Today’s Current Affairs: 24th August 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Glacial Lakes : National Disaster Management Authority Study

The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) has finalised a list of 189 “high-risk” glacial lakes for mitigation measures to reduce the risk emanating from them.
- Glacial Lakes is a body of water that originates from a glacier.
- It typically forms at the foot of a glacier, but may form on, in, or under it.
- ISRO categorised glacial lakes into four broad categories based on how they were formed — moraine-dammed, ice-dammed, erosion-based, and ‘others’.
- As glaciers move, they erode the terrain under them, leaving depressions and grooves on the land.
- When they churn up rock and soil, they etch ridges of debris known as moraines.
- Most glacial lakes form when a glacier retreats and meltwater fills the hole left behind.
- However, natural dams, formed out of ice and terminal moraines, can also form glacial lakes.
- An ice dam forms when a surging glacier, which can move up to 100 times faster than an average glacier, may dam up meltwater as it closes off a valley or fjord and prevents it from draining.
- Dams formed by moraines can be dense and stable, holding sizable lakes behind them for years.
- They can also be leaky, allowing the lake to drain slowly into nearby rivers.
- Glacial lakes are crucial sources of freshwater for rivers.
- However, they also pose significant risks, specifically of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs).
Gongronema sasidharanii : New Species

Gongronema sasidharanii, a new species of plant, was recently discovered from Pampadum Shola National Park in Kerala.
- Gongronema sasidharanii is a new species of plant discovered in Pampadum Shola National Park, Idukki District, Kerala.
- It is a plant with smooth stems and small urn-shaped creamy white to purplish-green flowers.
- This is also the first time the genusGongronema is being reported from south India.
- In India, the genus Gongronema has so far been represented by just three species found in northeast India, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, and West Bengal.
Pampadum Shola National Park:
- It is located in the eastern part of the Southern Western Ghats in Idukki District, Kerala.
Macrophages : New Study
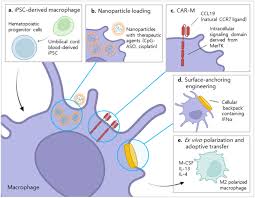
In a new paper published recently, a team of scientists describes the complex interplay between diseased liver cells and macrophages.
- Macrophages are a type of white blood cellthat plays an important role in the human immune system.
- They carry out various functions, including engulfing and digesting microorganisms, clearing out debris and dead cells, and stimulating other cells involved in immune function.
- The term macrophage is formed by the combination of the Greek terms “makro” meaning big, and “phagein” meaning eat.
- Macrophages form from monocytes, which themselves derive from the bone marrow
- Monocytes circulate through the blood for one to three days before migrating into tissues, where they become macrophages or dendritic cells(i.e., a type of antigen presenting cell that plays a role in linking the innate and adaptive immunity).
- Macrophages can be found within many organs in the body, including the liver, brain, bones, and lungs, as well as in the blood, particularly at sites of infection.
- They are essential for the maintenance and defence of host tissues, doing so by sensing and engulfing particulate matterand, when necessary, initiating a pro-inflammatory response.
- They can modify themselves to form different structuresin order to fight various different microbes and invaders.
- In this way, macrophages provide the first line of defense in protecting the host from infection.
- They are also involved in the development of non-specific or innate immunity.
- This type of immunity is a long-term immunity which is acquired when a macrophage ingests a microbe and presents the microbe’s antigen on its surface to alert other white blood cells to the presence of the invading particle.
- Other white blood cells then multiply and amount an immune response against the pathogen.
- Macrophages produce a variety of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that communicate with other cells of the immune system.
Quantum Nonlocality:
Scientists have demonstrated that a universal standard for measuring and quantifying non-local quantum correlations is not possible.
- While classical physics assumes locality, the principle of nonlocality is a feature of many interpretations of quantum mechanics.
- Nonlocality describes the apparent ability of objects to instantaneously know about each other’s state, even when separated by large distances (potentially even billions of light years), almost as if the universe at large instantaneously arranges its particles in anticipation of future events.
- Thus, in the quantum world, despite what Einsteinhad established about the speed of light being the maximum speed for anything in the universe, instantaneous action or transfer of information does appear to be possible.
- This is in direct contravention of the “principle of locality” (or what Einstein called the “principle of local action”), the idea that distant objects cannot have direct influence on one another, and that an object is directly influenced only by its immediate surroundings, an idea on which almost all of physics is predicated.
- Nonlocality occurs due to the phenomenon of entanglement, whereby particles that interact with each other become permanently correlated, or dependent on each other’s states and properties, to the extent that they effectively lose their individuality and, in many ways, behave as a single entity.
Nonlocality suggests that the “separate” parts of the universeare actually potentially connected in an intimate and immediate way.
State Of Healthcare In Rural India 2024:

