Table of Contents
Daily Current Affairs for Government Exams:
Today Current Affairs: 3rd February 2020 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Contents:
- Archimedes Principle
- World Wetlands Day
- Facial Recognition for Elections
- Project Digital Poompuhar
- Rakhigarhi to be Developed as an Iconic Site
- Inquiry into Study on Bats and Bat-Hunters
- 34th Surajkund International Crafts Mela
- Malta Abhiyan
- Bodo language
- Green India mission
- Portal Santusht
- Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana
- Other important current affairs
1.Archimedes Principle:
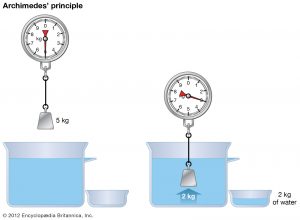
A video of an elephant being rescued in Jharkhand went viral recently, winning officials of the state forest department praise online. They applied the Archimedes Principle, or the ‘upward buoyant force theory’, to bring the elephant out of the well.
- In physics, the Archimedes Principle refers to the law of buoyancy (the ability or tendency of something to float in water or other fluids).
- According to the principle, when an object is completely or partially submerged in a fluid, whether gas or liquid, it is acted upon by an upward force (buoyancy) equal to the weight of the fluid it has displaced.
- The force acting downward on the object is the weight of the object. The upward force is the one given by the Archimedes Principle. The difference between the two forces is the net force acting on the object.
- If the buoyant force is more than the weight, the object rises; if it is less, the object sinks. If the net force is zero, the object remains in place, and neither rises nor sinks.
- In the case of the elephant rescued in Jharkhand, the forest officials pumped water into the well so that the elephant could float to the surface.
2.World Wetlands Day :

World Wetlands Day is celebrated every year on the 2nd of February. This day marks the date of the adoption of the Convention on Wetlands on 2 February 1971 in the Iranian city of Ramsar.
- The theme for 2020 is ‘Wetlands and Biodiversity’.
- Wetlands are ecosystems saturated with water, either seasonally or permanently. They include mangroves, marshes, rivers, lakes, deltas, floodplains, and flooded forests, rice-fields, coral reefs, marine areas no deeper than 6 meters at low tide, as well as human-made wetlands such as waste-water treatment ponds and reservoirs.
- Though they cover only around 6% of the Earth’s land surface, 40% of all plant and animal species live or breed in wetlands.
Status of Wetlands in India:
- Recently, the Ramsar Convention declared 10 wetlands from India as Ramsar sites taking the total number of Ramsar Sites in the country to 37.
- Wetlands declared as Ramsar sites are protected under strict guidelines of the convention.
- There are currently over 2,300 Ramsar Sites around the world.
- India has over 7 lakh wetlands, covering 4.5% of the country’s area, yet none of the wetlands has been notified under domestic laws.
- Wetlands are regulated under the Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2017.
3.Facial Recognition for Elections:

In the upcoming Telangana urban local bodies polls, the State Election Commission (SEC) will be using a facial recognition app for verification and real-time authentication of voters on the pilot basis in 10 selected polling stations.
- The use of facial recognition for election will be a first-of-its-kind in India.
- It will help to counter impersonation by voters during polling.
- The initiative will be implemented in the Kompally Municipality of Medchal Malkajgiri district of Telangana.
- The facial recognition is proposed as an additional tool to validate the identity of the voter in addition to the existing procedures prescribed including the use of photo electoral rolls, the insistence of photo ID proof in addition to the personal scrutiny by the polling agents appointed by the contesting candidates.
- The additional polling officer-in-charge of the mobile phone will work with a facial recognition system.
The app will display results of the verification based on the match established with the voters with an appropriate message. - Further, the photographs taken will not be stored or used for any other purpose. These photographs will be erased from the memory of the mobile phone used in the polling station and also the server of TSTS (Telangana State Technology Services).
4.‘Project Digital Poompuhar’:
The Department of Science and Technology (DST) has launched ‘Project Digital Poompuhar’ to recreate the Chola Dynasty port city (Poompuhar) in Tamil Nadu.
- The reconstruction of Poompuhar is a part of DST’s Indian Digital Heritage (IDH) project.
- An exhibition of its first project ‘Digital Hampi’ is currently on display at the National Museum.
- The Poompuhar project is a part of the second phase of IDH. The second phase will focus on the heritage sites that are currently underwater in Gujarat (eg. Dwarka) and Tamil Nadu.
- The Poompuhar is mentioned in works of Sangam Tamil literature which refers to the city located 30 km from the existing Poompuhar town in southern Tamil Nadu.
Project Digital Poompuhar
- The project involves underwater surveys and photography by remotely operated vehicles and remote sensing-based geodynamic studies to bring out comprehensive information on the time series evolution and extinction.
- It also involves the visualization of geodynamic processes of the last 20,000 years like land subsidence, sea-level rise, Cauvery’s migration, floods, tsunami, cyclones, and erosion.
- The study is also expected to provide scientific information not only on the life history of Poompuhar and the socio-cultural evolution but also the science and technological evolution and the disaster history of this region,
5.Rakhigarhi to be Developed as an Iconic Site:

