Today’s Current Affairs: 1st May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
TacticAI:
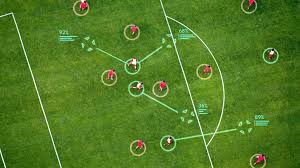
Google’s DeepMind developed and evaluated TacticAI in a multi-year research collaboration with experts from Liverpool Football Club.
- TacticAI is an AI system that can provide experts with tactical insights, particularly on corner kicks (football), through predictive and generative AI.
- It can be used by football team managers as an assistant for tactics.
- It is developed by Google’s DeepMind.
- It has been incorporated both a predictive and generative component to allow coaches to effectively sample and explore alternative player setups for each corner kick and to select those with the highest predicted likelihood of success.
- Corner kicks are apt for strategising by leveraging AI tools, primarily because they are moments when the game is effectively frozen and always starts from the same kind of position at the corner of the pitch while giving players an immediate opportunity to score.
- Strategies for corners are usually also decided long before the players actually go on to the pitch, so that there is no confusion on match day.
Doordarshan Logo : Changed Colour

National broadcaster Doordarshan (DD) has changed the colour of its historic flagship logo from red to saffron.
- Political parties accused the public broadcaster of adopting a colour closely associated with the ruling political party, especially because the change was made in the middle of the election process.
- DD said the change was only one of visual aesthetics.
- It was first aired on 15th September 1959, as a public service telecasting service.
- It became a broadcaster with daily transmissions of morning and evening shows in 1965, having transmission in Delhi.
- On 1st April 1976, It came under the Information and Broadcast Ministry and in 1982, Doordarshan became the National broadcaster.
Guidelines For The Elimination Of Corporal Punishment In Schools (GECP):

The Tamil Nadu School Education Department has released Guidelines for the Elimination of Corporal Punishment in Schools (GECP), focusing on safeguarding students’ physical and mental well-being.
- The guidelines, issued jointly by the Director of School Education and the Director of Elementary Education, address various forms of harassment, in line with the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- Measures include awareness camps, prompt complaint resolution, and the establishment of monitoring committees at each school. Affirmative actions against corporal punishment and promoting a positive environment are also emphasized. District-level officers are instructed to ensure schools implement these guidelines effectively.
- Corporal Punishment refers to the use of physical force against students as a means of discipline or punishment in educational settings.
- It can include actions such as hitting, spanking, or other forms of physical punishment inflicted by teachers or school authorities on students.
National Centre For Good Governance : MoU

A delegation from India visited Bangladesh for bilateral discussions on renewing the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India’s National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) and Bangladesh’s Ministry of Public Administration.
- The primary agenda of the visit is to negotiate the renewal of the MoU for the period 2024-2029, focusing on mid-career capacity-building programs for Bangladesh Civil Servants.
- The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG) is an autonomous institute under the aegis of the Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances, Government of India.
- Its mission is to facilitate governance reforms through studies, training, knowledge sharing, and the promotion of innovative ideas.
- Purpose and Functions:
- The NCGG focuses on public policy, governance, and reforms.
- It conducts policy-relevant research and prepares case studies.
- The centre curates training courses for civil servants from India and other developing countries.
- It collaborates with the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) to provide training to civil servants from various nations.
- The NCGG aims to enhance the capacity of civil servants in India and other developing countries.
Taam Ja Blue Hole:

Scientists have yet to reach the bottom of the Taam Ja’ Blue Hole in Mexico’s Chetumal Bay, which new measurements hint could be connected to a labyrinth of submarine caves and tunnels
- Taam Ja’ Blue Hole is the deepest known underwater sinkhole in the world.
- It sits in Chetumal Bay off the southeast coast of the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico.
- It is 390 feet (119 m) deeper than the previous record holder the 990-foot-deep (301 m) Sansha Yongle Blue Hole, also known as the Dragon Hole, in the South China Sea.
- Spread over an area of 13,660 square meters, the giant, underwater cavern has been named Taam Ja’ which means “deep water” in Mayan.
- The submerged blue hole has a nearly circular shape at its surface with steep sides that form a large conic structure covered by biofilms, sediments, limestone, and gypsum ledges.
Acceptance Sampling : VVPAT