The “State of Healthcare in Rural India, 2024” report was released by NGO Transform Rural India and Development Intelligence Unit.
- The survey covered 21 States including Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Maharashtra, Tamil Nādu, and Uttar Pradesh.
- The sample achieved included 52.5% male respondents and 47.5% female respondents.
Key Highlights of the Report:
- Only about 50% of rural households in the country have government health insurance, while 34% lack any health insurance coverage at all.
- 61% of surveyed households do not have life insurance.
- It revealed that there is a lack of diagnostic facilities in the rural areas mostly because of shortage of trained personnel.
- Only 39% of respondents have access to a diagnostic facility within commutable distance.
- 90% of respondents do not undergo routine health checkups unless recommended by a doctor.
- Only 12.2% of households have access to subsidised medicines from Pradhan Mantri Jan Aushadhi Kendras.
- Only 26% respondents had access to a government medical store located within the premises of a health facility that provides free medicines.
- 61% have access to a private medical store within commutable distance.
- 20% of the households reported no drainage system in their villages and only 23% had a covered drainage network system in their villages.
- 43% of households did not have any scientific system of waste disposal and they ended up with dumping their waste everywhere.
- Only 11% burn the dry waste and convert their wet waste into compost, while 28% reported that the local panchayat has made plans to collect household waste.
- 73% of the households with elderly members need constant care and the majority (95.7%) prefer family caregivers, predominantly female (72.1%), highlighting the need for caregiver training on home-based care.
- Only 3% of households have engaged in paid external caregivers.
- 10% rely on neighbourhood support in the absence of family caregivers.
- Majority of caregivers for pregnant women include husbands (62.7%), mothers-in-law (50%), and mothers (36.4%).
- The report emphasises the need for strong social networks, supportive environments, and capacity building for family caregivers.
- 45% of the respondents across gender most of the time have anxiety and worry that impacts their state of mind.
- Anxiety and worry impact mental health much more among the older population than the younger ones.
Bharatmala Pariyojana:

Nearly 50% of the Bharatmala Pariyojana Phase-I, a flagship road network expansion program, has been completed as of 31st March 2024 and is expected to be completed by 2027-28.
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways’ Vision 2047 aims to provide high-speed corridors within 100-150 km of all citizens and enhance passenger convenience by developing world-class amenities.
- This vision serves as the basis for the Master Plan for highways and related infrastructure in India.
- Bharatmala Pariyojana is an umbrella programme launched under the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- The first-phase of Bharatmala was announced in 2017 and was to be completed by 2022, but it could not be completed due to slow implementation and financial constraints.
- Bharatmala, Sagarmala, dry/land ports, and other infrastructure projects have been incorporated under PM Gati-Shakti Plan to enhance connectivity and logistics efficiency.
- While Bharatmala project aims to improve road connectivity, enhancing freight and passenger movement, Sagarmala project focuses on modernising ports and promoting coastal shipping to boost trade and maritime activities.
- Bharatmala focuses on enhanced effectiveness of already built infrastructure, multi-modal integration, bridging infrastructure gaps for seamless movement and integrating National and Economic Corridors.
- It aims to develop about 26,000 km of economic corridors, along with the Golden Quadrilateral (GQ) and North-South and East-West (NS-EW) Corridors, to carry the majority of the freight traffic on roads.
- Inter-State Corridor and Feeder Routes: This would ensure first mile and last mile connectivity.
- About 8,000 km of interstate corridors and about 7,500 km of feeder routes have been identified for improving the effectiveness of these corridors.
- The Bharatmala project is being funded from various sources including Central Road and Infrastructure Fund cess, remittances, additional budgetary support, monetisation of national highways, Internal and Extra Budgetary Resources, and private sector investment.
National Space Day 2024:

India celebrated its first National Space Day on 23rd August 2024. It is celebrated to mark the safe and soft landing of Vikram Lander of Chandrayaan-3 mission, on the lunar surface on 23rd August 2023.
- Additionally, the recent findings based on Chandrayaan-3, represent the first analysis of the Moon’s southern topsoil composition and support the hypothesis of the sea of molten material on the lunar surface.
- National Space Day Celebrated on 23rd August, commemorates India’s space achievements, particularly Chandrayaan-3’s success.
- With the launch of Chandrayaan-3 in 2023, India became the fourth nation to successfully land on the Moon and the first to reach its southern polar region.
- It highlights India’s space exploration capabilities and aims to inspire future generations to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM), contributing to India’s ongoing space endeavours.
- Theme for 2024: The theme for National Space Day 2024 is ‘Touching Lives while Touching the Moon: India’s Space Saga’.
Jan Poshan Kendras:

The Indian government has launched a pilot project to rename and transform 60 Fair Price Shops (FPS) across Gujarat, Rajasthan, Telangana, and Uttar Pradesh into “Jan Poshan Kendras.”
- This move aims to enhance the nutritional offerings available to beneficiaries under the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PMGKAY).
- The project also includes the introduction of several new digital tools and support systems designed to enhance transparency and operational efficiency.
- Under this initiative, FPSs will begin selling additional items beyond subsidised grains to address the income challenges faced by ration dealers while improving the nutritional offerings available to beneficiaries under the PMGKAY.
- Currently, 0.54 million FPSs distribute, on average, 60-70 million tonnes of food grain annually under PMGKAY, free of cost, to over 800 million beneficiaries.
- The government sees scope for generating additional income from FPS as a large number of people visit these outlets to get their monthly entitlement of grains.
- Further, the government aims to convert around 100,000 fair price shops into “nutri-hubs” in the next three years.
- These Kendras will provide a diverse array of nutrition-rich food items, including pulses and dairy products, in addition to subsidised grains.
- 50% of the space in these Kendras will be allocated for storing nutritional products, while the remaining space will be used for other household items.
- FPSs will receive loans and invoice financing from the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) to support their transformation and operations.
- The initiative includes collaborations with organisations like AMUL for dairy products and Business-to-Business eCommerce (or eB2B) platforms such as Udaan and Jumbotail for sourcing materials.
- The initiative includes the launch of several new digital tools:
- FPS Sahay: An application providing paperless, presence-less, and collateral-free financing for ration dealers.
- Mera Ration App 2.0: An app designed to give consumers information about the public distribution system.
- Quality Management System (QMS): It is a digital application for integration of Quality Control labs in the Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD) and Food Corporation of India (FCI).
PROMPT, DRIPS And JALVIDYUT : Union Minister Of Power

The Union Minister of Power has launched 3 online platforms – PROMPT, DRIPS and JALVIDYUT DPR to enhance the efficiency, transparency, and effectiveness of the power sector. The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) assisted by NTPC has developed these online portals.
Portal for Online Monitoring of Projects-Thermal (PROMPT):
- It will enable real-time online tracking and analysis of thermal power projects under construction in India.
- This platform is designed to swiftly identify and address issues that cause delays in the construction of thermal power plants
Disaster Resilient Infrastructure for Power Sector (DRIPS):
- This online portal has been developed to swiftly identify power disruptions across the country caused by natural disasters such as cyclones, earthquakes, and floods.
- It will connect designated nodal officers across the power sector to ensure rapid restoration in affected areas.
JAL VIDYUT DPR:
- The JAL VIDYUT DPR (Monitoring Survey and Investigation Activities of Hydroelectric Projects and Pumped Storage Projects) platform will offer real-time updates on the status of hydroelectric pumped storage projects under construction across the country.
- This platform aims to enhance management and coordination in the construction of these plants.
- The Central Electricity Authority (CEA) was established in 1951 under the Electricity (Supply) Act of 1948 and later replaced by the Electricity Act of 2003.
- It operates under the Ministry of Power and prepares the National Electricity Plan. It also approves new hydroelectric power plants, and carries out various other functions.
- It is composed of a Chairman and 6 full-time members by the Central Government.
- It is headquartered at New Delhi.
Gentoo Penguin:

Sphen, the famous gentoo penguin known for his same-sex partnership with Magic, has died at the age of 11 in Australia.
- Scientific name: Pygoscelis papua
- It is found exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere, primarily between 45° and 65° south latitude.
- It inhabits the Antarctic Peninsula and several sub-Antarctic islands, with a significant population on the Falkland Islands in the South Atlantic Ocean.
- It is notable for the two white wedges around their eyes, connected by a line across the head, which distinguish them from other penguin species.
- Their heads are mostly black, adorned with small flecks of white feathers.
- It is typically found along shorelines, which enables the Penguins to quickly access food sources while staying close to their nests.
- They use a range of vocalisations, from honks to brays, which help partners identify each other within the colony.
- Conservation status: This species is classified as “Least Concern” on the IUCN Red List, indicating a stable population.
Tagging Of Horseshoe Crabs:

The Zoological Survey of India and Odisha Forest Department have begun tagging horseshoe crabs to study their population, habitat, and migratory routes.
- Horseshoe Crabs are ancient marine arthropods, often referred to as “living fossils,” that inhabit shallow coastal waters with soft sandy or muddy bottoms.
- They are closely related to scorpions and spiders, not crabs, despite their name.
- These creatures spawn primarily on intertidal beaches during summer-spring high tides.
- Species of Horseshoe Crabs:
- American Horseshoe Crab (Limulus polyphemus): Found along the eastern coast of the USA and in the Gulf of Mexico; listed as Vulnerable by the IUCN.
- Tri-spine Horseshoe Crab (Tachypleus tridentatus): Endangered species found in the Indo-Pacific region.
- Coastal Horseshoe Crab (Tachypleus gigas): An Indo-Pacific species found in coastal waters of India, Southeast Asia, China, and Japan.
- Mangrove Horseshoe Crab (Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda): Found in the Sundarbans mangroves of West Bengal and other parts of the Indo-Pacific.
- India hosts two species: Tachypleus gigas and Carcinoscorpius rotundicauda. These species are predominantly found along the northeastern coast, particularly in Odisha and West Bengal.
- Conservation Status:
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 (India): Horseshoe crabs are listed under Schedule IV, offering them legal protection
- IUCN Red List: American Horseshoe Crab: Vulnerable
- Tri-spine Horseshoe Crab: Endangered
- Coastal and Mangrove Horseshoe Crabs: Currently listed as Data Deficient.
Nestlé Announces Laurent Freixe to Succeed Mark Schneider as CEO:
Nestlé, the global food and beverage giant, has announced a pivotal change in its top leadership. This transition comes at a crucial time for the company as it navigates through various market challenges.
11th Puthiya Thalaimurai Tamilan Awards:
The 11th edition of the Puthiya Thalaimurai Tamilan Awards recently honored outstanding individuals across various fields, recognizing both seasoned professionals and emerging talents. This prestigious event showcased the rich diversity of accomplishments in Tamil Nadu and beyond
Bandhan Bank Launches Avni Savings Account for Women:
Bandhan Bank, celebrating its Foundation Day, introduced Avni, a savings account tailored specifically for women. This launch is accompanied by the Bandhan Bank Delights loyalty program, designed to offer rewards, discounts, and exclusive benefits.
Odisha CM Majhi Launches Subhadra Scheme:
Odisha Chief Minister Mohan Majhi has unveiled the Subhadra scheme, a significant initiative under the BJP government. The scheme promises ₹50,000 to one crore women aged 21 to 60 over the next five years, with a total budget allocation of ₹55,825 crore.
Replenishment Of Balances In FASTag:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has updated its e-mandate framework to include the auto-replenishment of balances in FASTag and the National Common Mobility Card (NCMC). Under the new rules, these auto-replenishment transactions, which occur when balances fall below a customer-defined threshold, will no longer require a pre-debit notification.
Global Property Price Index:
Manila ranked first with a 26 per cent annual rise during the quarter. Mumbai and Delhi are at the second and third positions, respectively, among 44 cities globally in annual price rise of prime residential properties during the June quarter, Knight Frank said in a report.
Goldman Sachs Lowers India’s 2024 and 2025 GDP Growth Forecasts:
Goldman Sachs has revised India’s GDP growth forecasts for 2024 and 2025, anticipating slower expansion due to reduced government expenditure and other economic factors. The bank now projects a growth rate of 6.7% for 2024 and 6.4% for 2025, down by 20 basis points each from previous estimates.
Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd:
Tata Power Solar Systems Ltd (TPSSL) has signed an agreement with ICICI Bank to provide financing for solar units to residential and corporate customers. As part of the agreement, the customers can avail themselves of loans up to Rs 90 lakh with collateral-free options and tenure extending up to 5 years.
GoI Approves Unified Pension Scheme for Government Employees:
To enhance retirement benefits for government employees, the Union Cabinet on Saturday approved the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS). This new scheme is set to benefit approximately 23 lakh government employees and will serve as an alternative to the existing National Pension System (NPS).
RBI Governor Secures:
Prime Minister of India recently congratulated Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor Shaktikanta Das for receiving an ‘A+’ rating in the Global Finance Central Banker Report Cards 2024, marking his second consecutive achievement of this high honour. Shaktikanta Das is one of only three central bankers globally to receive an “A+” rating, alongside Denmark’s Christian Kettel Thomsen and Switzerland’s Thomas Jordan.
RBI Intensifies Scrutiny on P2P Lending Platforms:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has intensified its regulatory scrutiny on Non-Banking Financial Company–Peer to Peer Lending Platform (P2P) lending platforms following the discovery of multiple regulatory violations, including high levels of non-performing assets (NPAs). RBI identified violations, including unauthorised deposit acceptance and unusually high balances in escrow accounts raised concerns during RBI’s review.




