Today’s Current Affairs: 27th May 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
What Is Wind Shear?
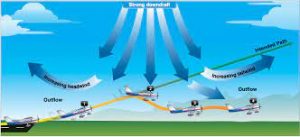
The concept of wind shear has gained increased attention due to its crucial role in determining whether a storm intensifies into a destructive hurricane.
- Wind shear is a meteorological phenomenon that refers to a sudden change in wind speed and/or wind direction over a relatively small distance.
- It is mainly of 2 types:
- Vertical Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly with increasing altitude.
Common examples include low-level jet streams and wind shear associated with thunderstorms. - Horizontal Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly over a horizontal distance.
- In this case, the wind might be blowing from the west at one spot, but then suddenly switch to blowing from the north just a bit further on.
- Common examples include frontal systems and sea breezes
- Vertical Wind Shear: Occurs when wind speed and/or direction changes rapidly with increasing altitude.
Gopi Thotakura : First Space Tourist From India

Gopi Thotakura, an India-born commercial pilot based in the US, became the first space tourist from India. She, along with five other space tourists, made a short recreational trip to space.
- Space tourism is a niche segment of the aviation industry that seeks to give tourists an experience of space travel for recreational, leisure, or business purposes.
- Space travel begins at about 100 km altitude from Earth, after crossing the Karman line, which is widely accepted as the boundary line separating the Earth’s atmosphere from outer space.
- Anything flying below this altitude is called an aircraft while those crossing this line get classified as a spacecraft.
- Types:
- Suborbital: Here, flights take passengers to the edge of space, where they can experience weightlessness for a few minutes.
- Orbital: Here, flights take passengers into orbit around the Earth. This gives them a chance to see the planet from space and experience weightlessness for a longer period of time.
- In 2021, Virgin Galactic’s founder Richard Branson and Blue Origin’s founder Jeff Bezos first rocketed into space on brief suborbital flights.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha Evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan Scheme:

The Ministry of Renewable Energy recently issued a warning to farmers on PM-KUSUM website against fake websites and mobile applications that provide fake online application forms and demand registration fees for installing solar water pumps under PM Kusum scheme.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme was launched in 2019 for de-dieselisation of the farm sector and enhancing the income of farmers.
- It is aimed at ensuring energy security for farmers in India, along with honouring India’s commitment to increase the share of installed capacity of electric power from non-fossil-fuel sources to 40% by 2030 as part of Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs).
- It aims to add Solar capacity of about 34,800 MW by March 2026 with the total Central Financial support of Rs 34,422 crore.
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE). It is being implemented by the designated departments of the State Government.
- Under the Scheme, a central government subsidy upto 30% or 50% of the total cost is given for the installation of standalone solar pumps and also for the solarization of existing grid-connected agricultural pumps.
- Further, farmers can also install grid-connected solar power plants up to 2MW, under the Scheme on their barren/fallow land.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:

A recent study challenges the perceived heart health benefits of fish oil supplements rich in omega-3 fatty acids, raising concerns about their impact on cardiovascular health.
- Fatty Acids are the building blocks of the fat in our bodies and in the food we eat.
- During digestion, the body breaks down fats into fatty acids, which can then be absorbed into the blood.
- Fatty acid molecules are usually joined together in groups of three, forming a molecule called a triglyceride.
- Triglycerides are also made in our bodies from the carbohydrates that we eat.
- The two main types of fatty acids are saturated fat and unsaturated fat.
- Saturated fats are sometimes known as “bad” or “unhealthy” fats because they increase your risk of certain diseases like heart disease and stroke.
- Unsaturated fats (polyunsaturated and monounsaturated) are considered “good” or “healthy” fats because they support your heart health when used in moderation.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- They are polyunsaturated fatsthat perform important functions in your body. Your body can’t produce the amount of omega-3s you need to survive.
- So, omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients, meaning you need to get them from the foods you eat.
- They are found in foods, such as fish and flaxseed, and in dietary supplements, such as fish oil.
- The three main omega-3 fatty acids are alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
Pre-Packaged Insolvency Resolution Process:

The Pre-packaged Insolvency Resolution Process (PPIRP) has resulted in the full settlement of operational creditors’ claims in five cases.
- Pre-packaged Insolvency Resolution Process was introduced in April 2021 in the wake of Covid pandemic, to deal with stress of small and mid-sized companies.
- The idea was that resolution of distressed MSMEs requires different treatment due to the unique nature of their businesses.
- Pre-packaged insolvency process is an alternate and speedier resolution mechanism for micro, medium and small enterprises in financial distress.
- It involves the debtor and its creditors negotiating and agreeing on a resolution plan before initiating the formal insolvency process.
- Once approved by the creditors, the pre-packaged resolution plan is submitted to the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) for approval.
- It is similar to an out-of-court settlement process.
- The debtor and creditor work on a draft resolution plan before formally initiating the insolvency process.
- Once finalised and approved by the required majority of creditors, the plan is submitted to NCLT.
- The pre-packaged insolvency process is initiated voluntarily by the debtor.
- Since the resolution plan is negotiated and finalised before filing with NCLT, it reduces the time taken for resolution compared to the corporate insolvency resolution process, with minimal disruptions.
Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve:

