Today’s Current Affairs: 20th May 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
World Food Prize 2025:

Brazilian scientist Mariangela Hungria recently won the 2025 World Food Prize for her pioneering work in reducing the use of chemical fertilisers and developing biological seed and soil treatments to boost crop yields and nutrition.
- Brazilian microbiologist Mariangela Hungria is the winner of the 2025 World Food Prize for her work with biological seed and soil treatments.
- Hungria’s research enables crops to utilize soil bacteria for nutrients, increasing yields and reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
- World Food Prize is an international award recognizing the achievements of individuals that have advanced human development by improving the quality, quantity, or availability of food in the world.
- It is also known as the Nobel Prize for Food and Agriculture.
- It recognizes contributions in any field involved in the world food supply, such as food and agriculture, science and technology, manufacturing, marketing, nutrition, economics, poverty alleviation, political leadership, and the social sciences.
- The Prize was founded in 1986 by Dr. Norman E. Borlaug, recipient of the 1970 Nobel Peace Prize.
- It is now administered by the World Food Prize Foundation with support from numerous sponsors.
- It is a $500,000 award formally presented at the Laureate Award Ceremony in mid-October, on or around World Food Day, in conjunction with the Borlaug Dialogue international symposium in Des Moines, Iowa, USA.
- S. Swaminathan was named the first World Food Prize Laureate, receiving the award in 1987 for developing and spearheading the introduction of high-yielding wheat and rice varieties into India during the 1960s.
Type 2 Diabetes : New Initiative
The CBSE has directed affiliated schools to establish “Sugar Boards” to monitor and reduce sugar consumption among students primarily to lower the risk of Type 2 diabetes and obesity in children.
- T2D, the most common type of diabetes, is a disease that occurs when the blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high.
- Blood glucose is the main source of energy and comes mainly from the food.
- Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps glucose get into the cells to be used for energy.
- In T2D, the body doesn’t make enough insulin or doesn’t use insulin well.
- Too much glucose then stays in the blood, and not enough reaches the cells.
- Type 2 diabetes may be caused by a combination of factors:
- Being overweight or having obesity
- Not being physically active
- Genetics and family history
- Researchers estimate that T2D affects about 3% of the world’s population.
- T2D most commonly affects adults over 45, but people younger than 45 can have it as well, including children.
- Symptoms: Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms at all. If you do have them, the symptoms develop slowly over several years.
- They might be so mild that you do not notice them. The symptoms can include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Increased hunger
- Feeling tired
- Blurred vision
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Sores that do not heal
- Unexplained weight loss
- Treatment for T2D involves managing your blood sugar levels.
- Many people are able to do this by living a healthy lifestyle.
- Some people may also need to take diabetes medicines, which may include pills or medicines you inject under your skin, such as insulin.
E-Passports : India Joined

India has joined over 120 nations in issuing biometric e-passports, offering enhanced security, faster immigration, and global compliance.
- An e-passport (electronic or biometric passport) is an upgraded version of the traditional passport. It combines a conventional booklet with an embedded Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) chip and antenna in the back cover.
- This chip securely stores the holder’s personal and biometric data, including:
- Name, date of birth, passport number, and other demographic details
Biometric facial data and fingerprints
Digital signature for secure authentication
Security Features of E-Passports
RFID Chip & Antenna: Stores encrypted personal and biometric data, making unauthorized access or tampering extremely difficult.
Basic Access Control (BAC): Stops unauthenticated access to the chip by restricting scanning equipment to only authorized devices.
Passive Authentication (PA): Authenticates stored information and identifies tampering.
Extended Access Control (EAC): Introduces an additional layer of security to biometric data such as fingerprints.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Digitally signs the data, ensuring authenticity and preventing forgery or unauthorized data changes.
Benefits of E-Passports
Enhanced Security: Strong protection against forgery, duplication, and identity theft due to encrypted biometric data and digital signatures.
Faster Immigration: Automated e-gates and digital verification reduce manual checks and waiting times at airports.
Global Acceptance: Compliance with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) standards ensures smooth travel and easier visa processing worldwide.
Privacy: New e-passports no longer print the residential address on the last page; it is stored digitally and accessible only to authorised officials.
- Name, date of birth, passport number, and other demographic details
Mosura Fentoni:

