Today’s Current Affairs: 19th July 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Last Universal Common Ancestor:

In a new study, scientists have said the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) could have formed just 300 million years after the earth formed.
- Researchers believe all three branches of life namely bacteria, archaea, and eukarya originated from a single cell, called the last universal common ancestor (LUCA).
- LUCA had a small genome with about 2.5 million bases and 2,600 proteins, sufficient for survival in its unique environment.
- LUCA’s metabolites might have created a secondary ecosystem for other microbes to emerge, and it possibly had immunity genes to fight off viruses.
- Though there is no fossil evidence to support the existence of LUCA, modern genomes share so many features that provide some insights.
- However, the theory of the molecular clock allowed scientists to reconstruct the ‘tree of life’.
- As per theory, the rate at which mutations are added or removed from a population’s genome is proportional to the rate of acquiring new mutations, which is constant.
- The mutation rate varies between species.
- Based on the findings, researchers created a method to estimate the time between evolutionary events by using known mutation rates and linking genomes to specific events like the evolution of the first mammal or the age of fossils as benchmarks.
- Based on the earlier findings of fossils in the Pilbara Craton in Australia, the earliest life forms were believed to be date back to 3.4 billion years ago.
- Overall, these findings are crucial for understanding how life began and evolved on Earth and for seeking similar life forms elsewhere in the universe.
- These evolutionary insights will boost efforts to engineer synthetic organisms for various processes on Earth and to create or manage ecosystems on other planets in the future.
Inverse ETF:

Sebi’s new asset class proposal for high-risk investors is expected to provide access to advanced strategies like long-short equity funds and inverse ETFs
- An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) is a type of investment fund that holds a collection of assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities and is traded on stock exchanges, much like individual stocks.
- ETFs offer investors a way to diversify their portfolios with a single investment and are known for their lower fees and ease of trading.
- An Inverse ETF is designed to provide returns that move in the opposite direction of a specific index or benchmark.
- If the underlying index declines in value, the Inverse ETF aims to increase in value by the same percentage, effectively allowing investors to profit from a market downturn.
4th Periodic Review Of The ICCPR:

India successfully concluded its 4th periodic review by the Human Rights Committee under the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) in Geneva.
- The ICCPR is an important international human rights treaty that, along with other key documents, forms the International Bill of Human Rights.
- It obligates countries to protect and preserve basic human rights such as the right to life, freedom of speech, and gender equality.
- Adopted by the UN General Assembly in 1966, ICCPR came into force in 1976 and has been ratified by 173 countries including India in 1979, undergone three previous reviews, with the latest in 2024.
- The 4th periodic review covered diverse issues including anti-corruption measures, non-discrimination, women’s and minority rights, counter-terrorism, judicial framework , and privacy laws.
UNEP Foresight Report 2024:

The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) released a report titled “Navigating New Horizons: A Global Foresight Report on Planetary Health and Human Wellbeing, 2024.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- 85% of the 169 SDG targets are off track and 37% of the targets have shown no progress or have regressed since 2015, as of the latest 2023 SDG Progress Report.
- 42.85% of the targets for SDG 6 (Clean Water and Sanitation), SDG 13 (Climate Action), SDG 14 (Life Below Water), and SDG 15 (Life on Land) are either stagnating or regressing.
- 60% of environmental indicators remain either deteriorating or unclear in their status.
- The UNEP report identified 8 critical shifts with 18 potential signals of change.
- Rapidly Changing Relationship Between Humans and Environment: Human activities are predicted to affect over 90% of land by 2050. Up to 46% of species may face extinction.
- Global temperatures are projected to rise 2.1-3.9°C by 2100.
- Greenhouse gas emissions, mainly from fossil fuels, are driving these changes, with developed nations responsible for most emissions.
- The global competition for critical resources is reshaping international security. Demand outpaces supply, amplifying volatility and potential conflicts, especially in regions with concentrated reserves.
- The most fundamental resources, water and food, face growing threats from climate change and unsustainable management, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations.
- The key drivers of rapid advancement of digital technologies and AI include mobile devices, internet access, and the growth of AI that offer prospects for progress, their environmental implications require consideration.
- There are over 8.89 billion mobile subscriptions, with around 5.6 billion users owning a device. As per ITU reports, 67.4% of the world’s population were internet users in 2023.
Common Services Centres Special Purpose Vehicle:

