well as pay the net present value (ranging between ₹10-15 lakh per hectare.)
Changes made:
- The latest version of the rules, which consolidates changes to the Act over the years from various amendments and court rulings, was made public in June 2022.
- Allows Private plantations: The rules make a provision for private parties to cultivate plantations and sell them as land to companies who need to meet compensatory forestation targets.
- No mention of tribals and forest-dwelling communities whose land would be hived off for developmental work.
- Prior to the updated rules, state bodies would forward documents to the FAC that would also include information on the status of whether the forest rights of locals in the area were settled.
- No consent of Gram Sabha needed: The new rules that a project, once approved by the FAC, will then be passed on to the State authorities who will collect the compensatory fund and land, and process it for final approval.
- Previously consent of gram sabha, or the governing body in villages in the area, was required to give written consent to the diversion of the forest.
- Defined forest land: Those deemed forests listed by state governments up to 1996. Land which belonged to Railways or other ministries and on which forest has come up will no longer be considered forests.
- No approval is needed for Strategic Projects: e.g. strategic and security projects of national importance
- Allows building in Forests: Right to construct structures for bonafide purposes including forest protection measures and residential units (up to an area of 250 sq meters as one-time relaxation).
Beti Bachao Beti Padhao:

Beti Bachao Beti Padhao will now be extended across the country.
- BBBP is the Centre’s flagship programme (under the Women and Child Development Ministry) for women’s empowerment, which focuses on the education of girls child and improving the sex ratio.
- It was launched in January 2015 to address sex-selective abortion and the declining child sex ratio which was at 918 girls for every 1,000 boys in 2011.
- It is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and Ministry of Human Resource Development.
- The programme is operational in 405 districts at present.
- WCD ministry published comprehensive guidelines for Mission Shakti.
Guidelines include:
- Aim for zero-budget advertising ( nearly 80% of the fund has been used for advertising in BPPP)
- Encouraging greater spending on activities that have an on-ground impact such as:
- promoting sports among girls
- self-defence camps
- construction of girls’ toilets
- making available sanitary napkin vending machines and sanitary pads, especially in educational institutions
awareness about PC-PNDT Act.
Off-Budget Borrowings:

The Centre has relaxed norms for adjusting states’ off-budget loans and said such liabilities of the last fiscal year can be adjusted against their borrowing ceilings for the next four years till March 2026.
- The move will free up resources for states to fund their capital expenditures in the current fiscal year.
- As per a study by Crisil Ratings, off-balance sheet borrowings by states are estimated to have reached a decadal high of 4.5 per cent of gross domestic product (GDP), or about Rs 7.9 lakh crore, in 2021-22.
Off-budget borrowings:
- It refers to loans taken by state government entities, special purpose vehicles, etc, where principal and interest would be repaid from the state government’s own budget, instead of the cash flows or revenues generated by the borrowing entity.
- Such borrowings bypass the net borrowing ceiling fixed for states in a fiscal year by routing loans outside the state budget through government-owned companies or statutory bodies.
- Since the responsibility for repayment lies with states, it adversely impacts their revenue and fiscal deficit.
Key Highlights:
- States restored off-budget borrowing to fund capital expenditure: Over the last two years, many states have resorted to off-budget borrowing to fund their capital expenditures and minimize the impact of the economic downturn induced by COVID-19.
- As per norms, state governments are required to take the Centre’s approval for fresh borrowing over the limit set for a particular financial year.
- Relief to states: ICRA Chief Economist said the modification regarding off-budget borrowings is likely to provide substantial relief to some states and allow them additional borrowing space in the current fiscal year.
- Off-budget borrowings are to be equated with the states’ own debt: To bring transparency to state finances, the Centre informed states that off-budget borrowings are to be equated with the states’ own debt and any such fund raised by the governments in 2020-21 and 2021-22 would need to be adjusted out of the borrowing ceiling this year.
- Ceiling on borrowing: The Centre has fixed the net borrowing ceiling of states at Rs 8,57,849 crore or 3.5 per cent of GSDP. States are also eligible for additional borrowing of 0.50 per cent of GSDP linked to reforms in the power sector.




