Today Current Affairs: 25th January 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Farmer law:

Farmers insist that the laws be repealed. Over the years, Parliament has repealed several laws and there have also been precedents of the government not bringing law into force for several years after it has been passed.
Bringing/Repealing a Law:
- Parliament has the power to make a law and to remove it from the statute books (a law can be struck down by the judiciary if it is unconstitutional).
- A Bill is a draft proposal, which needs to be passed in the Lower and Upper House, and only after the President gives his assent, it becomes an Act.
- Repeal means to revoke, abrogate or cancel particularly a statute. Any statute may repeal any Act in whole or in part, either expressly or impliedly by enacting matters contrary to and inconsistent with the prior legislation.
President’s Assent:
- Article 111 of the Constitution specifies that the President can either sign off on the Bill or withhold his consent.
- A Bill is sent to Parliament for reconsideration if the President withholds his assent on it. And if Parliament sends it back to the President, he has no choice but to approve it. Thus, the President enjoys only a ‘suspensive veto’.
Making Law Operational:
- Rules & Regulation: Parliament gives the government the responsibility of making rules and regulations for efficient functioning of the Act.
- The government not only has the power to make rules but can also suppress rules made by it earlier.
- If the government does not make rules and regulations, a law or parts of it will not get implemented.
- The Benami Transactions Act of 1988 is an example of a complete law remaining unimplemented in the absence of regulations.
Time Period: Parliament has recommended that the government make rules within six months of passing a law.
- A parliamentary committee has observed that this recommendation is “being followed in breach by various ministries”.
Inequality Virus Report by Oxfam International:

The Inequality Virus Report, released by Oxfam International, has found that the Covid pandemic deeply increased the existing inequalities in India and around the world.
- The report states that Covid has the potential to increase economic inequality in almost every country at once – the first time this has happened since records began over a century ago.
Impact of the Pandemic on Rich vis-a-vis Poor:
- India introduced one of the earliest and most stringent lockdowns in the face of the pandemic and its enforcement brought the economy to a standstill, triggering unemployment, hunger, distress migration, and untold hardship in its wake.
- The rich were able to escape the pandemic’s worst impact; and while the white-collar workers isolated themselves and worked from home, a majority of the not-so-fortunate Indians lost their livelihood.
- The wealth of Indian billionaires increased by 35% during the lockdown and by 90% since 2009 to USD 422.9 billion, ranking India sixth in the world after the USA, China, Germany, Russia and France.
Impact on Informal Sector:
- India’s large informal workforce was the worst hit as it made up 75% of the 122 million jobs lost.
- Informal workers had relatively fewer opportunities to work from home and suffered more job loss compared to the formal sector.
- The 40-50 million seasonal migrant workers, typically engaged working in construction sites, factories etc. were particularly distressed.
Impact on Education:
- Over the past year as education shifted online, India saw the digital divide worsening inequalities.
- On the one hand, private providers experienced exponential growth yet, on the other, just 3% of the poorest 20% of Indian households had access to a computer and just 9% had access to the internet.
- It noted that the long disruption of schooling risked doubling the rate of out of school, especially among the poor.
Health Inequalities:
- Oxfam found that since India does not report case data desegregated by socio-economic or social categories, it is difficult to gauge the distribution of the disease amongst various communities.
- India currently has the world’s second-largest cumulative number of Covid-19 positive cases and globally, the poor, marginalized and vulnerable communities have higher rates of Covid-19 prevalence.
- The spread of disease was swift among poor communities, often living in cramped areas with poor sanitation and using shared common facilities such as toilets and water points.
Sanitation Facility:
- Only 6% of the poorest 20% households had access to non-shared sources of improved sanitation, compared to 93% of the top 20% households in India.
- In terms of caste, just 37.2% of Scheduled Castes (SCs) households and 25.9% of Scheduled Tribes (STs) households had access to non-shared sanitation facilities, compared to 65.7% for the general population.
Gender Disparities:
Employment:
- The unemployment rate among women rose from an already high 15% before Covid to 18%.
- This increase in unemployment of women can result in a loss to India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of about 8% or USD 218 billion.
- Of the women who retained their jobs, as many 83% were subjected to a cut in income according to a survey by the Institute of Social Studies Trust.
Health:
- Beyond income and job losses, poorer women also suffered healthwise because of the disruption in regular health services and Anganwadi centers.
- It is predicted that the closure of family planning services will result in 2.95 million unintended pregnancies, 1.80 million abortions (including 1.04 million unsafe abortions), and 2,165 maternal deaths.
Domestic Violence:
- The pandemic also fueled domestic violence against women. As of November 2020, cases of domestic violence rose by almost 60% over the past 12 months.
Green Bonds:

As per a recent study by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the cost of issuing green bonds has generally remained higher than other bonds in India, largely due to asymmetric information.
Green Bonds:
- A green bond is a debt instrument with which capital is being raised to fund ‘green’ projects, which typically include those relating to renewable energy, clean transportation, sustainable water management etc.
- A bond is a fixed income instrument that represents a loan made by an investor to a borrower (typically corporate or governmental).
- Bonds traditionally paid a fixed interest rate (coupon) to investors.
Growth:
- In 2007, green bonds were launched by few development banks such as the European Investment Bank and the World Bank. Subsequently, in 2013, corporates too started participating, which led to its overall growth.
Regulation:
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has put in place disclosure norms for issuance and listing of green bonds.
Benefits:
- Enhances Reputation: Green bonds enhance an issuer’s reputation, as it helps in showcasing their commitment towards sustainable development.
- Fulfillment of Commitments: Ability to meet commitments, for signatories to climate agreements and other green commitments.
- India’s Intended Nationally Determined Contribution (INDC) document puts forth the stated targets for India’s contribution towards climate improvement and following a low carbon path to progress.
- Raised at Lower Costs: Green bonds typically carry a lower interest rate than the loans offered by the commercial banks.
- With an increasing focus of foreign investors towards green investments, it could help in reducing the cost of raising capital.
- Sunrise Sectors: These green bonds have been crucial in increasing financing to sunrise sectors like renewable energy, thus contributing to India’s sustainable growth.
Details of RBI’s Recent Study:
- Current Share:
- Green bonds constituted only 0.7% of all the bonds issued in India since 2018.
- However, bank lending to the non-conventional energy (renewable energy) constituted about 7.9% of outstanding bank credit to the power sector, as of March 2020.
- Most of the green bonds in India are issued by the public sector units or corporates with better financial health.
Birds of the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve, released by the ZSI:

The publication, Birds of the Sundarban Biosphere Reserve, released by the ZSI, not only documents the avifauna of the Sunderbans but also serves as a comprehensive photographic field guide for the region.
- The scientists said of the 428 birds listed, some, like the masked finfoot and the Buffy fish owl, are recorded only from the Sunderbans.
- The area is home to nine out of 12 species of kingfishers found in the country as well rare species such as the Goliath Heron and the spoon-billed sandpiper.
- The Indian Sunderbans, which covers 4,200 sq. km, also includes the Sunderban Tiger Reserve of 2,585 sq. km — home to about 96 royal Bengal tigers (as per the last census in 2020).
- It is a world heritage site and a Ramsar site (a wetland site designated to be of international importance).
- India has over 1,300 species of birds and if 428 species of birds are from the Sunderbans, it means that one in every three birds in the country is found in the unique ecosystem.
National Voters Day:

The Election Commission of India is celebrating the 11th National Voters Day on 25th January 2021.
- The National Voters’ Day has been celebrated on January 25 every year since 2011, all across the country to mark the foundation day of Election Commission of India, i.e. 25th January 1950.
- The main purpose of the NVD celebration is to encourage, facilitate and maximize enrolment, especially for the new voters.
- The theme for this year’s NVD, ‘Making Our Voters Empowered, Vigilant, Safe and Informed’.
- During the event, the Honourable President of India will confer the National Awards for the year 2020-21 and launch ECI’s Web Radio:‘Hello Voters’.
ECI’s Web Radio:‘Hello Voters’:
- This online digital radio service will stream voter awareness programs.
- It will be accessible through a link on the Election Commission of India website.
- The programming style of Radio Hello Voters has been envisaged to match that of popular FM radio services.
- It will provide information and education on electoral processes through songs, drama, discussions, sports, stories of elections, etc. in Hindi, English, and regional languages from all over the country.
The National Awards for the Best Electoral Practices:
- These will be conferred on State and District level officers for their outstanding performance in the conduct of elections in different spheres such as IT initiatives, Security Management, Election Management during COVID-19, Accessible Election, and contribution in the field of voter awareness and outreach.
- National Awards will also be given to important stakeholders like national icons, CSOs, and media groups for their valuable contribution towards voters’ awareness.
National Girl Child Day:
The National Girl Child Day is celebrated in India every year on January 24.
- It was started by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 2008.
Objectives of the day
-
- To spread awareness about Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) Scheme Which was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in January 2015 at Panipat in Haryana.
- Generating awareness on the issue of declining Child Sex Ratio (CSR) and create a positive environment around valuing the girl child.
- National Education Policy (NEP)-2020has introduced the “Gender Inclusion Fund for targeting the development of girl child.
- The fund will focus on ensuring 100% enrolment of girls in schooling and a record participation rate in higher education.
2K TIME TRIAL:

The two-kilometer time trial — set at eight minutes and 15 seconds for fast bowlers and 8:30 for batsmen, spinners and wicketkeepers — has become mandatory for India’s centrally-contracted cricketers.
- On a standard athletics track, the distance is covered in five laps of 400 metres each.
- The timings can be measured with a stop-watch or an electronic clock.
- The 2k time trial is a speed-endurance test, according to Ramji Srinivasan, the 2011 World Cup-winning Indian team’s strength and conditioning coach.
- If an athlete meets the standard set for the time trial, he or she can be termed ‘fit’. Another benefit of the time trial is that it will help to redraw the fitness schedule of a cricketer if needed.
- According to Srinivasan, Sri Lanka, South Africa, and New Zealand also put cricketers through the time-trial test.
- In the Yo-Yo test, two cones are placed 20 metres apart.
- At the first beep, the athlete starts and must reach the cone at the other end before the second beep, and then turn and run back to cross the starting point before the third beep.
- As the Yo-Yo test level gets tougher, the frequency of the beeps increases and the number of shuttles (up and down runs) also goes up before a player gets a short break.
- Yo-Yo tests have been used in football for ages.
Assam government is setting up three-degree colleges in the Bodo region:
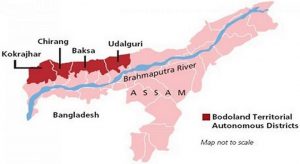
The Union Home Minister Amit Shah said the Assam government is setting up three-degree colleges in the Bodo region. Tributes are being paid to Shri Upendra Nath Brahma by opening an institute in his name.
- Upendranath Brahma (1956 – 1990) was an Indian Bodo social activist and the former president of All Bodo Students’ Union.
- Brahma was born in Boragari village of Dotma, a small township at the Kokrajhar district of Assam.
- The title of Bodofa (Guardian of Bodos) was posthumously conferred upon Brahma on 8 May 1990 in recognition of his vision and leadership. His life is celebrated each year on the anniversary of his death, which is now called Bodofa Day.
- The Bodo is the largest ethnolinguistic group in Assam.
- They are concentrated mainly in the Bodoland Territorial Region of Assam.
Limited Liability Partnership (LLP):