The Tamil Nadu Forest Department recently commenced a three-day-long elephant census at Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve.
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve is located at the junction of the Eastern and Western Ghatsin the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve, in the Erode District of Tamil Nadu.
- Its area is contiguous with the Mudumalai Tiger Reserve, Bandipur Tiger Reserve (Karnataka), and Biligiri Rangaswamy Temple Tiger Reserve and Wildlife Sanctuary (Karnataka).
- Together, these reserves—forming the Nilgiris biosphere landscape— have the biggest tiger population in the world, at over 280 tigers.
- It was declared a tiger reserve in 2013. It forms a vital link between the Eastern and Western Ghats, creating a continuous habitat for tigers and other wildlife.
- It is subtropical and dry.
- The summers are hot and dry; the monsoons are wet and cooler, with river flooding.
- Some of the prominent rivers in the region include the Bhavani, Moyar, and Noyyal rivers.
- It is home to several indigenous tribal communities, including the Irula and Kurumba tribes.
Cost Inflation Index:

The income tax department has notified the Cost Inflation Index for the current fiscal beginning April 2024.
- Cost Inflation Index is used to adjust the purchase price of assets on the basis of inflation.
- It is notified under the Income-tax Act, 1961 every year.
- It helps an individual to ascertain the inflation-adjusted current price of an asset.
- It also helps in calculating capital gains from a transfer or sale of capital assets after taking inflation into account.
- Capital gain refers to the profit acquired from the sale/transfer of any capital assets, including land, property, stocks, shares, trademarks, patents, etc.
- Normally, an asset is required to be retained for more than 36 months (24 months for immovable property and unlisted shares, 12 months for listed securities) to qualify as ‘long-term capital gains’.
- It helps taxpayers offset the impact of inflation as the difference between the purchase and sale price could be substantial due to rising prices.
- The application of the Cost Inflation Index for capital gain adjusts the purchase price of assets based on their sale price, resulting in smaller earnings and a lower tax amount.
- From FY 2023-24, the indexation benefit on long-term capital gains from non-equity mutual fund schemes has been removed.
- A taxpayer will continue to use the CII number to calculate long-term capital gains from house property, land, and building in the event of a sale.
Shallow Aquifer Management:
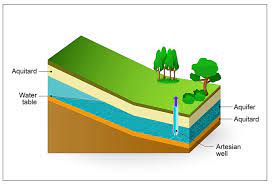
The Greater Hyderabad Municipal Corporation (GHMC) in a latest intervention has taken up Shallow Aquifer Management (SAM) model on a pilot basis in the city.
- Shallow Aquifer Management is a sustainable urban water management technique and addresses persistent issues of groundwater depletion, drying up of borewells and check quick flooding of city streets.
- The project’s concept is to drill shallow water injection borewells to a depth of 100-120 feet and pump out water in the shallow aquifers.
- This is done so that the layers underneath get recharged whenever there is rainfall, while collecting water from the surrounding watershed and channelling it through recharge pits.
- Thus, the underground layers are recharged, and water table rises.
- It is part of Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) scheme of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Nodal implementing agency: National Institute of Urban Affairs
- In 2022, the Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) initiated a SAM pilot across 10 cities in nine states: Bengaluru (Karnataka), Chennai (Tamil Nadu), Dhanbad (Jharkhand), Gwalior (Madhya Pradesh), Hyderabad (Telangana), Jaipur (Rajasthan), Kolkata (West Bengal), Pune and Thane (Maharashtra) and Rajkot (Gujarat).
World Thyroid Day 2024:

World Thyroid Day is observed annually on May 25th to raise awareness about the thyroid gland and the various conditions that affect it.
- The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple.
- It’s a part of your endocrine system and controls many of your body’s important functions by producing and releasing thyroid hormones, like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
- These hormones affect every cell in the body.
- They support the rate at which the body uses fats and carbohydrates.
- They help control body temperature.
- They have an effect on heart rate.
- They help control how much protein the body makes.
- Thyroid Disease is a general term for a medical condition that keeps your thyroid from making the right amount of hormones.
- Thyroid disorders are very common and mainly occur in women, although anybody-men, teenagers, children, and babies, too, can be affected.
- The two main types of thyroid disease are
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid): Not enough thyroxine is produced for the body’s needs. This is the most common thyroid disorder.
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid): Too much thyroxine is produced for the body’s needs.
AstroSat Mission:

A team of Indian astrophysicists has used observations from AstroSat to discover the aperiodic modulation of high-energy X-ray photons in Swift J1727.8-1613, a black hole binary source.
- AstroSat Mission is the first dedicated Indian astronomy mission aimed at studying celestial sources in the X-ray, optical and UV spectral bands simultaneously.
- AstroSat, with a lift-off mass of 1515 kg, was launched on September 28, 2015, into a 650 km orbit by PSLV-C30 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota.
- AstroSat carries a total of five scientific payloads enabling imaging, studying the temporal and spectral properties of galactic and extra- galactic cosmic sources in a wide range of wavelengths on a common platform.
- One of the unique features of AstroSat mission is that it enables simultaneous multi-wavelength observations of various astronomical objects with a single satellite.
- The spacecraft control centre at Mission Operations Complex (MOX) ofISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), Bengaluru, manages the satellite during its entire mission life.
- The main scientific objectives of AstroSat mission are:
- To understand the high energy processes in interacting binary systems with a compact object accreting matter from a companion star.
- Study star birth regions and high-energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new transient X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep-field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
Gliese 12b : Exoplanet

Using NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) and many other telescopes, two teams of astronomers have discovered a temperate, Earth-sized exoplanet named Gliese 12b.
- Gliese 12b is a newly discovered temperate, Earth-sized exoplanet orbiting a cool red dwarf called Gliese 12, located in the constellation Pisces.
- Red dwarfs have lower luminosity, which means their habitable zones are much closer to the star.
- Gliese 12 is about 27% the size of our sun and 60% of its temperature.
- Gliese 12 b is located 40 light-years away, which is relatively close in astronomical terms.
- Since its star is so much smaller than the sun, Gliese 12b still falls within the habitable zone—the ideal distance away from a star where liquid water can exist—even though it completes its orbit every 12.8 days.
- Gliese 12 b is roughly the size of Earth or slightly smaller, making it comparable to Venus.
- This similarity in size makes Gliese 12 b an excellent subject for studying rocky planets.
- Its mass is approximately 3.87 times that of Earth.
- It receives 1.6 times more energy from its star than Earth does from the Sun, and about 85% of what Venus experiences.
- The estimated surface temperature of Gliese 12 b is 107°F (42°C), assuming it has no atmosphere.
Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS):
- It is a NASA mission to discover exoplanets around nearby bright stars.
- It was launched on April 18, 2018, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket out of Cape Canaveral.
- Orbit: TESS circles Earth in a unique high Earth orbitof 12 to 15 days, which is inclined in a way that the telescope’s sky view is largely free from obstructions by our bright planet and the Moon.
- The prime mission ended on July 4, 2020, and TESS is now on an extended mission.
- TESS is finding planets ranging from small, rocky worlds to giant planets, showcasing the diversity of planets in the galaxy.
Top Startup Cities : PitchBook

PitchBook recently released its 2024 global Venture Capital ecosystem rankings, spotlighting the top 50 startup cities worldwide.
- Mumbai secured the 32nd spot, Bengaluru ranked 34th, and Gurugram made it to 48th place.
- The report highlights a surge in innovation and growth in the global startup landscape, attracting significant investments and fostering multi-billion-dollar valuations.
- The top five cities were:
- San Francisco Bay Area, USA
- New York City, USA
- Beijing, China
- Shanghai, China
- Los Angeles, USA
- India has emerged as the 3rd largest ecosystem for startups globally as of 31st May 2023.
- India ranks 2nd in innovation quality with top positions in the quality of scientific publications and the quality of its universities among middle-income economies.
- PitchBook, renowned for its comprehensive financial data and insights, serves as a vital resource in the capital markets, with offices in London, New York, San Francisco, and Seattle
Zero Debris Charter:

Twelve nations signed the Zero Debris Charter at the ESA/EU Space Council, committing to making space activities debris-neutral by 2030.
- The signatories include Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Germany, Lithuania, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Sweden, and the United Kingdom, alongside the European Space Agency (ESA) as an International Organisation.
- This initiative, first introduced at the ESA Space Summit in November 2023, aims to lead global efforts in space debris mitigation and remediation.
- The Zero Debris Charter aims to achieve debris-neutrality in space by 2030.
- The Charter is part of ESA’s comprehensive Zero Debris approach, which involves significant internal reforms and the development of debris mitigation technologies under its Space Safety Programme.
- ESA estimates over one million pieces of space debris larger than one-centimetre orbit Earth, posing severe risks to satellites and astronauts.




