Today Current Affairs: 3rd August 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
India Assumes UNSC Presidency:

India assumed the presidency of the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) for the month of August 2021.
- This will be the country’s first presidency during its 2021-22 tenure as a non-permanent member of the Security Council.
- India began its two-year tenure as a non-permanent member of the UNSC in January 2021.
- This is India’s eighth term on the UNSC.
India’s UNSC Presidency:
- India will decide the UN body’s agenda for the month and coordinate important meetings on a range of issues.
- It is going to organise key events in three major areas of maritime security, peacekeeping and counter-terrorism.
- The Security Council will also have on its agenda several important meetings including Syria, Iraq, Somalia, Yemen, and the Middle East.
- The Security Council will also be adopting important resolutions on Somalia, Mali, & United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon.
- Prime Minister (PM) Narendra Modi will be the first Indian PM to preside over a meeting of the UNSC.
- The last time an Indian PM was engaged in this effort was the then PM PV Narasimha Rao in 1992 when he attended a UNSC meeting.
Provincial Status To Gilgit-Baltistan: Pakistan
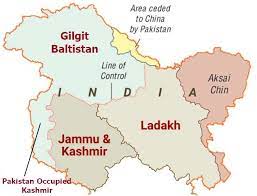
It has been reported that, Pakistani authorities have finalised a law (26th Constitutional Amendment Bill), to award provisional provincial status to strategically located Gilgit-Baltistan.
About Gilgit-Baltistan:
- Gilgit-Baltistan is one of the disputed territories of India.
- It is a chunk of high-altitude territory located on the north western corner of the Union Territory of Ladakh.
- It is located strategically as it borders Pakistan, Afghanistan and China.
- The region is claimed by India as part of the erstwhile princely state of Jammu & Kashmir as it existed in 1947 at its accession to India.
- Maharaja Hari Singh, the last Dogra ruler of J&K, had signed the Instrument of Accession with India on 26th October 1947.
- However, it has been under Pakistan’s control since 4th November, 1947, following the invasion of Kashmir by tribal militias and the Pakistan army.
- Following this invasion, India moved to the United Nations Security Council to raise the issue of Pakistan’s invasion, on 1st January 1948.
The UN Security Council passed a resolution:
- Calling for Pakistan to withdraw from all of Jammu and Kashmir and then India had to reduce its forces to the minimum level following which a plebiscite would be held to ascertain people’s wishes.
- However, no withdrawal was ever carried out and it remains a point of contention between two countries.
Current Status:
- Gilgit-Baltistan is an autonomous region now and after the bill is passed, it will become the 5th province of the country.
- Currently, Pakistan has four provinces namely Balochistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab, and Sindh.
- Presently, it has been ruled mostly by executive orders.
- Until 2009, the region was simply called Northern Areas.
- It got its present name only with the Gilgit-Baltistan (Empowerment and Self-Governance) Order, 2009, which replaced the Northern Areas Legislative Council with the Legislative Assembly.
Ashwagandha For Promoting Recovery From COVID-19:

India and the UK have collaborated to conduct a study on ‘Ashwagandha (AG)’ for promoting recovery from Covid-19.
- After the trial’s success, ‘Ashwagandha’ will be a proven medicinal treatment to prevent infection and be recognised by the scientific community worldwide.
- This is the first time that the Ministry of Ayush has collaborated with a foreign institution to investigate its efficacy on Covid-19 patients.
- Ashwagandha’ (Withania somnifera), commonly known as ‘Indian winter cherry’, is a traditional Indian herb that boosts energy, reduces stress and makes the immune system stronger.
- All India Institute of Ayurveda (AIIA), an autonomous body under the Ministry of Ayush, and the LSHTM recently signed a MoU to conduct clinical trials of ‘Ashwagandha’ on 2,000 participants in three U.K. cities — Leicester, Birmingham and London (Southall and Wembley).
- While there have been several studies on ‘Ashwagandha’ to understand its benefits in various ailments, this is the first time the Ministry of Ayush has collaborated with a foreign institution to investigate its efficacy on COVID-19 patients”.
Section 66A Of The Information Technology Act:

The Centre has said that the Ministries of Information and Technology and Home Affairs had done their best to disseminate knowledge about the Supreme Court judgment in Shreya Singhal case on Section 66A. Despite this, many cases have been registered under this section.
- The Centre has made the following observations:
- Since the police and public order were “State subjects” under the Constitution, the onus lies with the states to implement the apex court’s 2015 judgment quashing the ‘draconian’ section 66A of Information and Technology Act.
Law enforcement agencies share equal responsibility to comply with the apex court judgment. They take action against cyber crime offenders as per the law.
- Since the police and public order were “State subjects” under the Constitution, the onus lies with the states to implement the apex court’s 2015 judgment quashing the ‘draconian’ section 66A of Information and Technology Act.
- On July 5, the Supreme Court had expressed shock and dismay over police continuing to register cases under section 66A despite it being quashed six years ago.
- As of March 2021, a total of 745 cases are still pending and active before the district courts in 11 states, wherein the accused persons are being prosecuted for offences under Section 66A of the IT Act.
- Section 66A defines the punishment for sending “offensive” messages through a computer or any other communication device like a mobile phone or a tablet.
- A conviction can fetch a maximum of three years in jail and a fine.
- It empowered police to make arrests over what policemen, in terms of their subjective discretion, could construe as “offensive” or “menacing” or for the purposes of causing annoyance, inconvenience, etc.
What Are Integrated Theatre Commands?