Scientists have recently described Mosura fentoni, an ancient three-eyed predator that lived approximately 506 million years ago.
- Mosura fentoni is an extinct species of radiodont, a group of early arthropods, and was a marine predator during the Cambrian period.
- The species is named after “Mothra,” the fictional moth kaiju, due to its resemblance to a hovering moth and its unique body structure.
- The fossils were primarily found in the Burgess Shale of the Canadian Rockies, a site renowned for the exceptional preservation of soft-bodied organisms.
- The discovery highlights the unexpected diversity and evolutionary experimentation among early arthropods, offering rare insights into their internal anatomy and evolutionary convergence with modern arthropods.
Gyan Bharatam Mission : In News

The Prime Minister of India will launch the revamped National Manuscripts Mission-now restructured as the “Gyan Bharatam Mission”-on June 9, 2025.
- The Gyan Bharatam Mission is a comprehensive national initiative under the Ministry of Culture, Government of India, dedicated to the systematic survey, documentation, conservation, and digitisation of India’s vast manuscript heritage.
- The mission builds upon and revamps the earlier National Mission for Manuscripts (NMM), which was established in 2003 and functions under the Indira Gandhi National Centre for the Arts (IGNCA).
- Objective of Gyan Bharatam Mission
- To survey, document, conserve, and digitize over one crore (10 million) manuscripts housed in academic institutions, museums, libraries, and private collections across India.
- To create a National Digital Repository of Indian Knowledge Systems, making ancient wisdom accessible to researchers, students, and the public worldwide.
- Gyan Bharatam Mission Targets more than one crore manuscripts, making it the largest manuscript preservation initiative in India’s history.
- Establishment of a centralized, accessible digital platform for India’s traditional knowledge systems, enabling AI-driven archiving, metadata tagging, and translation tools.
- Active engagement with academic institutions, museums, libraries, private collectors, and international organizations for research, preservation, and dissemination.
- Adoption of advanced scientific techniques for restoration, preservation, and digitization, including AI and 3D imaging.
- Budget allocation for the mission increased from ₹3.5 crore to ₹60 crore, with a total outlay of ₹482.85 crore for 2024-31.
- Manuscripts will be made accessible for academic research, education, and public knowledge, both nationally and globally.
Jammu & Kashmir Public Safety Act, 1978:

Jammu & Kashmir Police have recently invoked the Public Safety Act against 23 individuals in Srinagar, citing their involvement in subversive activities and threats to national security and public order.
- Jammu & Kashmir Public Safety Act, 1978 is a preventive detention law originally enacted by the J&K State Legislature and now applicable to the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir.
- Its primary objective is to empower authorities to detain individuals to prevent actions prejudicial to the security of the state or maintenance of public order.
- The PSA permits authorities to detain individuals without formal charges or a trial, even if they are already in custody or recently granted bail.
- Detainees under the PSA cannot seek bail or appoint a lawyer to represent them, leaving them with limited legal representation options.
- The only way to challenge a PSA detention is through a habeas corpus petition filed by the detained person’s relatives in higher courts.
- Even if a PSA detention order is quashed by the High Court or Supreme Court, the government can issue a fresh detention order.
- The District Magistrate who issues the detention order is legally protected, as the PSA considers such actions done “in good faith.”
- Section 8 of the PSA broadly defines grounds for detention, including promoting enmity, instigation, or any acts threatening public harmony, with final decisions left to district authorities.
- The PSA allows detention for up to one year for disturbing public order and two years for activities harmful to state security.
Deadly Nipah virus’ transmission from animals to humans:
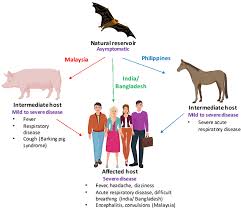
Health experts and physicians have raised concerns about the deadly Nipah virus’ transmission from animals to humans in Kerala.
- The Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus that can spread from animals to humans, as well as through contaminated food or direct human-to-human transmission.
- Nipah virus encephalitis is caused by an RNA (ribonucleic acid) virus belonging to the family Paramyxoviridae, genus Henipavirus, and is closely related to the Hendra virus.
- NiV was first identified in domestic animals such as pigs, dogs, cats, goats, horses, and sheep.
- The virus is transmitted by fruit bats of the genus Pteropus and is present in their urine, feces, saliva, and birthing fluids.
- NiV causes encephalitic syndrome in humans, with symptoms like fever, headache, drowsiness, confusion, and coma, often leading to death.
- The fatality rate is 40% to 75%.
- Diagnosis is done via real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) from body fluids. No vaccines exist for humans or animals.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has designated Nipah as a priority disease.
Nicaragua Withdrawal from UNESCO:

