Today’s Current Affairs: 21st Dec 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Andriamamelo Cave : Rock Art Drawings

Unique, prehistoric rock art drawings have been discovered in the Andriamamelo Cave in western Madagascar.
- Andriamamelo Cave is situated in the western Madagascar.
- It is located in karstified limestone of the Paysage Harmonieux Protege de Beanka.
- This is part of an extensive karst region that includes the Parc National de Bemaraha to the south, a UNESCO World Heritage site, and the little-studied Antsingimavo karst area to the north.
Key findings:
- In this cave truly pictorial art, depicting images of nature with human-like and animal-like figures have been discovered.
- The dramatic discoveries contained several surprises, including hints at some remarkable cultural connections.
- First, scenes depicted in some cases linked up fairly directly to Egyptian religious motifs from the Ptolemaic period (300-30 BCE).
- Second, other inferences from symbols and writing on the walls showed connections to the Ethiopian and Afro-Arab worlds.
- Finally, prevalent symbology and motifs evoked a two-millennia-old cave art style from Borneo.
- At least three extinct animals of Madagascar which was thought to have been extinct for many centuries may be depicted – a giant sloth lemur, elephant birds and a giant tortoise.
- Egyptian connections are hinted at in eight major images, including a falcon (Horus); the bird-headed god Thoth; the ostrich goddess Ma`at and two human-animal figures which were similar to Anubis – an ancient Egyptian god usually depicted as a man with a canine head.
North Korea Test-Fired Solid-Fuel Missiles:

North Korea test-fired an Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) powered by solid fuel.
- Solid-fuel missiles do not need to be fuelled immediately ahead of launch.
- They are often easier and safer to operate, and require less logistical support.
- They are harder to detect and more survivable than liquid-fuel weapons.
- Solid propellants are a mixture of fuel and oxidiser.
- Metallic powders such as aluminium often serve as the fuel, and ammonium perchlorate, which is the salt of perchloric acid and ammonia, is the most common oxidiser.
- The fuel and oxidiser are bound together by a hard rubbery material and packed into a metal casing.
- When solid propellant burns, oxygen from the ammonium perchlorate combines with aluminium to generate enormous amounts of energy and temperatures of more than 5,000 degrees Fahrenheit (2,760 degrees Celsius), creating thrust and lifting the missile from the launch pad.
Blue Dragons : Spotted

Blue dragons (Glaucus atlanticus) have been spotted on the beach and in waters near the shore in Besant Nagar in Chennai.
- The blue dragon (Glaucus atlanticus) is a type of mollusc known as a nudibranch.
- They also are known as blue sea slugs, blue angels, and sea swallows.
- It rarely grows larger than three centimetres long.
- An air bubble stored in its stomach keeps the blue dragon afloat.
- It can be found drifting on the surface of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian oceans in temperate and tropical waters.
- They feed on venomous siphonophores such as the Portuguese man-o-war and bluebottle, which also occur in ocean surface waters.
- The dragons appear immune to the nematocysts stinging cells of these jellyfish-like creatures.
- They incorporate these cells into multiple finger-like structures protruding from their body which provides them with a potent form of protection from predators.
- The slug isn’t venomous all on its own, however, it stores the stinging nematocysts created by the creatures on which it feeds.
- Its sting can cause problems, especially to children and elderly.
- One sting from this little creature can lead to nausea, pain, vomiting, acute allergic contact dermatitis, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Telecommunications Bill 2023 : Introduced In Lok Sabha

