Today’s Current Affairs: 25th June 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Gender-Neutral School Textbooks:

Kerala’s government is promoting gender neutrality by revamping school textbooks to depict men and other family members participating in domestic chores, breaking traditional gender stereotypes.
- This initiative aims to foster inclusivity among children from an early age. New instructional materials, featuring fathers engaged in kitchen activities traditionally associated with women
- The initiative to revamp school textbooks and promote gender-neutral education depicts several ethical values:
- It Promotes gender equality by challenging traditional roles and stereotypes.
- It Encourages an inclusive outlook by representing diverse family dynamics.
- It Highlights the importance of shared household responsibilities.
- Fosters respect for all genders by depicting men and women as equal contributors.
- It Empowers children to question and reshape societal norms.
- It Advocates for fair treatment and opportunities for all genders in both public and private spheres.
Digital Payments Intelligence Platform : RBI

The RBI has formed a committee chaired by A.P. Hota to explore a proposal to set up a Digital Payments Intelligence Platform that will harness advanced technologies to mitigate payment fraud risks.
- Domestic payment frauds surged by 70.64% to Rs 2,604 crore in the six months ending March 2024, with the number of cases rising to 15.51 lakh from 11.5 lakh.
- The RBI also plans to increase the threshold for bulk deposits from Rs 2 crore to Rs 3 crore for commercial banks and small finance banks, with local area banks set at Rs 1 crore.
- It also allows banks flexibility in setting interest rates based on their needs and Asset-Liability Management (ALM) projections.
- The RBI plans to allow automatic balance replenishment for Fastag and NCMC under the e-mandate framework, exempting the need for a 24-hour pre-debit notification.
- The RBI plans to integrate UPI Lite into the e-mandate framework, enabling automatic reloads of the wallet when its balance drops below a user-set threshold, eliminating the need for extra authentication or pre-debit notifications.
- The Reserve Bank plans to update rules for exporting and importing
National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme:

The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister, has approved the proposal of the Ministry of Home Affairs for the Central Sector Scheme “National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme (NFIES)”.
- National Forensic Infrastructure Enhancement Scheme aims to enhance forensic infrastructure across the country by establishing off-campus laboratories of the National Forensic Sciences University in 28 States and all Union Territories.
Outlay and Duration: - The scheme has a total financial outlay of Rs. 2,254.43 crore during the period from 2024-25 to 2028-29.
- Components:
- Establishment of Campuses of the National Forensic Sciences University (NFSU) across the country.
- Establishment of Central Forensic Science Laboratories in the country.
- Enhancement of existing infrastructure of the Delhi Campus of the NFSU.
- It aims to address the shortage of trained forensic manpower, strengthening the capacity and capabilities of the National Forensic Sciences University.
- The establishment of new Central Forensic Science Laboratories across the country is intended to alleviate the caseload and pendency in the existing forensic laboratories.
- With the enactment of the New Criminal Laws, which mandates forensic investigation for offences involving punishment of 7 years or more, a significant increase in the workload of forensic science laboratories is expected.
- High-quality, trained forensic professionals are expected to contribute to an efficient criminal justice process, leveraging advancements in technology and evolving crime patterns.
- The scheme is intended to support the government’s objective of achieving a high conviction rate of more than 90%.
National Green Hydrogen Mission : In News

The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) has increased the yearly allocation of Green Ammonia for the fertiliser sector from 550,000 to 750,000 tonnes to meet rising demand, enhancing support for Green Hydrogen in India.
- India launched the National Green Hydrogen Mission (NGHM) in January 2023.
- The Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) is implementing the NGHM with a target to achieve a production capacity of 5 million tonnes per annum of Green Hydrogen in the country by the year 2030.
- The Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition (SIGHT) programme, under NGHM, provides incentives for the manufacturing of electrolysers and the production of green ammonia.
- Under NGHM a dedicated portal was launched to provide information on the mission and steps for developing the green hydrogen ecosystem in India.
- India has also released scheme guidelines for the use of Green Hydrogen in steel, transport, and shipping sectors.
- The Department of Science and Technology has initiated Hydrogen Valley Innovation Clusters to foster innovation and promote the green hydrogen ecosystem in India.
High Court Struck Down Bihar 65% Quota Rule:

The Patna High Court struck down the Bihar government’s decision to increase the reservation quota from 50% to 65% for Backward Classes (BC), Extremely Backward Classes (EBC), Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) in educational institutions and government jobs.
- This move by the Bihar government has raised important questions about the legal limits on reservation policies in India.
What is the Background of the High Court’s Ruling? - In November 2023, the Bihar government issued gazette notifications to raise the quota for deprived castes from 50% to 65%.
- This decision was taken following a caste-based survey report, which showed the need for increased representation of BC, EBC, SC and ST communities.
- The Bihar Assembly unanimously passed the Bihar Reservation Amendment Bill in November 2023 to implement this 65% quota.
- A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) was filed challenging the Bihar government’s decision to increase reservations beyond 50%.
- The Patna High Court ruled that the 65% quota violated the 50% limit set by the Supreme Court in the Indira Sawhney case (1992).
- The court argued that the state government’s decision was not based on “adequate representation” in government jobs, but on the proportional population of these communities.
- The court also noted that together with the 10% Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) quota, the bill has pushed total reservation to 75%, which is unconstitutional.
Reciprocal Exchange Of Logistics Agreement:

The India-Russia mutual logistics agreement named the Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement (RELOS) is now ready for finalisation.
- It will facilitate military cooperation between India and Russia, including joint exercises, training, and disaster relief efforts.
- The Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement (RELOS) between India and Russia is a significant administrative arrangement that will enhance military cooperation between the two nations.
- This agreement is designed to streamline military logistics support, making joint operations and long-distance missions more efficient and cost-effective for both India and Russia.
Indus Water Treaty:
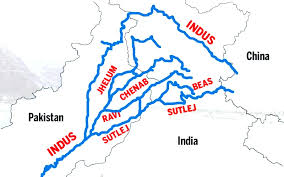
A Pakistani delegation recently arrived in Jammu as part of ongoing discussions concerning the 1960 Indus Water Treaty (IWT).
- Indus Water Treaty (IWT) is a treaty signed between India and Pakistan regulating the use and distribution of the Indus River system.
- It was signed by then-Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and former Pakistan President Ayub Khan in 1960.
- The treaty was brokered by the World Bank, which too is a signatory to the treaty.
- The pact sought to divide the water of the Indus River and its tributaries (Sutlej, Beas, Ravi, Jhelum, and Chenab) equitably among the two countries.
- Under the treaty, water from three eastern rivers, Beas, Ravi and Sutlej, was allocated to India, and water from the three western rivers – Chenab, Indus and Jhelum were allocated to Pakistan.
- Pakistan roughly got 80% of the water in the Indus drainage system.
- The treaty also permits both countries to use the other’s rivers for certain purposes, such as small hydroelectric projects that require little or no water storage.
- The treaty is overseen by the Permanent Indus Commission (PIC), a bilateral body with commissioners from both countries tasked with implementing and managing treaty provisions, and resolving any questions, differences, or disputes that may arise.
- The World Bank’s role is to appoint a neutral expert in case of ‘technical’ differences, failing which the differences escalate to a dispute for international arbitration.
Kolar Gold Fields : Reviving Gold Mining

The Karnataka government recently cleared a proposal of the Centre for reviving gold mining and auctioning of 13 tailing dumps at Kolar Gold Fields (KGF) by the Bharat Gold Mines Ltd. (BGML).
- Kolar Gold Fields (KGF) is a mining area in the Kolar District of Karnataka, 100 km from Bengaluru.
- It is estimated that gold has been mined in KFG for over 2000 years.
- KGF’s modern success is generally attributed to the firm John Taylor & Sons, after John Taylor III took control of the mines in 1880 and established what was at one time the deepest and most productive gold mine in the world.
- KGF was the first Indian city to be electrified in 1902.
- At its peak, KGF was home to 30000 mine workers and their families and was a multiethnic community with experienced miners recruited from around the world.
- The mines were run by the company up until 1956, when they were taken over by the Government of Mysore, who employed John Taylor & Sons as mining consultants.
- Although the annual production in some years was more than 95 percent of India’s gold output, the mines declined and finally closed in 2001.
Stryker Armoured Infantry Combat Vehicles:

