Today Current Affairs: 5th July 2022 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Foreign Contribution(Regulation) Act (FCRA):

The Union Home Ministry has amended certain rules related to the Foreign Contribution(Regulation) Act (FCRA), allowing Indians to receive up to ₹10 lakh in a year from relatives staying abroad without informing the authorities.
- The earlier limit was ₹1 lakh.
- In a notification, the Ministry also said that if the amount exceeds it, the individuals will now have 90 days to inform the government, instead of 30 days earlier.
New Rules:
- Increasing limit for foreign contributions: It allows Indians to receive up to ₹10 lakh in a year from relatives staying abroad without informing the authorities. The earlier limit was ₹1 lakh.
- Increasing number of days to inform authorities: In a notification, the Ministry also said that if the amount exceeds it, the individuals will now have 90 days to inform the government, instead of 30 days earlier.
- Increasing number of Compoundable offences: It made five more offences under the FCRA“compoundable” instead of directly prosecuting the organizations or individuals. Earlier, only seven offences under the FCRA were compoundable.
- Information about bank accounts: The amended rules have given individuals and organizations or NGOs 45 days to inform the home ministry about the bank accounts that are to be used for the utilization of such funds.
- Omission of provision b in rule 13: The government has also“omitted” provision ‘b’ in rule 13, which dealt with declaring foreign funds.
- Transparency in the utilization of funds: Now, anyone receiving foreign funds will have to follow the existing provision of placing the audited statement of accounts on receipts and utilization of the foreign contribution, including income and expenditure statement, receipt and payment account, and balance sheet, within nine months of the closure of the financial year on its official website or on the website as specified by the Centre.
125th Birth Anniversary Of Alluri Sitarama Raju:

PM Modi to launch the year-long celebrations on the 125th birth anniversary of Alluri Sitarama Raju, enabling a new generation to be aware of the heroics of Alluri and the sacrifices he made for the tribal community.
- Alluri Sitarama Raju (1897 – 1924) was an Indian revolutionary who waged an armed campaign against British colonial rule in India. He was nicknamed “Manyam Veerudu” (Hero of the Jungle) by local villagers for his heroic exploits.
- Born in present-day Andhra Pradesh, he became involved in anti-British activities in response to the 1882 Madras Forest Act
- The act restricted the free movement of Adivasis (tribal communities) in their forest habitats and prevented them from practising a traditional form of agriculture known as podu (shifting cultivation).
- Initially, Sitarama Raju, under the influence of Gandhi’s Non-cooperation movement, inspired thetribals to seek justice in the local panchayat courts and boycott the colonial courts.
- Led the Rampa Rebellion/Manyam Rebellion of 1922.
- In 1924, Raju was taken into police custody, tied to a tree, and shot by public execution, effectively ending the armed rebellion.
Earthquake Of Magnitude 5.9 In Afghanistan:
Recently a powerful earthquake of magnitude 5.9 on the Richter scale struck a remote town in Afghanistan, killing over a thousand and injuring many more.
- According to the theory of plate tectonics, the Earth’s crust and upper mantle are made of large rigid plates that can move relative to one another. Slip on faults near the plate boundaries can result in earthquakes.
- The point inside the Earth where the earthquake rupture starts is called the focus or hypocentre. The point directly above it on the surface of the Earth is the epicentre.
- Seismic waves: Any elastic material when subjected to stress, stretches in a proportional way, until the elastic limit is reached. When the elastic limit is crossed, it breaks.
- Similarly, the Earth also has an elastic limit and when the stress is higher than this limit, it breaks.
- Then there is a generation of heat, and energy is released. Since the material is elastic, the energy is released in the form of elastic waves.
- These propagate to a distance determined by the extent of the impact. These are known as seismic waves.
Partnership For Global Infrastructure And Investment (PGII):

On June 26, the G-7 grouping of the world’s “most industrialised nations” Canada, France, Germany, Italy, the U.K., Japan and the U.S. along with the European Union (EU) launched a U.S.-led $600 billion Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII) at their summit in Germany’s Schloss Elmau, where India was among five special invitees.
- The initiative was billed as a “values-driven, high-impact, and transparent infrastructure partnership to meet the enormous infrastructure needs of low- and middle-income countries and support the U.S. and its allies’ economic and national security interests.”
- Officials also made it clear that the PGII would offer a counter to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) for projects worldwide that was formally launched five years ago.
India’s Flora And Fauna:

