Today’s Current Affairs: 15th Dec 2023 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Ban On Onion Exports:

The Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) has announced a ban on onion exports until March 2024, issuing a notification converting the export policy of onions from ‘Free’ to ‘Prohibited’.
- The current supply shortage, caused by early depletion of 2022-23 rabi season stocks and anticipated lower kharif 2023 output, along with increased festive demand, has led to a significant rise in onion prices.
- The government has also revised the stock limit for wheat, the stock limit has been halved to 1,000 tonnes for wholesalers, and for retailers to 5 tonnes.
- By restricting onion exports, the government aims to prevent price surges or fluctuations within the domestic market.
- To combat spiraling prices, the Centre had imposed a Minimum Export Price of USD 800 per tonne on onions in October 2023. Earlier, in August, the government imposed a 40% export duty on onions.
- Onions have a history of significant price volatility, and an export ban helps in stabilizing prices, making them more affordable for local consumers.
National Energy Conservation Day 2023:

The National Energy Conservation Day, observed on 14th December annually, serves as a platform to highlight India’s achievements in energy efficiency.
- It is hosted by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency under the Ministry of Power, Government of India, the event is integral to the Energy Conservation Act 2001’s mandate to promote and regulate energy efficiency.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency, established in 2002, operates with a mission to reduce the energy intensity of India’s economy through self-regulation, market principles, and collaboration with designated consumers and agencies, aligning with the Energy Conservation Act’s regulatory and promotional functions.
Diel Vertical Migration:
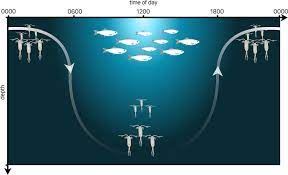
Diel Vertical Migration (DVM), a synchronized movement observed in deep-sea marine animals, particularly zooplankton, where they swim up to the ocean’s surface at night and return to deeper waters during the day.
- This migration serves as a survival strategy, allowing them to feed on phytoplankton in the safer darkness while avoiding daytime predators.
- DVM is a crucial player in the Earth’s carbon cycle.
- Animals in the mesopelagic i.e middle water between 200m to 1000m layer actively remove carbon from the upper ocean as they consume surface-dwelling plankton.
- When these organisms return to deeper waters, they transport the carbon with them.
- DVM is the largest daily migration on the planet by biomass, occurring in all oceans.
- DVM contributes to carbon sequestration, as migratory animals become part of the food chain in the twilight zone, passing on carbon to their predators.
- The carbon-rich waste produced by these predators eventually sinks to the ocean floor
Global Status Report On Road Safety 2023 : WHO

The World Health Organization (WHO) has reported a 5% decrease in annual road traffic deaths worldwide from 2010 to 2021, totaling 1.19 million fatalities
- According to the WHO’s Global Status Report on Road Safety 2023, India witnessed a rise in road traffic fatalities from 1.34 lakh in 2010 to 1.54 lakh in 2021, reflecting a 15% increase.
- This contrasts with 108 UN member nations that reported a decrease in road traffic deaths.
- Ten countries, including Belarus, Denmark, Japan, and the United Arab Emirates, successfully reduced road traffic deaths by over 50%.
- 35 countries achieved notable progress, experiencing a reduction in fatalities ranging from 30% to 50%.
- Road traffic crashes have become the leading cause of death for children and youth aged five to 29 years, ranking as the 12th leading cause of death across all age groups. Two-thirds of these deaths occur among people of working age.
- The global motor vehicle fleet increased by 160% since 2010.
- Annual fatality rates per 1 lakh vehicles dropped from 79 deaths to 47 deaths, marking a 41% reduction.
- The report highlights regional disparities, with 28% of global road traffic deaths occurring in the WHO’s South-East Asia Region.
- Other significant contributions come from the Western Pacific Region (25%), the African Region (19%), the Region of the Americas (12%), the Eastern Mediterranean Region (11%), and the European Region (5%).
- Worldwide four-wheel vehicle occupants constitute 30% of fatalities, pedestrians make up 23%, and powered two- and three-wheeler users contribute 21%.
- Cyclists and users of micro-mobility devices, including e-scooters, account for 6% and 3% of fatalities, respectively.
Norovirus : Surge In Cases In UK
The United Kingdom has witnessed a significant increase in norovirus cases in recent weeks, with nearly 1,500 confirmed cases reported by the beginning of this month.
- This surge, amounting to a 60% rise compared to the same period last year, poses challenges for healthcare resources and staff, as highlighted by the Royal College of Emergency Medicine Scotland.
- It is commonly known as the “winter vomiting bug,” norovirus is a highly contagious virus causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- Unlike the flu, norovirus is not preventable with a vaccine.
- Norovirus leads to inflammation in the stomach or intestines, resulting in acute gastroenteritis.
- Symptoms typically manifest 12 to 48 hours after exposure, with most individuals recovering within one to three days.
- The virus spreads easily through contact with an infected person, and there is no specific medication for norovirus.
- The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends drinking plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration, a common concern with norovirus.
- Regular handwashing with soap and water is crucial, as the virus can persist in the feces of recovered individuals for at least two weeks.
Barracuda: India’s Fastest Solar-Electric Boat