Union Budget (2020-21) has proposed to develop Rakhigarhi (Hisar district, Haryana) as an iconic site.
- 4 other archaeological sites in Hastinapur (Uttar Pradesh), Shivsagar (Assam), Dholavira (Gujarat) and Adichanallur in (Tamil Nadu) will also be developed as iconic sites with onsite museums.
Rakhigarhi:
- Rakhigarhi is the largest Harappan site in the Indian subcontinent.
- Other large sites of Harappan civilization on the Indian sub-continent are Harappa, Mohenjodaro and Ganveriwala in Pakistan and Dholavira (Gujarat) in India.
- At Rakhigarhi, the excavations are being done to trace its beginnings and to study its gradual evolution from 6000 BCE (Pre-Harappan phase) to 2500 BCE.
- The site was excavated by Amarendra Nath of ASI.
Recently, a study of DNA from skeletal remains excavated from the Harappan cemetery at Rakhigarhi found that the people in the Harappan Civilization have an independent origin. This study negates the theory of the Harappans having Steppe pastoral or ancient Iranian farmer ancestry.
6.Inquiry into Study on Bats and Bat-Hunters:

The government has ordered an inquiry into a study conducted in Nagaland by researchers from China, US, and India on bats and humans carrying antibodies to deadly viruses like Ebola.
- The study is investigated for how the scientists were allowed to access live samples of bats and bat hunters (humans) without due permission.
- The inquiry comes at a time when people worldwide are grappling with the spread of novel coronavirus (nCoV) from China.
- Bats are harvested in an annual ritual by a Naga Tribe in Nagaland. The study conducted research on individuals who participated in the ritual.
. Diseases Linked to Bats
- All bats can carry viruses. Many high-profile epidemics have been traced to bats.
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) antibodies were found in insectivorous bats.
- Ebola antibodies were found in the Hammer-headed fruit bat.
- Indian Flying Fox, hosts over 50 viruses.
- Rabies
7.34th Surajkund International Crafts Mela:

The President of India inaugurated the 34th Surajkund International Crafts Mela in Surajkund, Haryana on February 1, 2020.
- The Mela is organized by the Surajkund Mela Authority & Haryana Tourism in collaboration with Union Ministries of Tourism, Textiles, Culture, and External Affairs.
- The Surajkund Mela is unique as it showcases the richness and diversity of the handicrafts, handlooms and cultural fabric of India, & is the largest crafts fair in the world.
- The Mela was initiated in 1987 to promote the pool of skilled artisans, who used indigenous technology, but were suffering due to the cheaper machine-made imitations.
- The fair was upgraded to an international level in 2013.
- Himachal Pradesh is the ‘Theme State’ and Uzbekistan is the ‘Partner Nation’ for the Year 2020.
- England will participate for the first time in the Surajkund Mela.
8.Malta Abhiyan:

The Indian Navy recently launched a unique coastal security exercise in Kolkata. The exercise was conducted to create awareness about coastal security to the local community.
- The Indian Navy conducted the Coastal Security Exercise, Malta Abhiyan in the Sunderbans region and the exercise is unique of its kind.
- Two naval boats were flagged off the Sunderbans till Hemnagar along the International Trade Protocol route between India and Bangladesh.
- The Naval officer created awareness to the local community along the route.
- The route is sensitive as deadly equipment can be dropped off easily and thus it was chosen by the Indian Navy.
The Sunderbans is a Mangrove Delta Forest formed at the confluence of Brahmaputra, Ganga and Meghna rivers. The Delta is vulnerable for its vastness and complexities. It covers over 10,000 square kilometers in India and 6,017 square kilometers in Bangladesh.
9.Bodo language:
Bodo language is one of the key thrust areas in the Bodo Accord which was signed recently.
- Bodo language Estimated to have 1.5 million speakers (Census 2011), Bodo is listed in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution.
- It is spoken in Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Meghalaya, and West Bengal.
- While Bodo is officially written in the Devanagri script, the language has a history of having been written in at least three different scripts until, in 1974, the Government recognized Devanagari as its official script. In the first decade of the 20th century, Bodos started writing in the Assamese/Bangla script. Then they also used Roman Script.
- In the pre-13th century era, it was called Deodhai.
Accord, 2020 regarding Bodo language:
- It was only in 2003, under the then Bodo Accord, that the language was listed in the Eighth Schedule. And it was the first tribal language to be included in the Eight Schedule.
- In Assam, it has enjoyed the status of official associate language in undivided Goalpara district since 1986.
- Now the 2020 Accord makes Bodo the associate official language throughout Assam.
- The new Accord also promises to establish a separate directorate for Bodo medium schools, provincialize schools and colleges in the BTAD (Bodoland Territorial Autonomous District) and establish a Cultural Complex-cum-Centre of Excellence in Kokrajhar for protection and promotion of the language.
10.Green India Mission:

A sum of Rs 343.08 crore has been released under the Green India Mission (GIM) for undertaking afforestation activities over an area of 126,916.32 hectares (ha) in 13 states, according to the Economic Survey 2019-20.
- GIM is one of the eight missions launched under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
- GIM, launched in February 2014, is aimed at protecting, restoring and enhancing India’s diminishing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Objectives of the Mission:
- To protect, restore and enhance India’s falling forest cover.
- To respond to climate change through a combination of adaptation as well as mitigation measures.
- To increased forest-based livelihood incomes.
- To enhance annual Carbon sequestration by 50 to 60 million tonnes in the year 2020.
11. Portal Santusht:

The Portal Santusht is an Implementation Monitoring Cell that was launched by the Ministry of Labor and Employment in January 2020. The portal addresses the delivery of public services, transparency, accountability, schemes, and policies at the grass-root level.
- The portal aims to address the speedy redressal of grievances of workers and employers.
- It monitors services that are provided by health insurance and EPFOs (Employment Provident Fund Organization).
- Also, it monitors the services provided by the ESICs (Employment State Insurance Corporation) to the formal sector workers.
- The ESIC is a statutory body administered by the Ministry of Labour and Employment. The Corporation can raise loans, acquire movable and immovable properties. It can also set up hospitals in collaboration with the state governments for the benefit of the employees. The ESIC is governed by the ESI (Employment State Insurance) Act.
- The EPFO is also a statutory body formed and operated under the Employment Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952. It is also operated under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
11.Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana.:

- Madhya Pradesh bagged the first position for the implementation of Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana.
- Anupam Rajan (Principal Secretary) will receive the award at a function in New Delhi.
- Indore district has also bagged the first place for better performance of the scheme.
- The objective of the Matru Vandana Yojana is to provide incentives of Rs. 5000 for the loss of wages of working women, to ensure their proper rest and nutrition.
Other important current affairs:
1. Prolonged monsoon and unseasonal rains have helped to rejuvenate the waterholes in Bandipur Tiger Reserve, Karnataka.
- There are 370 big and small waterholes (a depression in which water collects from where animals usually drink) in Bandipur and 85% of them are full.
- At Bandipur, the majority of waterholes dry up by February and March leading to severe water stress situations for animals. But this year, it is expected that the depletion of water levels will take a little longer.
- Also, in the areas of water stress, 37 solar-powered borewells have been arranged that will function to replenish the waterholes periodically to further minimize the water scarcity.
2. The Corona Virus death toll has increased to 360. The WHO has also declared International Health Emergency over the outbreak of the virus.
- The health ministers of G7 grouping that comprises of USA, Canada, UK, France, Germany, Italy, and Japan are to meet to discuss the epidemic being caused by the Coronavirus.
- The Ministers will discuss a joint response to the epidemic.
- The virus has so far reached 24 countries and infected 14,500 people.
3. Pakistan which is facing the worst locust attacks in decades has declared National Emergency.
- The emergency was declared to tackle the insects that are destroying crops in Punjab province, the main region of agricultural production.
- The locusts are currently in the India-Pakistan border along the Cholistan.
- Usually, these Locusts move to Iran after some time.
- However, this time due to low temperatures they are still in Pakistan.
- By the end of January 2020, the Indian border of Gujarat and Rajasthan were attacked by desert locusts from Pakistan and Iran.
- They mainly attacked the oil seed-producing regions. It included rapeseed and cumin seed plants in Gujarat in around 17,000 hectares and 360,000 hectares of land in Rajasthan.
4. India and Maldives signed 5 Memorandum of Understandings to establish Addu Tourism in 5 islands of Addu Atoll.
- Tourism is to be developed at a cost of 2.49 million USD. Addu is a city in the Maldives that contains several inhabited Islands.
- Along with tourism, the countries also signed the 6th MoU agreement to set up a bottled water plant in Hoarafushi.
- The tourism development and the water plant falls under India’s High Impact Community Development Scheme.
- Under the scheme, India assists the Maldives in developing projects based on the needs of the communities of the islands.
5. The report of the Fifteenth Finance Commission, along with an Action Taken Report, has been tabled in Parliament.
- The Commission, headed by N K Singh, had submitted its Report to the President in December 2019.
- The Finance Commission is constituted by the President under article 280 of the Constitution, mainly to give its recommendations on the distribution of tax revenues between the Union and the States and amongst the States themselves.
- Two distinctive features of the Commission’s work involve redressing the vertical imbalances between the taxation powers and expenditure responsibilities of the center and the States respectively and equalization of all public services across the States.
6. The Maldives re-joined the Commonwealth, more than three years after the Indian Ocean island nation quit amid mounting criticism of its human rights.
- In 2016, the Maldives pulled out of the Commonwealth.
- The Maldives has been formally reinstated into the Commonwealth as its 54th member state.
7. Finance minister Nirmala Sitharaman’s Union Budget for 2020-21, presented on February 1, 2020, proposed Rs 8,000 crore over five years for National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications.
- Quantum technologies comprise quantum computing, quantum communication, quantum optics, quantum information processing, quantum internet, and quantum artificial intelligence.
8. The Ministry of MSME (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) on February 3, 2020, provided an update on the SFURTI scheme being implemented.
- A total amount of Rs 2.3 crores has been sanctioned for the scheme in the budget 2020.
- The scheme SFURTI-Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional industries was launched in 2005.
- It enhances the production of Khadi industries and artisans.
- Also, under SFURTI, the scheme for rural industries Service Centre (RISC) is being implemented.
- The scheme for Product Development, Design Intervention and Packaging is also implemented under SFURTI.
9. The Budget 2020-21 that was presented by the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitaraman increased the National Calamity Contingent Duty.
- The imposed duty is expected to witness a price rise of 7% in the sales of cigarettes.
- The NCCD is the tax imposed on pan masala, cigarettes, cellular phones, and other tobacco products. It was introduced under the Finance Act, 2001
- The Tobacco Institute of India believes that increasing the NCCD will incentivize illegal cigarette trading in the country. Currently, the illegal cigarettes account to one-fourth of the Indian Cigarette market.
10. As of January 2020, 723 Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendras (PMKK) have been established in the country.
- Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) scheme for skill development is being implemented through its institutional framework in the country with the objective to improve the occupational skills and technical knowledge of the neo literate
- PMKVY does not mandate the establishment of permanent skill development centers as it is a demand-driven scheme.
11.ICICI Bank launches ‘iBox’ self-service delivery tool for customers to collect their deliverables like debit cards and checkbooks from the bank bran
- It enables customers to conveniently collect key banking deliverables on all days, 24×7.
- The first-of-its-kind initiative is available at 50 branches in 17 cities




