Today Current Affairs: 29th December 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Iran Nuclear Talks Set To Resume:

Iran nuclear talks set to resume after five months:
- The international talks have resumed in Vienna to revive the 2015 Iran nuclear deal, known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, or JCPOA.
- The talks are held between the remaining partners to the deal — Iran, China, Russia, Germany, France and the U.K.
- The talks seek to bring back the United States, after it withdrew from the accord in 2018 under then President Donald Trump and began imposing sanctions on Iran.
About the Iran Nuclear Deal:
- Also known as the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
- The JCPOA was the result of prolonged negotiations from 2013 and 2015 between Iran and P5+1 (China, France, Germany, Russia, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Union, or the EU).
- Under the deal, Tehran agreed to significantly cut its stores of centrifuges, enriched uranium and heavy-water, all key components for nuclear weapons.
- Trump pulled the U.S. out of the accord in 2018. Besides, he opted for a “maximum pressure” campaign by imposing sanctions and other tough actions.
- Iran responded by intensifying its enrichment of uranium and building of centrifuges, while maintaining its insistence that its nuclear development was for civilian and not military purposes.
- Again, In January 2020, following the drone strike on Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps commander Gen. Qasem Soleiman, Iran announced that it would no longer observe the JCPOA’s restraints.
- The collapse of the JCPOA drags Iran towards nuclear brinkmanship, like North Korea, which has created major geopolitical instability in the region and beyond.
5G:
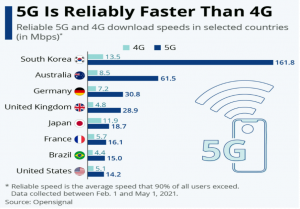
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) said that Gurugram, Bengaluru, Kolkata, Mumbai, Chandigarh, Delhi, Jamnagar, Ahmadabad, Chennai, Hyderabad, Lucknow, Pune, and Gandhi Nagar would be among the first cities to get 5G services in 2022.
- 5G or fifth generation is the latest upgrade in long-term evolution (LTE) mobile broadband networks.
- It mainly works in three bands — low-, mid- and high-frequency — all of which have their uses as well as limitations.
- While the low-band spectrum has shown great promise in terms of coverage, the maximum Internet speed is limited to 100 Mbps (megabits per second).
- The mid-band spectrum offers higher speeds than low-band, but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals.
- High-band offers the highest speed among the three, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength.
Counter-Terrorism Committee Of United Nations Security Council (UNSC):

India will chair the Counter-Terrorism Committee of United Nations Security Council (UNSC) in January 2022 after 10 years.
- The Counter-Terrorism Committee was established by Security Council resolution 1373 adopted unanimously on 28 September 2001 in the wake of the 9/11 terror attacks in the US.
- The Committee was tasked with monitoring implementation of resolution 1373 which requested countries to implement a number of measures aimed at enhancing their legal and institutional ability to counter terrorist activities at home and around the world.
- This includes taking steps to criminalize the financing of terrorism, freezing any funds related to persons involved in acts of terrorism, deny all forms of financial support for terrorist groups, suppress the provision of safe haven, sustenance or support for terrorists and share information with other governments on any groups practicing or planning terrorist acts.
- Besides, the Committee monitors steps taken to cooperate with other governments in the investigation, detection, arrest, extradition and prosecution of those involved in terror acts and criminalizes active and passive assistance for terrorism.
Fake Sun:

