Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 19th February 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- India’s Economic Growth.
- Kala Kumbh: Ministry of Textiles.
- Northern European Enclosure Dam.
- Bodo language.
- The International IP Index.
- India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy for Sustainable Development.
- Continuation of Pakistan in Grey List.
- 22nd Law Commission of India approved by the Union Cabinet:.
- Assisted Reproductive Technology Bill.
- Times Higher Education Ranking
- Chief Vigilance Commissioner (CVC):
- Aditya- L1 mission.
- Other important current affairs
1. India’s Economic Growth:

A US-based think tank World Population Review in its report said that India emerged as the world’s fifth-largest economy by overtaking the UK and France in 2019.
- India’s economy is the fifth-largest in the world with a GDP of $2.94 trillion, overtaking the UK and France in 2019 to take the fifth spot. The size of the UK economy is $2.83 trillion and that of France is $2.71 trillion.
- In purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, India’s GDP (PPP) is $10.51 trillion, exceeding that of Japan and Germany.
- Due to India’s high population, India’s GDP per capita is $2,170 (for comparison, the US is $62,794).
The US-based World Population Review is an independent organization without any political affiliations.
2. Kala Kumbh: Ministry of Textiles:

The Ministry of Textiles is organizing ‘Kala Kumbh – Handicrafts Thematic Exhibition’ in various parts of the country from 14th – 23rd February 2020.
- The objective is to promote Geographical Indication (GI) crafts and heritage of India.
- The GI tag for goods corresponds to a specific geographical location or origin (e.g., a town, region, or country). As of August 2019, 178 GI handicraft products were registered from all over India. These include Madhubani Painting (Bihar), Kondapalli Bommallu (Andhra Pradesh), etc.
- The exhibition is being organized through the Office of Development Commissioner (Handicrafts) under the Ministry of Textiles.
- It is sponsored by the Export Promotion Council for Handicrafts (EPCH).
- The EPCH was established under the Companies Act in the year 1986-87 and is a non-profit organization, with an object to promote, support, protect, maintain and increase the export of handicrafts.
3. Northern European Enclosure Dam:
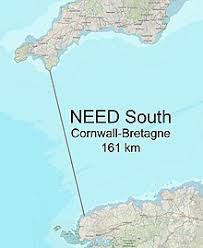
Scientists have proposed the construction of the Northern European Enclosure Dam (NEED) enclosing all of the North Sea to protect economic regions of 15 Northern European countries from Sea-level Rise (SLR) as a result of climate change.
- The proposed NEED aims to construct two dams of a combined length of 637 km.
- The first between northern Scotland and western Norway (476 km) and the second between France and southwestern England (161 km).
- The project intends to separate the North and Baltic Seas from the Atlantic Ocean to protect Northern Europe against SLR.
- The project classifies the solutions to SLR into three categories namely, taking no action, protection, and managed retreat and categorizes NEED into the second category.
- NEED is expected to have the least direct impact on people’s daily lives and can be built at a reasonable cost.
It can be implemented in other regions in the world including the Persian Gulf, the Mediterranean Sea, the Baltic Sea, the Irish Sea, and the Red Sea.
4. Bodo language.:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi acknowledged the signing of the Bodo Peace Accord among the Centre, Assam government and Bodo groups by writing these tweets in the Bodo language. The language is one of the key thrust areas in the Bodo Accord
- Estimated to have 1.5 million speakers (Census 2011), Bodo is listed in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
- It is spoken in Assam, where the Bodo tribe constitutes about 5-6% of the population, and in Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Meghalaya, and West Bengal.
- While Bodo is officially written in the Devanagri script, the language has a history of having been written in at least three different scripts — until, in 1974, the Government recognized Devanagari as its official script.
Bodo Peace Accord 2020:
- The 2020 Accord makes Bodo the associate official language throughout Assam.
- The new Accord also promises to establish a separate directorate for Bodo medium schools, provincialize schools and colleges in the BTAD (Bodoland Territorial Autonomous District) and establish a Cultural Complex-cum-Centre of Excellence named after the late social activist Bodofa Upendranath Brahma in Kokrajhar for protection and promotion of the language.
5. The International IP Index:

The International IP Index was released by the Global Innovation Policy Center (GIPC) of the US Chambers of Commerce, a top American industry body.
- India has been ranked 40th out of 53 countries on the 2020 index. India was placed at 36th position among 50 countries in 2019.
- India’s score, however, increased from 36.04 percent (16.22 out of 45) in 2019 to 38.46 percent (19.23 out of 50) in 2020, a 2.42 percent jump in the absolute score. However, India’s relative score increased by 6.71 percent.
- Since 2016, India has improved the speed of processing for patent and trademark applications, increased awareness of IP rights among Indian innovators and creators, and facilitated the registration and enforcement of those rights.
- Two new Index economies (Greece and the Dominican Republic) scored ahead of India. The Philippines and Ukraine leapfrogged India.
6. India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy for Sustainable Development :