The Barracuda, India’s fastest solar-electric boat, was ceremoniously launched at the Navgathi Panavally Yard in Alappuzha.
- It is jointly developed by Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders and Navalt, the cutting-edge Barracuda stands as a testament to collaborative innovation in the maritime sector.
- The Barracuda which is named after the swift long fish, is designed by Navalt for workboat purposes.
- It Boasts a top speed of 12 knots and a remarkable range of 7 hours on a single charge, the 14-meter long and 4.4-meter wide vessel is equipped with twin 50 kW electric motors, a marine-grade LFP battery, and 6 kW solar power.
- It can accommodate 12 passengers, promising a noise-free, vibration-free, and pollution-free journey.
Ranthambore National Park : Safari Vehicles With (GPS) Trackers

The Ranthambore National Park administration plans to implement stringent monitoring of safari vehicles with Global Positioning System (GPS) trackers.
- Ranthambore National Park is located in the Sawai Madhopur district of southeastern Rajasthan.
- It lies at the junction of the Aravali and Vindhya hill ranges.
- It was the former hunting grounds of the Maharajas of Jaipur.
- It derives its name from the Ranthambore Fort situated within its precincts.
- It was on 1st November, 1980, that Ranthambore was declared a national park, while the forests located beside it were named Sawai Man Singh Sanctuary and Keladevi Sanctuary.
- It is characterised by rugged terrain with dense forests, lakes, and ancient ruins.
- The vegetation of the Ranthambhore is tropical dry deciduous and tropical thorn type due to its hilly track; water is confined to narrow valleys and some lakes.
- The Chambal River in the south and the Banas River in the north bound the park.
- There are several lakes in the park known as Padam Talab, Raj Bagh Talab, and Malik Talab.
- Its flagship species is Bengal tiger.
Anthrax Outbreak:

The World Health Organisation (WHO) has reported a significant anthrax outbreak in Zambia, marking an alarming spread of the disease across nine out of the country’s ten provinces.
- Anthrax is a highly infectious disease that is caused by the gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria known as Bacillus anthracis.
- It affects animals like cows, sheep, and goats, as well as wild herbivores.
- Even humans can get sick if they come in contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products.
- Anthrax bacteria also occur naturally in soil.
- The disease manifests in three forms depending on the route of infection: cutaneous, gastrointestinal, and inhalational.
- Cutaneous anthrax, the most common form, presents with itchy bumps that develop into black sores, often accompanied by fever and muscle aches.
- It can be diagnosed by identifying Bacillus anthracis in blood, skin lesions, or respiratory secretions through laboratory culture, PCR, or ELISA tests.
- While there is no specific test to determine exposure to anthrax, public health investigations play a crucial role in identifying potential cases.
- It is available and includes antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, or levofloxacin.
Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary : Migratory Birds Started Arriving

With the onset of the winter season, hundreds of migratory birds have started arriving at Kazhuveli bird sanctuary.
- Kazhuveli Bird Sanctuary is located in the state of Tamil Nadu.
- It lies adjacent to the Bay of Bengal along the east coast.
- It is one of the major wetlands on the Coromandel Coast after Pulicat Lake.
- The lake is connected to the Bay of Bengal by the Uppukalli Creek and the Yedayanthittu estuary and is visited for nesting by migratory birds on the Central Asian flyway.
- The southern part of the wetland has been reserved land since 2001.
- It is listed as one of Tamil Nadu’s 141 prioritised wetlands, Kazhuveli is also a wetland of international significance and a potential Ramsar site
- Kazhuveli has varied habitats including sloping wetlands preferred by shore birds, darters and waders, birds on floating vegetation and open grasslands preferred by different species of birds and fauna.
- The lake has a feeding ground for long-distance migrants from the cold subarctic regions of Central Asia and Siberia including Black-tailed Godwits, Eurasian Curlew, White Stork, Ruff and Dunlin.
ENACT Partnership:

Six new countries and a United Nations agency joined the ENACT Partnership.
- Enhancing Nature-based Solutions for an Accelerated Climate Transformation (ENACT) was launched by Germany and Egypt along with the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
- It was launched at the Conference of Parties (COP27), which took place at Sharm el-Sheikh, Egypt in 2022.
- Other member countries: Canada, European Union, France, Japan, Malawi, Norway, Republic of Korea, Slovenia, Belgium, Pakistan, Spain, the Netherlands, Switzerland and the United States.
- It is an ambitious global initiative that seeks to coordinate global efforts to address climate change, land and ecosystem degradation, and biodiversity loss through Nature-based Solutions.
- It aims to:
- Enhance the protection from and resilience to climate impacts of at least 1 billion vulnerable people.
- Secure up to 2.4 billion hectares of healthy natural and sustainable ecosystems, and significantly increase global mitigation efforts through protecting and restoring carbon-rich ecosystems.
SO2 Emission Reduction Technology : Analysis

An analysis by the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air (CREA) has found less than 8% of India’s coal-based power plants have installed the SO2 emission reduction technology recommended by the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) to keep Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) emissions in check
- Only a combined capacity of 16.5 Gigawatts(GW) of coal plants have installed FGDs and Circulating Fluidised Bed Combustion (CFBC) boilers equivalent to 5.9 GW across India.
- The CREA analysis found that 92 % of the country’s coal power plants function without FGDs.
- Blanket extension of the deadline for all coal power plants without checking on their progress by MoEF&CC and Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) played a major role in derailment of emission controls from coal-based electricity generation units.
- The MoEF&CC introduced emission standards in 2015 for regulating PM, SO2, NOx, and Hg (Mercury) emissions.
- The deadline has been extended four times for units in Delhi and the National Capital Region (NCR) and three times for most other units across the country.
- India’s energy generation installed capacity stands at 425 GW.
- The thermal sector holds a predominant position within the overall installed capacity, encompassing coal (48.6%), gas (5.9%), lignite (1.6%) and a minimal share (<0.2%) from diesel.