Top scientists from China have claimed to have successfully created a ‘fake Sun’. The artificial Sun created by China is about ten times hotter than the real Sun, around which our planet revolves.
- It is called the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), also known as ‘Artificial Sun’ experiment.
- In June, it set a new record, where it achieved a plasma temperature of 216 million Fahrenheit (120 million C) for 101 seconds.
- Experts focused their giant array of almost 200 laser beams onto a tiny spot to create a mega blast of energy – eight times more than they had ever done in the past.
- Although the energy only lasted for a very short time – just 100 trillionths of a second – the scientists were able to create more energy than they are using.
- In this experiment, scientists used two isotopes of hydrogen, giving rise to helium.
- It is believed that the temperature at the core of the Sun is 15 million C, which also means that the temperature produced by (EAST) is nearly seven times that of the Sun.
- It is a significant step in the country’s quest to unlock clean and limitless energy, with minimal waste products.
EAST:
- The artificial Sun experiment is being developed through a reactor, with the help of nuclear fusion.
- The mission mimics the energy generation process of the sun.
- The reactor consists of an advanced nuclear fusion experimental research device located in Hefei, China.
- It is one of three major domestic tokamaks that are presently being operated across the country.
- The EAST project is part of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) facility, which will become the world’s largest nuclear fusion reactor when it becomes operational in 2035.
- The ITER project includes the contributions of several countries, including India, South Korea, Japan, Russia and the United States.
- The ‘artificial sun’ EAST replicates the nuclear fusion process carried out by the sun and stars.
- For nuclear fusion to occur, tremendous heat and pressure are applied on hydrogen atoms so that they fuse together.
- The nuclei of deuterium and tritium — both found in hydrogen — are made to fuse together to create a helium nucleus, a neutron along with a whole lot of energy.
- Here, fuel is heated to temperatures of over 150 million degrees C so that it forms a hot plasma “soup” of subatomic particles.
- With the help of a strong magnetic field, the plasma is kept away from the walls of the reactor to ensure it does not cool down and lose its potential to generate large amounts of energy.
- The plasma is confined for long durations for fusion to take place.
Retrospective Taxation:

British energy major Cairn Energy Plc has finally withdrawn the lawsuits filed against the Indian government and its entities overseas in a ₹10,247 crore retrospective tax case. The company is in the process of dropping cases filed in France and the Netherland, too.
- These lawsuits were filed to seize assets of Air India to recover the money from the Indian government.
- The Cairn’s decision to drop the lawsuits comes after an international arbitration award overturned the levy of ₹10,247 crore retro tax by India and directed it to refund the money to the company.
- In December 2020, a three-member international arbitral tribunal at the Permanent Court of Arbitration in the Netherlands ruled unanimously that the Indian government was “in breach of the guarantee of fair and equitable treatment”, and against the India-UK Bilateral Investment Treaty, and that the breach caused a loss to the British energy company and ordered compensation of $1.2 billion.
- Cairn had challenged the Indian government seeking taxes over an internal business reorganisation using the 2012 retrospective tax law, under the UK-India Bilateral Investment Treaty.
- In 2014, the Indian tax department had demanded Rs 10,247 crore in taxes.
- In 2015, Cairn Energy Plc commenced international arbitration proceedings against the Indian government.
Retrospective Taxation:
- It allows a country to pass a rule on taxing certain products, items or services and deals and charge companies from a time behind the date on which the law is passed.
- Countries use this route to correct any anomalies in their taxation policies that have, in the past, allowed companies to take advantage of such loopholes.
- Retrospective Taxation hurts companies that had knowingly or unknowingly interpreted the tax rules differently.
Shyama Prasad Mukherji Rurban Mission (SPMRM):

- Telangana stood first in the implementation of the Shyama Prasad Mukherji Rurban Mission (SPMRM).
- Tamil Nadu and Gujarat took the second and third positions respectively.
About Shyama Prasad Mukherji Rurban Mission:
- Launched in 2016, the programme is designed to deliver catalytic interventions to rural areas on the threshold of growth.
- It is now a Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
- Funding: Shared between the Centre and the State in a ratio of 60:40 for Plain area States and 90:10 for Himalayan and NE States.
- Main objective of the scheme is bridging the rural-urban divide-viz: economic, technological and those related to facilities and services
- Under the mission, the Central government in coordination with the district administration has taken measures to bring about multi-layered phased development of the rural gram panchayats and villages on the lines of urban cities with proper civic amenities keeping the soul of villages intact.
- A ‘Rurban cluster’, would be a cluster of geographically contiguous villages with a population of about 25000 to 50000 in plain and coastal areas and with a population of 5000 to 15000 in desert, hilly or tribal areas.
- These clusters typically illustrate potential for growth, have economic drivers and derive locational and competitive advantages.
- According to the 2011 Census, India has more than 6 lakh villages while there are around 7,000 towns and urban centres. Out of a total population the rural population accounts for 69% and urban population 31%.
- About 70% of the population lives in rural areas and about 50% of the overall labour force is still dependent on agriculture that is not productive enough.
- Large parts of rural areas in the country are not stand-alone settlements but part of a cluster of settlements, which are relatively proximate to each other.
- These clusters typically illustrate potential for growth, have economic drivers and derive locational and competitive advantages.
- These clusters, once developed, can then be classified as ‘Rurban’.
Sri Aurobindo:

PM Modi has announced that 150 universities across the country will be involved in writing papers on different aspects of spiritual leader Sri Aurobindo’s life and philosophy to commemorate his 150th birth anniversary.
- Sri Aurobindo was born on August 15, 1872, in Kolkata, West Bengal.
- He was a yogi, seer, philosopher, poet, and Indian nationalist who propounded a philosophy of divine life on earth through spiritual evolution.
- From 1902 to 1910 he partook in the struggle to free India from the British.
- In Pondichéry he founded a community of spiritual seekers, which took shape as the Sri Aurobindo Ashram in 1926.
- He was much influenced by the American Revolution, revolts in Italy and the medieval French revolts against England.
- He attended Congress sessions and at the same time, helped establish the Anushilan Samiti of Calcutta in 1902.
- He and his brother revolutionary Barin Ghose contributed articles to the magazine Jugantar which inspired many young people to take up revolutionary work.
- He was also a journalist, editing newspapers such as Bande Mataram.
- In May 1908, Aurobindo was arrested in connection with the Alipore Conspiracy Case.
- In 1914, he started publishing a magazine Arya.
- He wrote copiously and his greatest literary achievement was ‘Savitri’, an epic poem with about 24000 lines.
- He developed a kind of Yoga called Integral Yoga.
- Sri Aurobindo Ghosh was considered as a prophet of Indian nationalism. Along with Bankimchandra, Tilak and Dayanand, he developed the theory of nationalism in India.
- Sri Aurobindo’s theory of nationalism was based on Vedanta philosophy which saw unity and oneness in man and God.
- He declared that India was in fact Mother India which represented the united power and Shakti of millions of her children.
- Mother India represented the infinite energy of her people: He identified Mother India with God and maintained that it was God’s divine mission to set India free.
- He said that the village should retain its autonomy and self-government but at the same time, ‘should seek to promote national cohesion.
- The ideal of national Swaraj must be modeled on the old village community which was self-sufficient, autonomous and self-governing.
Typhoon Rai:
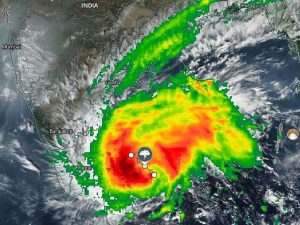
The official death toll of Typhoon Rai (locally named Odette) which hit parts of the Philippines in mid-December, was raised to 388.
- Rai is the strongest storm to hit the disaster-prone archipelago this year (2021).
- Typhoons are a kind of storm. The storms, depending on where they occur, may be called hurricanes, typhoons or cyclones.
- Typhoons: In the China Sea and Pacific Ocean.
- Hurricanes: In the West Indian islands in the Caribbean Sea and Atlantic Ocean.
- Tornados: In the Guinea lands of West Africa and southern USA.
- Willy-willies: In north-western Australia and
- Tropical Cyclones: In the Indian Ocean Region.
- The scientific name for all these kinds of storms is tropical cyclones.
- Tropical cyclones are intense circular storms that originate over the warm tropical oceans with speed more than 119 kilometres per hour and heavy rains.
- Tropical cyclones rotate counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere.
- The Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) Tokyo – Typhoon Centre assigns a typhoon a name. The name ‘Rai’ is contributed by Micronesia.
Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs):