Common Services Centres Special Purpose Vehicle (CSC SPV) celebrated 15 glorious years of its establishment.
- Common Services Centres Special Purpose Vehicle is incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India.
- It monitors the implementation of the Common Services Centers Scheme.
- Common Services Centres (CSC) scheme is one of the mission mode projects under the Digital India Programme.
- It provides a centralized collaborative framework for delivery of services to citizens through CSCs, besides ensuring systemic viability and sustainability of the scheme.
- Common Services Centre is an initiative of the Ministry of Electronics & IT (MeitY), Government of India.
- These act as the front-end delivery points for Government, private and social sector services to rural citizens of India, in an integrated manner.
Coalition Of Epidemic Preparedness Innovation:

Union Minister for the Ministry of Science & Technology inaugurated Asia’s first health research-related “Pre-clinical Network Facility” under the Coalition of Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) in Faridabad.
- Coalition of Epidemic Preparedness Innovation (CEPI) was launched in 2017 as an innovative partnership between public, private, philanthropic and civil organisations.
- It was founded in Davos (Switzerland) by the governments of Norway and India, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Wellcome Trust, and the World Economic Forum.
- Its mission is to accelerate the development of vaccines and other biologic countermeasures against epidemic and pandemic threats so they can be accessible to all people in need.
- CEPI has supported the development of more than 50 vaccine candidates or platform technologies against multiple known high-risk pathogens or a future Disease X.
- Central to CEPI’s pandemic-beating five-year plan for 2022-2026 is the ‘100 Days Mission’ to compress the time taken to develop safe, effective, globally accessible vaccines against new threats to just 100 days.
- The Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India is supporting the implementation of the Ind-CEPI Mission, “Epidemic preparedness through rapid vaccine development: Support of Indian vaccine development.
- It is done through a dedicated Program Management Unit (PMU) at Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC).
Spade-Toothed Whale:

A whale that was found dead on a beach in New Zealand recently has been identified by scientists as a spade-toothed whale, a species so rare it has never been seen alive.
- Spade-Toothed Whale are the world’s rarest whales, with no live sightings ever recorded.
- The species was first described in 1874 after a lower jaw and two teeth were collected from New Zealand’s Chatham Islands.
- The skeletal remains of two other specimens found off islands in New Zealand and Chile enabled scientists to confirm a new species.
- Two more recent findings of stranded whales off New Zealand’s North Island in 2010 and 2017 added to the small collection.
- Nothing is currently known about the whales’ habitat.
- The creatures deep-dive for food and likely surface so rarely that it has been impossible to narrow their location further than the southern Pacific Ocean, home to some of the world’s deepest ocean trenches.
- No one knows how many there are, what they eat, or even where they live in the vast expanse of the southern Pacific Ocean.
MV Sea Change:

The world’s first commercial passenger ferry powered by 100% hydrogen fuel, the MV Sea Change, was launched recently at the San Francisco Ferry Building.
- MV Sea Change is the world’s first commercial passenger ferry powered entirely by zero-emission hydrogen fuel cells.
- The 75-passenger ferry was built by All American Marine Shipyard for the compatriot shipowner SWITCH Maritime.
- The vessel, designed by Incat Crowther, is fitted with hydrogen-powered fuel cells producing electricity to power electric motors, enabling the vessel to operate for about 16 hours, traveling around 300 nautical miles, between refueling sessions.
- It can reach speeds up to 20 knots, and its service speed will be about 8-12 knots.
- It uses H2 fuel cells to generate electricity through the combination of H2 from storage tanks and oxygen from the ambient air.
- Unlike current diesel-powered ferries that emit pollutants, the hydrogen-powered Sea Change produces only heat and water vapor as byproducts.
- Passengers can even drink the emissions from an onboard water fountain.
Davis Strait:
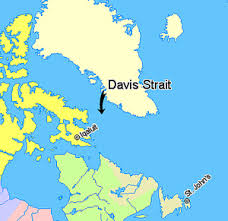
A microcontinent has been recently discovered in the Davis Strait, between Canada and Greenland.
- The discovery was made around the Davis Strait, a large stretch of water located between Canada’s Baffin Island and Greenland.
- The strait was formed millions of years ago when the tectonic plates between the two islands shifted, reconfiguring the Earth’s crust.
- This resulted in the formation of a thick continental crust in the ocean, which has now been declared a newly discovered primitive microcontinent.
- It has been named the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent since it formed owing to the tectonic evolution of the strait in the region.
- The microcontinent is 19–24 km thick thinned continental crust and is surrounded by two narrow bands of thin (15–17 km) continental crust.
- Davis Strait known as the northern arm of the Atlantic Ocean, the Davis Strait is situated north of the Labrador Sea amidst southwestern Greenland and southeastern Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada.
Asian Development Bank:

The Asian Development Bank (ADB) recently retained India’s GDP growth forecast for the current financial year at 7%.
- Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a multilateral development bankestablished on 19th December 1966.
- It is the principal international development finance institution for the Asia-Pacific
- It envisions a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty in the region.
- It provides assistance to its developing member countries, the private sector, and public-private partnerships through grants, loans, technical assistance, and equity investments to promote social and economic development.
- ADB maximizes the development impact of its assistance by facilitating policy dialogues, providing advisory services, and mobilizing financial resources through cofinancing operations that tap official, commercial, and export credit sources.
- Headquarters: Manila, Philippines.
INS Teg:

The Indian warship INS Teg has rescued nine sailors, including eight Indians and one Sri Lankan, who were on board the Comoros-flagged oil tanker, MT Falcon Prestige, that had capsized recently off the Oman coast.
- INS Teg is the first of three guided missile frigates of the modified INS Talwar-class that India commissioned Russian shipyard Yantar to build under Project-17 A (the other two are INS Tarkash and INS Trikand).
- INS Teg was commissioned into Navy service on 27 April 2012.
- The Talwar-class guided missile frigates are modified Krivak III-class frigates built by Russia.
- These ships use stealth technologies and a special hull design to ensure a reduced radar cross-section.
- Much of the equipment on the ship is Russian-made, but a significant number of systems of Indian origin have also been incorporated.
National Bank For Financing Infrastructure And Development : Increase The Capital Base

The government wants to increase the capital base of the National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development, or NaBFID, to 1 trillion through support from banks.
- National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development was set up in 2021, by an Act of the Parliament(The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development Act, 2021).
- It is a specialized Development Finance Institutionin India.
- Objectives is Addressing the gaps in long-term non-recourse finance for infrastructure development, strengthening the development of bonds and derivatives markets in India, and sustainably boosting the country’s economy.
- Regulated by and supervised by RBIas an All-India Financial Institution (AIFI).
- The principal idea behind the setup of NaBFID is to provide a dedicated and specialized institution focused on addressing the long-term financing needs of the infrastructure sector in India.
Chagos Archipelago:

The external affairs minister said that India will continue supporting Mauritius on the issue of the Chagos Archipelago in line with its stand on decolonization.
- Chagos Archipelago is an island group located in the central Indian Ocean and is about 1,000 miles (1,600 km) south of the southern tip of the Indian subcontinent.
- It is an overseas territory of the United Kingdom that was established on November 8, 1965.
- Its key islands include the Diego Garcia atoll, Danger Island, Egmont Islands, Eagle Islands, Nelsons Island, Peros Banhos atoll. (Diego Garcia island, which houses a strategic US military base).
- It experiences a tropical marine climate with high temperatures and elevated humidity levels. The island’s climate is heavily moderated by the trade winds which blow over the islands.
- The Chagos dispute centres around the archipelago in the Indian Ocean, which Britain claimed along with Mauritius in 1814.