The government introduced the Telecommunications Bill 2023 in the Lok Sabha.
- It seeks to repeal the Indian Telegraph Act, 1885, the Indian Wireless Telegraphy Act, 1933, and the Telegraph Wires (Unlawful Possession) Act, 1950.
- It also amends the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Act, 1997.
Key Provisions of Telecommunications Bill 2023:
- Prior authorisation from the central government will be required to provide telecommunication services, establish, operate, maintain, or expand telecommunications networks, or possess radio equipment.
- Existing licenses will continue to be valid for the period of their grant, or for five years, where the period is not specified.
- Spectrum will be assigned by auction, except for specified uses, where it will be allocated on an administrative basis.
- These include purposes such as national security and defense, disaster management, weather forecasting, transport, satellite services such as DTH and satellite telephony, and BSNL, MTNL, and public broadcasting services.
- The Bill introduces provisions for allocating spectrum to satellite Internet providers like OneWeb (supported by Bharti) and U.S.-based companies such as SpaceX’s Starlink.
- Presently, active authorizations have been granted to OneWeb and Jio, paving the way for satellite-based Internet services.
- Messages or a class of messages between two or more persons may be intercepted, monitored, or blocked on certain grounds.
- The government may take temporary possession of any telecom infrastructure, network, or services on occurrence of any public emergency or public safety.
- An officer authorized by the government may search premises or vehicles for possession of unauthorized telecom networks or equipment.
- The central government may prescribe standards and assessments for telecom equipment, infrastructure, networks, and services.
- Facility providers may seek a right of way over public or private property to establish telecom infrastructure.
- Right of way must be provided on a non-discriminatory and non-exclusive basis to the extent possible.
- The central government may provide for measures to protect users which include: prior consent to receive specified messages such as advertising messages, creation of Do Not Disturb registers, and a mechanism to allow users to report malware or specified messages.
- Biometric Authentication is mandatory for telecom customers to combat spam calls and messages.
- The Bill amends the TRAI Act to also allow individuals with: at least 30 years of professional experience to serve as the chairperson, and at least 25 years of professional experience to serve as members.
- The Universal Service Obligation Fund has been established under the 1885 Act to provide for telecom services in underserved areas.
- The Bill retains this provision, renames the fund as Digital Bharat Nidhi, and also allows its use for research and development.
- It has removed over-the-top (OTT) services and apps from the definition of telecommunication services, in a big relief to communication service providers such as WhatsApp and Telegram.
- The Ministry of Electronics and IT will handle the regulation of OTT apps under the potential Digital India Act, not included in the Telecom Bill.
- The Bill specifies various criminal and civil offenses. Providing telecom services without authorisation, or gaining unauthorized access to a telecom network or data, are punishable with imprisonment up to three years, a fine up to two crore rupees, or both.
- Breaching terms and conditions of authorisation is punishable with a civil penalty up to five crore rupees.
- The central government will appoint an adjudicating officer to conduct inquiries and pass orders against civil offenses under the Bill.
- The officer must be of the rank of joint secretary and above.
- A measure initially established post the India-China border conflict in 2020 to prevent the importation of telecom equipment from potentially adversarial nations is now integrated into the law.
National Culture Fund : Fund Received From Non-Government Sources

The Union Minister for Culture, Tourism And Development informed in the Lok Sabha that the National Culture Fund (NCF) received Rs. 3.70 Crore From Non-Government Sources during the last five Years.
- National Culture Fund was set up by the Government of India as a Trust under the Charitable Endowment Act, 1890 through a Gazette Notification in 1996.
- It was established as a funding mechanism distinct from the existing sources and patterns of funding for the arts and culture in India.
- It will enable institutions and individuals to support arts and culture directly as partners with its government.
- It aims to mobilise extra resources through Public-Private Partnership (PPP) towards promoting, protecting & preserving India’s Cultural Heritage (Tangible & Intangible).
- It is managed and administered by a Council and an Executive Committee to actualize those policies.
- The Council is chaired by the Union Minister of Culture and has a maximum strength of 24 including both the Chairman and Member Secretary.
- It has members representing the corporate and public sector, private foundations and non-profit organisations.
- The purpose for this structure is to increase non-government representation in the decision-making process.
- The Executive Committee is chaired by the Secretary, Ministry of Culture
- The donations to the national Culture Fund will be eligible for tax benefit under the Income Tax Act.
109th Indian Science Congress:

Lovely Professional University(LPU) withdrew from hosting 109th Indian Science Congress (ISC), raising concern about the event’s viability.
- The ISC is a prestigious and influential scientific organization that meets annually in the first week of January.
- It was founded in 1914 to stimulate scientific research in India.
- The Indian Science Congress Association (ISCA) is the official body that organizes the event.
- ISCA, is a professional body under the Department of Science & Technology, Ministry of Science & Technology.
- The theme of the 109th ISC is “The Global Perspective on Science and Technology for Sustainable Future”.
Katabatic Winds:
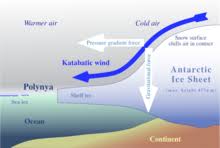
A surprising phenomenon has been observed in the Himalayas, where ‘katabatic’ winds are triggered when high temperatures affect high-altitude ice masses.
- This leads to cold air blowing to lower-altitude areas, potentially slowing down the effects of the global climate crisis in some regions.
- The study reveals that a temperature gap between air above the mountains and cooler air in contact with ice masses causes increased turbulent heat exchange, leading to stronger cooling of the surface air mass.
- Anabatic Winds are upslope winds driven by warmer surface temperatures on a mountain slope than the surrounding air column.
- Katabatic winds are downslope winds created when the mountain surface is colder than the surrounding air and create a downslope wind.
Earthquake In Northwestern China:

An earthquake in northwestern China killed at least 131 people.
- At least 127 people have been killed and hundreds of others were injured after an overnight earthquake hit northwestern China in a remote and mountainous region while many were asleep at home.
- The earthquake was the most deadly China has experienced in nine years.
- An earthquake is the shaking or trembling of the earth’s surface.
- It is caused by the seismic waves or earthquake waves that are generated due to a (sudden release of energy in the earth’s crust shallow-focus earthquakes or upper mantle some shallow-focus and all intermediate and deep-focus earthquakes.
- Earthquake are by far the most unpredictable and highly distructive of all the natural disasters
People With Blood Disorder Not Eigible For Reservation:
The Centre’s decision to exclude individuals with thalassemia, sickle cell disease, and haemophilia, from government job reservations, despite their recognition as disabilities in the Right to Persons with Disabilities(RPWD) Act of 2016, prompts concerns.
- The government provides 4% reservation in government jobs for specific disabilities, including total loss of vision and low vision, complete loss of hearing and low hearing, locomotor disability, etc.
- Government cites Section 34 of RPWD Act, 2016, stating that persons with blood disorders, including thalassemia, are not eligible for job reservation in government establishments.
- Activists express dissatisfaction, asserting that excluding disabilities recognized in the Act from job reservations defeats the Act’s purpose.
- Thalassemia Blood disorder affects haemoglobin Reduced ability to produce normal haemoglobin
- Haemophilia is a Bleeding disorder, deficiency of clotting factor Prolonged bleeding, difficulty in clotting
- Sickle Cell Disease is a Genetic blood disorder, abnormal hemoglobin Altered red blood cell shape, circulation issues
Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana : Graduates Not Preferred For Railway Jobs

Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw said that Indian Railways’ ‘Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana’ graduates are not preferred for railway jobs.
- The statement comes as a response to a query by BJP MP Narayana Koragappa regarding job preferences for the trained youth.
- Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana launched in September, 2021.
- Ministry of Railway.
- Objective is imparting training skills to the youth across several trades to bring qualitative improvement.
- Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana is a skill development scheme with a special focus on providing training for jobs that are relevant to the Railways.
- It is a sub-scheme under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
- The training is imparted in fourteen (14) industry-relevant technical trades such as Electrician, Welder, Machinist, Fitter etc.
- The training is provided free of cost to the candidates.
- There is no provision for providing employment under this scheme.
- Participants will be selected from applications received online, following a transparent mechanism based on marks in matriculation.
- Candidates, who have passed class X and are aged between 18 and 35 are eligible to apply.
- After the end of the program, trainees have to pass a standardized assessment followed by a certificate in the allotted trade by the National Rail and Transportation Institute.
Lathyrism : Neurological Disease
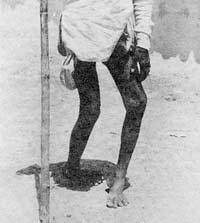
Grass pea, also known as khesari dal, has been historically infamous for causing lathyrism, a neurological disease leading to lower limb paralysis.
- In the late 19th century, an outbreak of lathyrism linked to grass pea led to its ban in India in 1961 under the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act.
- Despite the ban, grass pea cultivation continued, and researchers developed low-toxin varieties.
- In 2015, an expert committee recommended lifting the ban, emphasizing its potential for food security amid climate change.
- Lathyrism is a neurological disorder caused by eating too much grass pea (Lathyrus sativus).
- It’s also known as neurolathyrism
- Lathyrism is one of the oldest known neurotoxic disorders.
- It’s a skeletal disorder caused by the toxin BAPN, which inhibits the copper-containing enzyme lysyl oxidase