Recently, the India-Norway Task Force on Blue Economy for Sustainable Development was inaugurated jointly by both the countries. This task force was launched during the Norwegian Prime Minister’s visit to India earlier in 2019.
- The two countries also commenced a new collaboration on Integrated Ocean Management & Research.
- The bilateral collaboration intends to manage the resources in the oceans in a sustainable manner.
- The India-Norway cooperation in the field of oceans is based on a shared interest in the blue economy and the sustainable use of marine resources.
- Both countries also desire to advance scientific knowledge about oceans.
- The purpose of the task force is to develop and follow up joint initiatives between the two countries.
- It also intends to mobilise relevant stakeholders from both Norway and India at the highest level, and ensure continued commitment and progress across ministries and agencies.
7. Continuation of Pakistan in Grey List:

The International Co-operation Review Group (ICRG) of the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has recommended that Pakistan be retained on the “Grey List”, given the country’s failure to completely implement the 27-point action plan to check terror financing.
- It needs to be noted that a recommendation by the ICRG is a precursor to the final decision at the FATF plenary session, and is usually not overturned.
- Since 2007, the ICRG has analyzed high-risk jurisdiction and recommended specific action to address the money laundering/terror financing risks emanating from them.
- The FATF Plenary is the decision making body of the FATF. It meets three times per year. The latest meeting will conclude on 21st February 2020 in which final decision with respect to Pakistan will be taken.
- The FATF meeting is being held a week after an anti-terrorism court in Pakistan sentenced Hafiz Saeed, the mastermind of the 2008 Mumbai attack and founder of Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT), to 11 years in two terror financing cases.
- The FATF plenary held in October 2019 had noted that Pakistan addressed only five out of the 27 tasks given to it in controlling funding to terror groups like the Lashkar-e-Taiba, Jaish-e-Mohammad (JeM) and Hizbul Mujahideen, responsible for a series of attacks in India.
- The FATF, then, strongly urged Pakistan to swiftly complete its full action plan by February 2020.
- Pakistan was placed on the grey list by the FATF in June 2018 and was given a plan of action to complete by October 2019 or face the risk of being placed on the blacklist with Iran and North Korea.
8. 22nd Law Commission of India approved by the Union Cabinet:

The Union Cabinet approved the 22nd Law Commission of India. The commission has been approved for a period of three years.
- The 22nd Law Commission will consist of a full-time Chairperson.
- It has four full-time members. Also, secretaries from the Department of Legal Affairs and Legislative department.
Law Commission of India
- It is a non-statutory body that is constituted by the GoI from time to time.
- It was constituted in 1955 for the first time. Since then it has been reconstituted every 3 years.
- So far, the Law Commission of India has submitted 277 reports.
The functions and objectives of the Law Commission are as follows
- To identify laws that shall be repealed immediately
- To examine the current laws in force and suggest ways to improve them
- To respond to requests made by other countries in framing their legal system
- To take measures that shall help to serve the poor legally
- To revise laws to simplify them.
9. Assisted Reproductive Technology Bill:

The Union Cabinet approved the Assisted Reproductive Technology (Regulation), Bill. The bill proposes to establish a national registry.
- The bill aims at setting up a national board and as a state board to implement a legal framework.
- The bill also proposes to establish a central database of banks and clinics all over the country.
- It will help in identifying people that are involved in illegal embryo sale and trafficking.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
- The ART is used to treat infertility. The technology works to remove an egg from a woman’s body and fertilize it with a man’s sperm to make an embryo.
- Need: India has become a surrogacy hub for foreign couples.
- Also, there are unethical practices that need to be brought under the legislation. The 228th report of LCI (Law Commission of India) recommended for suitable legislation towards the ART practices being followed in the country.
10. Times Higher Education Ranking:

The Times Higher Education Ranking was released in London. The ranking was titled “The Emerging Economies University Ranking 2020”.
- Around 11 Indian Universities were included in the top 100.
- However, China had more Universities than India in the ranking. Around 30 Universities of China were in the top 100.
- The Indian Institute of Science was ranked 16th among the top 100 Universities of emerging Economies.
- The ranking included 533 Universities from 47 countries all over the world. Out of these, 56 Indian Universities appeared in the ranking.
- Prestigious Institutes: The IIT Kharagpur moved up 23 places to 32nd rank, IIT Delhi improved by 28 places and was at 38th rank and IIT Madras was at 63rd rank climbing 12 places.
11. Chief Vigilance Commissioner (CVC):