Nicaragua has announced its withdrawal from the UNESCO in protest over the awarding of the UNESCO/Guillermo Cano World Press Freedom Prize to Nicaraguan newspaper La Prensa despite its opposition from the Nicaraguan government.
- UNESCO/Guillermo Cano World Press Freedom Prize was established in 1997 and is the UN’s only journalism award, presented every year on 3rd May, World Press Freedom Day.
- Named after Colombian journalist Guillermo Cano, it honors individuals or organizations for their contributions to press freedom.
- Past recipients include Myanmar journalists Kyaw Soe Oo and Wa Lone (2019) and Belarus’ top independent journalists’ group (2022).
- Nicaragua is largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras (north), Costa Rica (south), Pacific Ocean (west), Caribbean Sea (east).
- Colonized by both Spain and Britain, gained independence in 1821, became fully independent in 1838 after briefly joining the Central American Federation.
- Predominantly mestizo ethnic group (mixed Indigenous and European ancestry).
RBI to Issue New Rs 20 Banknotes with Governor Sanjay Malhotra’s Signature:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced that it will soon release new Rs 20 denomination banknotes bearing the signature of the newly appointed RBI Governor, Sanjay Malhotra. These banknotes will be part of the Mahatma Gandhi (New) Series and will retain the same design, features, and motifs as the notes currently in circulation. The issuance of new Rs 20 banknotes with the signature of Governor Sanjay Malhotra has drawn attention due to the customary practice of updating legal tender to reflect changes in the RBI’s top leadership.
OpenAI Introduces Codex to Automate and Accelerate Coding Tasks:
OpenAI has unveiled Codex, a powerful new cloud-based AI coding agent capable of autonomously handling a range of software engineering tasks in parallel. From writing new features and running tests to fixing bugs and drafting pull requests, Codex aims to boost developer productivity by operating within a secure sandbox environment that uses a developer’s codebase as context. Launched on May 16, 2025, under research preview, the tool is initially available to ChatGPT Pro, Enterprise, and Team users.
Carlos Alcaraz Clinches First Italian Open Title in Style:
Carlos Alcaraz defeated Jannik Sinner 7-6 (5), 6-1 to win his first-ever Italian Open title on May 18, 2025. The victory marks Alcaraz’s 7th Masters 1000 title and further solidifies his dominance on clay, especially after Sinner’s return from suspension. This win also ends Sinner’s incredible 26-match winning streak.
India Opens Nuclear Energy Sector to Private Operators with Liability Reform:
The Indian government is planning to allow private sector operators to participate in the country’s nuclear energy sector for the first time. Alongside this move, it also proposes to limit their liability, a step seen as essential to attract private investments and technology partnerships. This development comes in the backdrop of the United States permitting its firms to manufacture nuclear equipment and undertake design work in India, reflecting deepening Indo-U.S. civil nuclear cooperation.
NSDL Reports Robust FPI Investment in May Amid Economic Stability:
Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs) have demonstrated a renewed interest in Indian equity markets, infusing ₹4,452.3 crore between May 13 and 16, 2025, according to data from the National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL). With this, the total net investment by FPIs in May has reached ₹18,620 crore, marking a significant rebound in foreign investor sentiment after months of outflows earlier this year.This week saw a surge in FPI inflows into Indian equities, driven by easing global uncertainties and improved domestic economic outlook. Despite a turbulent start to 2025, the inflow of ₹18,620 crore in May points to a strong turnaround in investor confidence.