The Company Law Committee (CLC) has recommended that 12 offences under the Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) Act 2008 be decriminalised and that LLPs be allowed to issue Non-Convertible Debentures (NCDs) to raise funds with the aim of improving ease of doing business for LLP firms.
- The Company Law Committee (CLC) was set up by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs in September 2019 to promote Ease of Living in the country by providing Ease of Doing Business to law-abiding corporates and fostering improved corporate compliance for stakeholders at large.
Company Law Committees (CLC’s) Recommendations:
- Decriminalisation of Offences:
- Several offences related to timely filings, including annual reports and filings on changes in partnership status of the LLP, not related to fraud have been recommended for decriminalisation.
- While none of these provisions recommended for decriminalisation currently have prison terms as a possible punishment, the committee has recommended that companies be required to pay penalties for non-compliance, instead of fines which are imposed after a partner or the LLP is found guilty of misconduct by a court.
- Risk Involved in Imposing Fines:
- The Committee has noted that there is a risk of a convicted person being disqualified or becoming ineligible for various posts in the case of fines imposed by courts, which would not be the case for penalties imposed by an appropriate authority.
- Authority to Levy Penalties:
- The Registrar of Companies (ROC) would have the authority to levy penalties for any contravention of provisions of the LLP Act.
- ROC appointed under Section 609 of the Companies Act covering the various States and Union Territories are vested with the primary duty of registering companies and LLPs floated in the respective states and the Union Territories.
- Permission to Issue NCDs:
- LLPs which are currently not allowed to issue debt securities should be permitted to issue NCDs to facilitate raising of capital and financing operations.
- Beneficiaries:
- The move is likely to benefit startups and small firms in sectors which require heavy capital investment.
Limited Liability Partnership
- It is a partnership in which some or all partners (depending on the jurisdiction) have limited liabilities.
- In an LLP, each partner is not responsible or liable for another partner’s misconduct or negligence.
- The LLP can continue its existence irrespective of changes in partners. It is capable of entering into contracts and holding property in its own name.
- The LLP is a separate legal entity, is liable to the full extent of its assets but liability of the partners is limited to their agreed contribution in the LLP.
Beti Bachao Beti Padhao Scheme:
The Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) Scheme has recently completed 6 years of its launch in 2015. On the occasion of National Girl Child Day (24th January), the performance of the BBBP scheme was discussed.
- The National Girl Child Day was started by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 2008.
About the Beti Bachao Beti Padhao (BBBP) Scheme:
Main Objectives:
- Prevention of gender-biased sex-selective elimination.
- Ensuring survival & protection of the girl child.
- Ensuring education and participation of the girl child.
- Protecting rights of Girl child.
Multisectoral Nationwide Campaign:
- BBBP is a national campaign and focussed multisectoral action in 100 selected districts low in Child Sex Ratio (CSR), covering all States and UTs.
- This is a joint initiative of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and Ministry of Human Resource Development.
Performance of BBBP Scheme:
- Sex Ratio at Birth:
- Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB) has improved by 16 points from 918 (2014-15) to 934 (2019-20), as per the Health Management Information System (HMIS) data.
- Out of 640 districts covered under BBBP, 422 districts have shown improvement in SRB from 2014-15 to 2018-2019.
- Notable Examples:
- Mau (Uttar Pradesh) from 694 (2014-15) to 951 (2019-20),
- Karnal (Haryana) from 758 (2014-15) to 898 (2019-20),
- Mahendergarh (Haryana) from 791 (2014-15) to 919 (2019-20), etc.
- Health:
- ANC Registration: Percentage of 1st Trimester ANC (AnteNatal Care) Registration has shown an improving trend from 61% in 2014-15 to 71% in 2019-20.
- Institutional Deliveries: Percentage of Institutional Deliveries has shown an improving trend from 87% in 2014-15 to 94% in 2019-20.
- Education :
- Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER): GER of girls in the schools at the secondary level has improved from 77.45 (2014-15) to 81.32 (2018-19) as per Unified District Information System for Education (UDISE) provisional data.
Toilet for girls: The percentage of schools with functional separate toilets for girls has shown improvement from 92.1% in 2014-15 to 95.1% in 2018-19.
- The BBBP scheme has been able to bring the focus on the important issues of female infanticide, lack of education amongst girls, and deprivation of their rights on a life cycle continuum.
- BetiJanmotsav is one of the key programs celebrated in each district.
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar:

32 children have been awarded the ‘Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar’ for their exceptional abilities and outstanding accomplishments.
- The Awards are given by the President of India in the week preceding Republic Day (26th January) every year.
Two Categories: The Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar is given under two categories:
-
- Bal Shakti Puraskar, and
- Bal Kalyan Puraskar.
Bal Shakti Puraskar:
- It is given by the Government of India every year to recognize exceptional achievements of children in various fields i.e., innovation, scholastic achievements, social service, arts & culture, sports and bravery.
- Eligibility: A child who is an Indian Citizen and residing in India and is between 5-18 years of age.
- Award: A medal, a cash prize of Rs. 1,00,000, book vouchers worth Rs.10,000, a certificate and citation.
- It was instituted in 1996 as the National Child Award for Exceptional Achievement, renamed from 2018 as Bal Shakti Puraskar.
PLI Scheme:

Approval accorded under PLI Scheme for Promotion of Domestic Manufacturing of critical Key Starting Materials (KSMs)/ Drug Intermediates and Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs).
Indian pharmaceutical industry:
- It is the 3rd largest in the world by volume.
- It has high market presence in several advanced economies such as the US and EU. The industry is well known for its production of affordable medicines, particularly in the generics space.
- However the country is significantly dependent on the import of basic raw materials, viz., Bulk Drugs that are used to produce medicines.
About the PLI scheme:
- To make India a manufacturing hub, the government had initially announced the PLI scheme for mobile phones, pharma products, and medical equipment sectors.
- Notified on April 1, 2020, as a part of the National Policy on Electronics.
- It proposes a financial incentive to boost domestic manufacturing and attract large investments in the electronics value chain.
- In November 2020, the Union Cabinet gave its approval to introduce the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme in 10 more sectors for enhancing India’s manufacturing capabilities and exports (Atmanirbhar Bharat).
Commission for Air Quality Management:

The Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in NCR and adjoining areas has begun the process of setting up a Decision Support System (DSS) having a web, GIS and multi-model based operational and planning decision support tool.
- This tool will help immensely in capturing the static and dynamic features of the emissions from various sources.
About the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM):
- The Commission for Air Quality Management was formed by an ordinance in October 2020, the “Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) in National Capital Region and Adjoining Areas Ordinance 2020”.
Composition:
- Chairperson: To be chaired by a government official of the rank of Secretary or Chief Secretary.
- It will be a permanent body and will have over 20 members.
- The Commission will be a statutory authority.
- The Commission will supersede bodies such as the central and state pollution control boards of Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, UP and Rajasthan.
- It will have the powers to issue directions to these state governments on issues pertaining to air pollution.
Exclusive jurisdiction over the NCR, including areas in Haryana, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan, in matters of air pollution, and will be working along with CPCB and ISRO, apart from the respective state governments.
Parker Solar Probe:

Parker Solar Probe Marks Seventh Successful Swing around the Sun.
- None are closer than Parker Solar Probe, which passed just 8.4 million miles (13.5 million kilometers) from the Sun’s surface while flying at 289,932 miles per hour on Jan 17.
- Now just over two years into its seven-year mission, the Parker Solar Probe spacecraft will eventually travel within 4 million miles of the Sun’s surface.
About the mission:
- NASA’s historic Parker Solar Probe mission will revolutionize our understanding of the sun, where changing conditions can propagate out into the solar system, affecting Earth and other worlds.
- Parker Solar Probe will travel through the sun’s atmosphere, closer to the surface than any spacecraft before it, facing brutal heat and radiation conditions — and ultimately providing humanity with the closest-ever observations of a star.
- In order to unlock the mysteries of the sun’s atmosphere, Parker Solar Probe will use Venus’ gravity during seven flybys over nearly seven years to gradually bring its orbit closer to the sun.
- The spacecraft will fly through the sun’s atmosphere as close as 3.9 million miles to our star’s surface, well within the orbit of Mercury and more than seven times closer than any spacecraft has come before.
- The primary science goals for the mission are to trace how energy and heat move through the solar corona and to explore what accelerates the solar wind as well as solar energetic particles.
Parker Solar Probe objectives:
- Trace the flow of energy that heats and accelerates the solar corona and solar wind.
- Determine the structure and dynamics of the plasma and magnetic fields at the sources of the solar wind.
- Explore mechanisms that accelerate and transport energetic particles.
FATF blacklisting:

Pakistan might be pushed into the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF) ‘blacklist’ next month as it continues to finance and tolerate terrorist organizations.
- According to a report, terrorist organisations, such as Jamaar-ud-Dawa (JuD) and Jaish-e-Muhammed (JeM), continue to operate with impunity in Pakistan.
FATF Blacklist:
- It is a list of countries that the intra-governmental organisation considers non-cooperative in the global effort to combat money laundering and the financing of terrorism.
- In October, the FATF decided that Pakistan will continue to be on its greylist and asked it to continue to work on implementing an action plan to address its strategic deficiencies.
- Pakistan is on the FATF’s grey list since June 2018 and the government was given a final warning in February 2020 to complete the 27 action points by June in the same year.
- The FATF extended the June deadline to September due to the spread of coronavirus that disrupted the FATF plenary meetings.
About FATF:
- The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an inter-governmental body established in 1989 on the initiative of the G7.
- It is a “policy-making body” that works to generate the necessary political will to bring about national legislative and regulatory reforms in various areas.
- The FATF Secretariat is housed at the OECD headquarters in Paris.
Roles and functions:
-
- Initially, it was established to examine and develop measures to combat money laundering.
- In October 2001, the FATF expanded its mandate to incorporate efforts to combat terrorist financing, in addition to money laundering.
- In April 2012, it added efforts to counter the financing of proliferation of weapons of mass destruction.