India and the United States are in advanced talks for the joint manufacture of the latest generation of Stryker armoured infantry combat vehicles (ICVs).
- The Stryker is a family of eight-wheel-drive combat armoured infantry combat vehicles (ICVs).
- It is jointly developed by General Dynamics Land Systems (GDLS) Canada and the General Dynamics Land Systems Division in the United States.
- It was the first new military vehicle inducted into US Army service since the Abrams tank in the 1980s.
- The Stryker can formulate a quick response to insurgencies or war-like situations, moving much faster than tanks on paved roads, thereby getting infantry squads into the fight more swiftly.
- The Stryker vehicles have demonstrated a better chance of surviving against improvised explosive devices (IEDs) compared to other light military vehicles.
- The Strykers can be transported via Chinook helicopters, which the Indian Air Force uses.
- It is a V-hull armoured infantry vehicle equipped with a 30 mm cannon and a 105 mm mobile gun.
- The Stryker hull is constructed from high-hardness steel.
- On top of this, the Stryker has a layer of ceramic tile armor, offering additional protection.
- It is manned by a two-person crew and can carry a nine-man infantry squad.
- It has a range of 483 kilometers and can reach a top speed of around 100 km/h.
New Plant Species: Discovered

Indian botanists and researchers have discovered two new species of plants from two bio-geographic hotspots of the country the Andaman and Nicobar islands and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Researchers discovered two new plant species namely Dendrophthoe longensis(from Andaman and Nicobar islands) and Petrocosmea arunachalense (from Arunachal Pradesh).
- Dendrophthoe longensis is an aerial stem-parasitic flowering plant species discovered from the Long Islands of middle Andamans.
- It was found on the specific host plant – Mango, Mangifera indicain the edge of evergreen forests, low land areas of tropical forests.
- The species is from the family Mistletoe – a group of hemi-parasitic flowering plants which exhibit a suite of remarkable adaptations associated with the hemi-parasitic habitat.
- The species is sparsely scattered and confined to a few localities of Long Island.
- Aerial stem-parasitic flowering mistletoe plants are under great pressure due to destruction of natural habitat and other anthropogenic activities especially timber harvesting of host tree species, developmental works which are causing population declines worldwide.
- Petrocosmea arunachalense is a very small herb and the researchers located it inside a cave indicating that the species requires less sunlight
- The species is completely white with purple blotch and the plant has a hairy texture.
- It is only the second known species from the genus Petrocosmea in India.
Intergovernmental Platform On Biodiversity And Ecosystem Services:

The Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) has been selected for the 2024 Blue Planet Prize.
- Intergovernmental Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services is an intergovernmental organisation established in 2012.
- It aims to strengthen the science-policy interface for biodiversity and ecosystem services for the conservation and sustainable use of biodiversity
- It provides policymakers with objective scientific assessments about the state of knowledge regarding the planet’s biodiversity, ecosystems and the benefits they provide to people, as well as the tools and methods to protect and sustainably use these vital natural assets.
- This independent body was inspired by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment.
- It is not a United Nations body. However, at the request of the
- IPBES Plenary and with the authorisation of the UNEP Governing Council in 2013, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) provides secretariat services to IPBES.
- India is a member country of this organisation.
- The governing body of IPBES (Plenary )– made up of the representatives of IPBES member States – usually meets once per year.
- Secretariat: It is located in Bonn, Germany
UNESCO Creative Cities Network:

Kozhikode, a city in north Kerala celebrated for its rich cultural heritage, has been officially declared as India’s first UNESCO City of Literature under the UNESCO Creative Cities Network.
- UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) was created in 2004 to promote cooperation with and among cities that have identified creativity as a strategic factor for sustainable urban development.
- Almost 300 cities around the world currently make up this network.
- Objective is placing creativity and cultural industries at the heart of their development plans at the local level and cooperating actively at the international level.
- UNESCO designates the creative cities in seven fields:craft, folk art, media arts, film design, gastronomy, literature, and music.
- Every year, UNESCO seeks applications from various cities across the globe to put them under its UCCN project.
- The applications in India are routed through the Ministry of Culture.