The VVPAT-based audit of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) is a typical case of “lot acceptance sampling”, a statistical quality control technique widely used in industry and trade.
- Acceptance Sampling is a statistical measure used in quality control.It allows a company to determine the quality of a batch of products by selecting a specified number for testing.
- It tests a representative sampleof the product for defects. The quality of this designated sample will be viewed as the quality level for the entire group of products.
- The process involves first, determining the size of a product lot to be tested, then the number of products to be sampled and finally the number of defects acceptable within the sample batch.
- Products are chosen at random for sampling. It does not assure the quality of the complete set of products from which the sample is derived.
- Acceptance sampling in its modern industrial form dates from the early 1940s.
- It was popularized by Dodge and Romig and originally applied by the U.S. military to the testing of bullets during World War II.
Inflation Expectations Survey Of Households And Consumer Confidence Survey : RBI

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently announced the launch of ‘Inflation Expectations Survey of Households’ and ‘Consumer Confidence Survey’.
- Inflation Expectations Survey of Households’ and ‘Consumer Confidence Survey’ are launched by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- They will provide useful inputs for the bi-monthly monetary policy.
- Inflation Expectations Survey of Households aims at capturing subjective assessments on price movements and inflation, based on their individual consumption baskets.
- This survey spans 19 cities, including Guwahati, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Kolkata, Lucknow, and Thiruvananthapuram.
- It seeks qualitative responses from households on price changes (general prices as well as prices of specific product groups) in the three months ahead as well as in the one-year ahead period.
- Additionally, it will collect quantitative data on current, three-month ahead, and one-year ahead inflation rates.
Great Rift Valley :Dam Burst

Many people died when a dam burst its banks near a town in Kenya’s Rift Valley, as heavy rains and floods battered the country.
- Great Rift Valley is one of the most extensive rifts on Earth’s surface that runs along part of East Africa.
- It is part of a larger feature called the East African Rift System (EARS).
- It runs from Jordan in southwestern Asia to the coast of the Indian Ocean in central Mozambique.
- It runs across many countries: Eritrea, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Malawi, Zambia, and Mozambique.
- The valley is situated in a region where three tectonic plates meet.
- It was formed about 40 million years ago when tectonic plates split and gave rise to the East African Rift.
- The area is geologically active and features volcanoes, hot springs, geysers and frequent earthquakes.
- A series of some thirty lakeslies along its length; the three largest in Africa are known as the Great Lakes and include Lake Tanganyika, the second deepest lake in the world, and Lake Victoria, the second-largest freshwater lake by surface area in the world.
- Many of Africa’s highest mountains—including Mount Kilimanjaro, Mount Kenya, and Mount Margherita—are in ranges fronting the Rift Valley.
- Rift Valley is a lowland region that forms where Earth’s tectonic plates move apart, or rift.
- They are found on land and at the bottom of the ocean, where they are created by the process of seafloor spreading.
- They differ from river valleysand glacial valleys in that they are created by tectonic activity and not the process of erosion.
Global Leaders Group On Antimicrobial Resistance:

The European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases and the Global Leaders Group (GLG) on AMR jointly organised a high-level event, ‘Forging partnerships between science and policy’.
- Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance consists of world leaders and experts from across sectors working together to accelerate political action on antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
- It performs an independent global advisory and advocacy role and works to maintain urgency, public support, political momentum and visibility of the AMR challenge on the global health and development agenda.
- It was established in November 2020 following the recommendation of the Interagency Coordination Group (IACG) on Antimicrobial Resistance to strengthen global political momentum and leadership on AMR.
- The inaugural meeting of the Group took place in January 2021.
- The Quadripartite Joint Secretariat (QJS) on Antimicrobial Resistance, a joint effort by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH) provide secretariat support for the Group.
- Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is the ability of bacteria and other microbes to resist the drugs used to inhibit or kill them.
- These microbes are sometimes referred to as ‘superbugs’ and are responsible for causing drug-resistant infections that are difficult to treat.
Project ISHAN:

India has started the process of unifying its four airspace regions under Project Indian Single Sky Harmonized Air Traffic Management at Nagpur (ISHAN).
- This initiative is expected to enhance air traffic management, benefiting airlines and passengers by making operations more efficient and safer.
- Challenges include technological implementation, process changes, and retraining of staff.
- Currently, Indian airspace is divided into 4 FIRs:
- Mumbai, Kolkata, Delhi, Chennai, and a sub-FIR in Guwahati, each managed separately.
- The Airports Authority of India (AAI) has called for expressions of interest to prepare a detailed project report for the Indian Single Sky Harmonized Air Traffic Management (ISHAN) initiative, centered in Nagpur.
- This consolidation is expected to streamline operations, enhance capacity, and alleviate congestion, benefiting both airlines and passengers.