Sanjay Kothari, Secretary to the President of India, will be the next Chief Vigilance Commissioner (CVC).The post of CVC has been vacant since June 2019.
About CVC:
- It is the apex vigilance institution created via executive resolution (based on the recommendations of Santhanam committee) in 1964 but was conferred with statutory status in 2003.
- It submits its report to the President of India.
- The Commission was set up on the recommendation of the K.Santhanam Committee on Prevention of Corruption.
- Consists of central vigilance commissioner along with 2 vigilance commissioners.
- They are appointed by the President of India on the recommendations of a committee consisting of Prime Minister, Union Home Minister and Leader of the Opposition in Lok Sabha (if there is no LoP then the leader of the single largest Opposition party in the Lok Sabha).
- Their term is 4 years or 65 years, whichever is earlier.
12. Aditya- L1 mission:

It is India’s first solar mission. It will be launched using the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) in XL configuration. The space-based observatory will have seven payloads (instruments) on board to study the Sun’s corona, solar emissions, solar winds and flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), and will carry out round-the-clock imaging of the Sun.
- Objectives: Study the sun’s outer most layers, the corona, and the chromospheres. Collect data about coronal mass ejection, which will also yield information for space weather prediction.
- Significance of the mission::The data from Aditya mission will be immensely helpful in discriminating between different models for the origin of solar storms and also for constraining how the storms evolve and what path they take through the interplanetary space from the Sun to the Earth.
Other important current affairs:
1. With 615 million speakers all over the world, Hindi is the third most spoken language in the world. English is at the top with 1,132 million speakers followed by Mandarin with 1,117 million speakers.
- On February 18, 2020, the Ethnologue published its yearly database on the living languages of the world. It covered more than 7,111 living languages.
- It also published data on languages that were gone out of usage in recent history and that included around 348 languages.
- It also said that Bangla is the 7th most spoken language in the world with 228 million native speakers.
- The Ethnologue is an annual publication that provides statistics of the living languages of the world. It is published by SIL International since 1951. The publication released this year in 2020 is its 22nd release.
2. Union Minister of Coal and Mines chaired “Chintan Shivir” – a two-day brainstorming session organized to find a way forward for the coal sector – at Kevadia in Gujarat
- India will stop importing thermal coal from Financial Year 2023-24.
- The Ministry of Coal will introduce a “Coal Minister’s Award” soon to recognize and appreciate best practices in coal production, productivity, safety, sustainability etc. by the coal companies.
- Various ways and means were discussed to achieve 1 billion tonnes (BT) coal production target by Coal India Limited (CIL) by Financial Year 2023-24.
- CIL could generate 5 GW of solar power by FY 2023-24 and could diversify into coal gasification with a target of 50 Million Tonnes by 2030 enabling a sustainable energy mix for the country.
3. GROSS BOX OFFICE RECEIPTS
- Gross box office receipts crossed the ₹10,000 crore mark for the first time in 2019, making it a historic year for cinema in India, according to Mumbai-based media consulting firm Ormax Media’s Indian Box Office Report 2019.
- Total gross earnings across all languages rose almost 12% last year to ₹10,948 crore, from ₹9,810 crore in 2018, according to the report. The reduction in GST slabs also helped boost net earnings at an even faster pace of 19% to ₹9,490 crore.
4.Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) will celebrate the Matribhasha Diwas across the country on 21st February with the theme ‘Celebrating our Multilingual Heritage.’
- Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) along with educational institutions and language institutions is celebrating the Matribhasha Diwas for the past three years to highlight the linguistic diversity of our country.
- International Mother Language Day (IMLD) is a worldwide annual observance held on 21st February by UNESCO to promote awareness of linguistic diversity. It was first announced by UNESCO in 1999 and was formally recognized by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2008.
5. The Delhi International Airport Limited (DIAL) has become the first airport in India to become free of single-use plastics. The airport committed itself to become single-use plastics free on the World Environment Day in 2018.
- DIAL has used eco-friendly alternatives to reduce the plastic use.
- The Plastic items that are exempted at the airport included sealed PET bottles, security tamper-evident bags, pre-packaged materials from manufacturers and compostable plastic bags.
6. From April 1, 2020, India will shift to Euro-VI emission compliant from Euro-IV grades that is being followed now. This means that India will shift towards a more clean form of fuel.
- As India shifts to Euro VI grades, it will join the select league of nations using pure and clean fuel. These fuels contain just 10 parts per million of Sulphur.