A table-top war-gaming exercise was held recently among the three services of the armed forces (Navy, Army and Airforce).
- The aim of this exercise was to evolve a consensus among the three services on the reorganisation of the forces into integrated tri-service theatre commands and fine-tune the model.
- India currently has 19 military commands with 17 of them service-oriented. While both the Army and the Air Force have seven commands each, the Navy has three.
- India also has a Tri-Service Command — Andaman and Nicobar Command — besides the Strategic Forces Command (SFC), which looks after the country’s nuclear stockpile.
- An integrated theatre command envisages a unified command of the three Services, under a single commander, for geographical areas that are of strategic and security concern.
- The commander of such a force will be able to bear all resources at his disposal — from the Army, the Indian Air Force, and the Navy — with seamless efficacy.
- The integrated theatre commander will not be answerable to individual Services.
- This will help in better planning and military response and also bring down cost.
- While the cost may go up in the immediate future since all theatres would have to be armed with sufficient systems, it will prove to be cost-effective in the long term as all acquisitions will be a unified one.
- It will provide a unified approach to fighting the future wars.
Goa Bhumiputra Adhikarini Bill, 2021:

The Goa Assembly passed the Goa Bhumiputra Adhikarini Bill, 2021.
- It recognises anyone living in the state for 30 years or more as a ‘Bhumiputra (son of the soil)’ and giving such a person the right to own his or her ‘small dwelling unit’ if ownership was undetermined so far.
- Once recognised as a Bhumiputra, an individual can stake claim to ownership of their house of not more than 250 sq m, built before April 1, 2019.
- The objective was to enable the ‘mool Goenkar (original Goan)’ to live with dignity.
- The Bill provides for the constitution of the Bhumiputra Adhikarini — a committee consisting of the Deputy Collector as its Chairperson.
- This Bill has open the floodgates for the migrant population that has been staying in densely populated areas in Goa and has no legality.
- This would recognise encroachments by slum-dwellers that are over 30 years old as Bhumiputras.
Kuthiran Tunnel:

Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari instructed to open one side of the Kuthiran Tunnel in Kerala.
- This is the first road tunnel in the state and will drastically improve connectivity to Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- The 1.6 km long tunnel is designed through Peechi- Vazahani wildlife sanctuary.
- The road will improve connectivity to important ports and towns in North – South Corridor without endangering wildlife.
25th Controller General Of Accounts (CGA):

Deepak Das took charge as the 25th Controller General of Accounts (CGA), with effect from August 1, 2021.
- Parent agency: Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance.
- It is the Principal Accounting Adviser to Government of India and is responsible for establishing and maintaining a technically sound Management Accounting System.
- Functions:The Office of CGA prepares monthly and annual analysis of expenditure, revenues, borrowings and various fiscal indicators for the Union Government.
- Under Article 150 of the Constitution, the Annual Appropriation Accounts (Civil) and Union Finance Accounts are submitted to Parliament on the advice of Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
- Along with these documents, an M.I.S Report titled ‘Accounts at a Glance’ is prepared and circulated to Hon’ble Members of Parliament.
- It is also responsible for coordination and monitoring the progress of submission of corrective/remedial action taken notes (ATNs) on the recommendations contained in Public Accounts Committee’s (PAC) reports as well as the Comptroller & Auditor General (CAG) reports through its web based Audit Para Monitoring System (APMS).
India And China Military Hotlines:

A hotline was established between the Indian Army in Kongra La, north Sikkim, and the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) at Khamba Dzong in the Tibet Autonomous Region to further the spirit of trust and cordial relations along the border. The event coincided with ‘PLA Day’ on August 1.
- India and China have two military hotlines in eastern Ladakh, among others at Chushul and Daulat Beg Oldi.
- These hotlines in various sectors go a long way in maintaining peace and tranquility at the borders.
- In February 2021, the Foreign Ministers of India and China had agreed to establish a new hotline between the Foreign Ministries to ensure “timely communication” in the backdrop of the Ladakh stand-off.
- This will be in addition to the long delayed hotline between the Indian Army’s Director General of Military Operations and China’s Western Theatre Command, which is expected to be established soon.
Mirabai Chanu:

Mirabai Chanu won the silver medal at the 2020 Summer Tokyo Olympics in Women’s 49 kg, becoming the first Indian weightlifter to win silver at the Olympics and the second Indian weightlifter after Karnam Malleswari to win an Olympic medal
- Saikhom Mirabai Chanu (born 8 August 1994) is an Indian weightlifter
- She won the silver medal at the 2020 Summer Olympics in Women’s 49 kg.
- Chanu had won the silver medal in the women’s 48 kg weight class at the 2014 Commonwealth Games, Glasgow; she went on to break the games record en route to the gold medal at the 2018 edition of the event held in Gold Coast.
- In 2017, she won the gold medal at World Weightlifting Championships held in Anaheim, California.
- She was awarded the Padma Shri and Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna award in 2018.