The State of India’s Livelihood (SOIL) Report 2021 has stated that just 1-5 % of Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs) have received funding under central government schemes introduced to promote them in the last seven years.
About the Report:
- Access Development Services, a national livelihoods support organisation has prepared the SOIL report.
- It has analysed only Farmer Producer Companies (FPC — FPOs registered under The Companies Act, 2013) since they make up a large majority of the organisations started in recent years.
- The number of FPOs registered as cooperatives or societies is very small.
Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs):
- The concept of ‘Farmer Producer Organisations (FPO)’ consists of collectivization of producers especially small and marginal farmers so as to form an effective alliance to collectively address many challenges of agriculture such as improved access to investment, technology, inputs, and markets.
- FPO is one type of Producer Organisation (PO) where the members are farmers.
- A PO is a legal entity formed by primary producers, viz. farmers, milk producers, fishermen, weavers, rural artisans, craftsmen.
- Voluntary Organisations: FPOs are voluntary organizations controlled by their farmer-members who actively participate in setting their policies and making decisions.
- They are open to all persons able to use their services and willing to accept the responsibilities of membership, without gender, social, racial, political or religious discrimination.
- Provide Education and Training: FPOs operatives provide education and training for their farmer-members, elected representatives, managers, and employees so that they can contribute effectively to the development of their FPOs.
Trincomalee Oil Tank Farms:

In the coming days, India and Sri Lanka are going to sign the long pending deal to jointly develop the Trincomalee oil tank farms.
- The signing of the deal will reflect a positive sign, amidst strained relationship between the two countries.
About Trincomalee Oil Tank Farms:
- The oil tank farm was built by the British during World War II as a refuelling station,
- It is located in ‘China Bay’ in close proximity to the internationally coveted deep water natural harbour of Trincomalee.
- The proposal of this joint development was envisaged 35 years ago, in the Indo-Lanka Accord 1987.
- It comprises 99 storage tanks, with a capacity of 12,000 kilolitres each, spread across Lower Tank farm and Upper Tank Farm.
- In 2003, Indian Oil Corporation set up its Sri Lankan subsidiary called Lanka IOC, to work on this oil farm.
- Currently, Lanka IOC runs 15 tanks. The new agreement is being negotiated for the remaining tanks.
Fourth Edition Of State Health Index:

NITI Aayog has released the fourth edition of the State Health Index for 2019–20.
- The report, titled “Healthy States, Progressive India”, ranks states and Union Territories on their year-on-year incremental performance in health outcomes as well as their overall status.
- Earlier, the Global Health Security (GHS) Index 2021, developed in partnership by the Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI) and the Johns Hopkins Center was released. India, with a score of 42.8 (out of 100) has slipped by 0.8 points since 2019.
- The State Health Index is an annual tool to assess the performance of states and UTs, which has been compiled and published since 2017.
- It is a weighted composite index based on 24 indicators grouped under the domains of ‘Health Outcomes’, ‘Governance and Information’, and ‘Key Inputs/Processes’.
Health Outcomes:
- It includes parameters such as neonatal mortality rate, under-5 mortality rate, sex ratio at birth.
Governance and Information:
- It includes parameters such as institutional deliveries, average occupancy of senior officers in key posts earmarked for health.
Key Inputs/Processes:
- It consists of proportion of shortfall in health care providers to what is recommended, functional medical facilities, birth and death registration and tuberculosis treatment success rate.
Developed By:
- NITI Aayog, with technical assistance from the World Bank, and in close consultation with the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW).
Focus of the Fourth Edition:
- Round IV of the report focuses on measuring and highlighting the overall performance and incremental improvement of states and UTs over the period 2018–19 to 2019–20.
Ranking of States:
- In terms of annual incremental performance, Uttar Pradesh, Assam and Telangana are the top three ranking states.
- Smaller States: Mizoram and Meghalaya registered the maximum annual incremental progress.
- Union Territories: Delhi, followed by Jammu and Kashmir, showed the best incremental performance.
- Overall: The top-ranking states were Kerala and Tamil Nadu among the ‘Larger States’, Mizoram and Tripura among the ‘Smaller States’, and Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu (DH&DD) and Chandigarh among the UTs.