- Sulfur emissions are the main reasons that choke pollution in major cities.
- With Indian Oil Corporations and all other leading refineries already adopting BS-VI petrol and diesel, India is already on track in implementing clean fuel in the country.
7. The foundation stone for a 50-meter high foundation stone laid at Dhanushkodi in Rameswaram. This is the fifth lighthouse in the region
- The lighthouse is to be built at a cost of Rs 8 crore rupees.
- The lighthouse is to be located opposite the old church that was destroyed in a cyclone in 1964. It will facilitate navigation to 33 to 37 km from the seashore.
- A radar is to be fixed at the top of the lighthouse for surveillance. The lighthouse is to completely operate with solar energy.
8. Soil Health Card Scheme, the GoI is marking Soil Health Card Day on February 19, 2020. The Soil Health Card Scheme was launched by PM Modi on February 19, 2015.
- The Scheme was launched in 2015 to evaluate soil fertility.
- It was introduced to issue soil health cards every two years. The aim of the scheme is to promote soil test in order to promote nutrient management.
9. Kerala CM launches ”Yodhavu” mobile app to combat drug menace
- Kerala Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan launched a mobile app ‘Yodhavu’ (Warrior), as part of efforts to curb the growing menace in the State.
- Through this app, the public can inform police about drug abuse and its distribution.
- A special feature of the application, introduced by the Kochi city police, was that the informer’s identity could be kept secret.
10. Shivaji Jayanti is celebrated in Maharashtra
- The birth anniversary of Maratha Warrior King ‘Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj’ is being celebrated in all over Maharashtra.
- Vice President M Venkaiah Naidu paid tributes to Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj on his birth anniversary.
- Shivaji Bhonsle was an Indian warrior king and a member of the Bhonsle Maratha clan.
- Shivaji carved out an enclave from the declining Adilshahi sultanate of Bijapur that formed the genesis of the Maratha Empire.
11. The National Company Law Appellate Tribunal has approved the Rs.19,700-crore resolution plan of JSW Steel to take over the bankrupt Bhushan Power and Steel.
- The approval comes with the immunity sought by the new owner against investigations being carried out against the erstwhile promoters of Bhushan Power and Steel.
- This comes after the government recently amended Section 32A of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code.
12. After Srinivas Gowda created a storm by covering 100 meters in 9.55 seconds recently, another Kambala runner Nishant Shetty has now overtaken the former by completing the same distance in 9.51 seconds.
- Kambala is a traditional slush track buffalo race held annually in coastal districts of Karnataka to entertain rural people of the area.
- The slushy/marshy paddy field track is used for Kambala.
- The sports season generally starts in November and lasts till March.
13. The 3rd Annual Review meeting on Swachh Iconic Places (SIP) was held recently at Baidyanath Dham Deoghar, Jharkhand.
- About Swachh Iconic Places (SIP): It is an initiative of the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation under Swachh Bharat Mission.
- Aims to take iconic places and their surroundings to higher standards of Swachhata, so that all visitors benefit and also take away home the message of cleanliness. Implementation of the project:
- It is a collaborative project with three other central Ministries: Urban Development, Culture, Tourism; all levels in the concerned States and more importantly, Public Sector and Private companies as partners.
- Places selected:
- Phase I iconic places are Ajmer Sharif Dargah, CST Mumbai, Golden Temple, Kamakhya Temple, MaikarnikaGhat, Meenakshi Temple, Shri Mata Vaishno Devi, Shree Jagannath Temple, The Taj Mahal, and Tirupati Temple.
- Phase II included Gangotri, Yamunotri, Mahakaleshwar Temple, Charminar, Convent, and Church of St. Francis of Assissi, Kalady, Gommateswara, BaidyanathDham, Gaya Tirth, and Somnath temple.
- Phase III includes Raghavendra Swamy Temple (Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh); Hazardwari Palace (Murshidabad, West Bengal); Brahma Sarovar Temple (Kurukshetra, Haryana); VidurKuti (Bijnor, Uttar Pradesh); Mana village (Chamoli, Uttarakhand); Pangong Lake (Leh-Ladakh, J&K); Nagvasuki Temple (Allahabad, Uttar Pradesh); ImaKeithal/market (Imphal, Manipur); Sabarimala Temple (Kerala); and Kanvashram (Uttarakhand).
14. Pakistan conducted a successful flight test of the air-launched nuclear-capable cruise missile Ra’ad-II.
- It has a range of 600 km.
- The system is equipped with state-of-the-art guidance and navigation systems ensuring the engagement of targets with high precision.
- Pakistan’s development of the Ra’ad could be seen as an attempt to match India’s BrahMos cruise missile.
15. Institute for Defense Studies and Analyses:
- Institute for Defense Studies and Analyses has been renamed as Manohar Parrikar Institute for Defense Studies and Analyses.
- IDSA is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Defense.
- Dedicated to objective research and policy-relevant studies on all aspects of defense and security.




