Today Current Affairs: 23rd February 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Amendments Made To The Right To Information Act:

The Supreme Court has criticized the Union government for having not filed a reply to a petition by parliamentarian Jairam Ramesh challenging the amendments made to the Right to Information Act for over a year.
- The petitioner argues that the amendments gave the Centre unparalleled powers to dictate the tenure, salaries and service conditions of the Chief Information Commissioner and Information Commissioners as per its “whims and fancies”.
- The petitioner contended that the RTI Amendment Act of 2019 and its Rules cripple the objectivity and independence of the Central Information Commission (CIC) by bringing under the yoke of the government.
- The Centre shall have the powers to set the salaries and service conditions of Information Commissioners at central as well as state levels.
- Term of the central Chief Information Commissioner and Information Commissioners: appointment will be “for such term as may be prescribed by the Central Government”.
- While the original Act prescribes salaries, allowances, and other terms of service of the state Chief Information Commissioner as “the same as that of an Election Commissioner”, and the salaries and other terms of service of the State Information Commissioners as “the same as that of the Chief Secretary to the State Government”, the amendment proposes that these “shall be such as may be prescribed by the Central Government”.
Centre For Development Of Advanced Computing (C-DAC):

Following instances of cyber attacks during the ongoing pandemic across its network, the Ministry of Railways has roped in the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) to educate its officials on Internet ethics, cyber hygiene, and best practices in the use of IT equipment, including mobile phones.
- This is a part of its National Cyber Security Strategy.
- Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC) is the premier R&D organization of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) for carrying out R&D in IT, Electronics and associated areas.
- The setting up of C-DAC in 1988 itself was to built Supercomputers in the context of denial of import of Supercomputers by the USA.
- Since then C-DAC has been undertaking the building of multiple generations of Supercomputer starting from PARAM with 1 GF in 1988
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease:
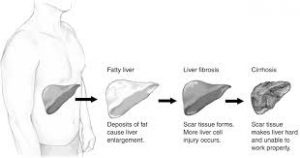
Union Health Minister Harsh Vardhan said that India has become the first country in the world to identify the need for action for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
He said this while launching the operational guidelines for integration of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with the National Programme for Prevention & Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is an umbrella term for a range of liver conditions affecting people who drink little to no alcohol.
- As the name implies, the main characteristic of NAFLD is too much fat stored in liver cells.
- NAFLD is increasingly common around the world, especially in Western nations.
- Some individuals with NAFLD can develop non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), an aggressive form of fatty liver disease, which is marked by liver inflammation and may progress to advanced scarring (cirrhosis) and liver failure.
- This damage is similar to the damage caused by heavy alcohol use.
National Technology Awards 2020:

A total of 12 companies have been selected for the National Technology Awards 2020 for the successful commercialization of innovative indigenous technologies.
- The awards are conferred by the Technology Development Board (TDB).
- Every year TDB seeks applications for prestigious National awards for commercialization of technologies under three categories – Indigenous technologies, MSME, and Startups.
Category 1: National Award For Successful Commercialization of Indigenous Technology:
- This award is given to an industrial concern that has successfully developed & commercialized indigenous technology.
- In case, the technology developer/provider and the company commercializing the technology are two different organizations, each is eligible for an award of Rs. 25 Lakh and a trophy.
Category 2: National Award For MSMEs:
- The award of Rs. 15 lakhs each in this category is given to selected MSMEs that have successfully commercialized the product based on indigenous technology.
Category 3: National Award For Technology Start-ups:
- This award is given to a technology start-up for promising new technology with potential for commercialization.
- The award in addition to the trophy includes a cash award of Rs. 15 Lakh.
- These awards conferred to various industries provide a platform of recognition to Indian industries and their technology provider, who have worked as a team, to bring innovation to the market and contributed to the vision of “Atmanirbhar Bharat”.
India’s Top Trade Partner:

China has again become India’s top trading partner in the year 2020. The reason was that India was still dependent on the import of heavy machines, telecom equipment, and home appliances from China.
- The provisional data from the trade between both countries in the year 2020 stood at $77.7 billion.
- However, the trade had decreased as compared to the 2019 trade total of $85.5 billion.
- The imports of heavy machines etc outweighed India’s efforts to cut down its dependence on trade.
- As a result of which, the bilateral trade gap of India with China was $40 billion in the year 2020.
- Total imports from China stood at $58.7 billion which was more than India’s combined imports from U.S. and U.A.E.
- The data further highlights that, India was able to lower the imports from its Asian neighbors despite there were demand disruptions amid the coronavirus pandemic.
NASA: Released The First Audio From Mars:

The United States space agency, NASA, released the first audio from Mars on February 22, 2021. It was a faint crackling recording of the wind that was captured by the Perseverance rover.
- NASA has also released the first video of the landing of the rover.
- The rover is on a mission to search if there is any sign of past life on the MARS (RED Planet).
- The rover sent a high-definition video clip of about three minutes and 25 seconds.
- Video shows the deployment of a red-and-white parachute having a 70.5-foot-wide canopy.
- Video further reveals the heat shield is dropping away after protecting Perseverance while it was entering into the MARS’ atmosphere.
- It also reveals that the rover touched-down the MARS surface in a cloud of dust in its Jezero Crater which lies to the north of MARS’ equator.
- NASA had launched the Perseverance rover on July 30, 2020.
- The mission landed on MARS on February 18, 2021. The prime mission is of just over two years however it will remain operational beyond that.
- The Predecessor of the Perseverance, Curiosity, is still functioning that was launched eight years back on Mars.
India and the Maldives have signed a defence Line of Credit agreement worth USD 50 million:

The agreement was signed during the visit by the External Affairs Minister of India to the Maldives.
Key Points
Defence Line of Credit:
- It was signed pursuant to the request by the Government of Maldives in April 2013 for India’s support and cooperation in enhancing the capability of the Maldives Defence Forces in maritime surveillance, and subsequent requests in October 2015 and March 2016.
- It is seen as key to India’s and Maldives’ strategic interests, particularly given China’s increasing footprint in the Indian Ocean Region.
Assistance to Build Dockyards:
- A dockyard will be developed at the Uthuru Thila Falhu (UTF) Naval Base with Indian assistance, a few miles northwest of Male, which will strengthen the Maldivian defence capabilities.
- The agreement is part of the defence action plan signed in 2016 by then Maldivian President Abdulla Yameen Abdul Gayoom during a visit to India.
- Indicating deepening security cooperation, an agreement to develop, support and maintain a Maldives National Defence Force Coast Guard Harbour at Sifavaru was also signed.
- India will also support the development of other infrastructure needed for the harbour, support the development of communications resources and radar services, and provide training.
Countering Terrorism:
- Agreed to convene the first meeting of the Joint Working Group on Counter-Terrorism, countering Violent Extremism and De-radicalisation at the earliest.
Review of Infrastructure Projects:
- A number of India-backed infrastructure projects including the National College of Policing and Law Enforcement Studies.
Collaboration at Multilateral Bodies: - Discussed collaboration at multilateral bodies like the General Assembly and Security Council of the United Nations Organisation.
- The Maldivian side assured India of its support for permanent membership of India at the “expanded and reformed” UN Security Council.
- India has also extended support for the candidature of the Maldives for the Presidency of the 76th session of the General Assembly.
Cooperation for Police Reforms:
- Noted progress on institutionalising linkages between the police organisations to support collaboration and cooperation in training management and exchange of trainers and trainees.
Iran And The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) Deal:

Iran and the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) have agreed to temporary measures to offset Iran’s decision to restrict access to inspectors.
- In December 2020, Iran’s Parliament passed the law demanding a suspension of some inspections if the USA failed to lift sanctions.
- Iran will stop the implementation of the voluntary measures as envisaged in the 2015 nuclear deal, as of 23rd February 2021.
- However, Iran will continue to implement fully and without limitation its Comprehensive Safeguards Agreement with the IAEA as before.
- Under a comprehensive safeguards agreement, the IAEA has the right and obligation to ensure that safeguards are applied to all nuclear material in the territory, jurisdiction, or control of the State for the exclusive purpose of verifying that such material is not diverted to nuclear weapons or other nuclear explosives.
- No access will be given to the IAEA beyond the safeguards of the Non-Proliferation Treaty.
- Iran would deny the IAEA real-time access to footage from surveillance cameras installed at some sites and, if sanctions are not lifted within three months, delete it