India added 540 species to its faunal database in 2021 taking the total number of animal species to 1,03,258. The country also added 315 taxa to the Indian flora during 2021, taking the number of floral taxa in the country to 55,048.
- Of the 540 faunal species, 406 are new discoveries and 134 new records to India.
- Thirteen new genera were also discovered in 2021. Among the new species discovered is one species from mammal, 35 reptiles and 19 species of pisces.
- The new mammal species discovered is Crocidura narcondamica, a white-toothed shrew, from Narcondam Island of the Andaman and Nicobar group of islands.
- Among the reptiles discovered in 2021, notable is Boiga whitakeri, or Whitaker’s cat snake, from the Western Ghats in Tamil Nadu.
- The most number of new discoveries was from the faunal group Hymenoptera, an order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants, in which 80 species, including one new genus, were discovered.
- With 1.03 lakh species of fauna, India contributes to 6.1% of faunal diversity in the world.
Australopithecus:

The fossils of our earlier human ancestors, located in a cave in South Africa, are a million years older than previously understood according to a new study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Science.
- The researchers analysed the fossilised remains of Australopithecus from Sterkfontein caves and argued they lived at the same time as their East African counterparts like the famous Lucy, complicating the way scholars have understood human evolution.
- Australopithecus, meaning “southern ape”, was a group of hominins or now-extinct early humans, that was closely related to and almost certainly the ancestors of modern humans.
- They inhabited the planet 4.4 million to 1.4 million years ago, likely encompassing a time period longer than our own genus, Homo. Their fossils have been found across sites in eastern, northern, central and southern Africa.
Sterkfontein caves:
- The “Cradle of Humankind” is a 47,000-hectare paleoanthropological site, declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.
- Located 40 km northwest of Johannesburg, it contains a complex system of limestone caves, where a significant number of hominin fossils have been found.
- Within this complex lies Sterkfontein, a complex system of caves that holds a long history of hominin occupation and contains the largest number of Australopithecus fossils in the world.
Operation NARCOS:

The Railway Protection Force recovered narcotics products valued over Rs. 7.40 Crore under Operation NARCOS.
- In order to bring attention to the menace of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, a month-long pan India drive against smuggling of narcotics through rail was launched under code name Operation “NARCOS” in the month of June-2022.
- RPF intensified its checks in trains and in identified black spots across the country in coordination with Narcotics Control Bureau and other Law Enforcement Agencies to target drug peddlers involved in this illegal trade.
- The contingent of RPF is an Armed Force of the Union of India. It is a security force under the ownership of Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways.
- The history of the RPF dates back to 1882 when various railway companies appointed their own guards for protection of railway property.
- The force was declared a statutory force in 1957 by an enactment of Parliament, subsequently declared as an Armed Force of the Union of India in 1985.
- RPF has been entrusted with responsibility for the safety of Railway property.
China’s New High-Tech Aircraft Carrier Fujian:

China unveiled its first indigenous aircraft carrier, the new-generation Fujian (Type 003).
- China now has the most number of aircraft carriers after the U.S.
- The Fujian has been named after China’s eastern coastal province which lies across from Taiwan.
- The Fujian joins two other carriers currently operated by China — Shandong (Type 001), commissioned in 2019, and the Liaoning (Type 002), bought second-hand from Ukraine in 1998.
- The Type 003 carrier more technologically advanced than its predecessors Shandong and Liaoning.
- Features:
- The Fujian’s displacement is 80,000 tonnes, much more than the existing Chinese carriers, and comparable to U.S. Navy aircraft carriers.
- The Fujian has been fitted with the latest launch technology — the Electromagnetic Aircraft Launch System (EMALS), first developed by the U.S. Navy.
- It also has a straight flat-top flight deck for take-offs and landings,
- The two existing vessels use a ski jump-style ramp.
- A ski-jump is an upward-curved ramp that allows aircraft to take off from a runway that is shorter than the aircraft’s required takeoff roll.
National Investigation Agency:

The Union Home Ministry handed over the probe into the barbaric killing of a pharmacist at Amravati in Maharashtra to the National Investigation Agency (NIA).
- The NIA is the Central Counter-Terrorism Law Enforcement Agency of India mandated to investigate all the offences affecting the sovereignty, security and integrity of India.
- It includes:
- Friendly relations with foreign states.
- Against atomic and nuclear facilities.
- Smuggling of arms, drugs and fake Indian currency and infiltration from across the borders.
- The offences under the statutory laws enacted to implement international treaties, agreements, conventions and resolutions of the United Nations, its agencies and other international organisations.
- It was constituted under the National Investigation Agency (NIA) Act, 2008.
- The agency is empowered to deal with the investigation of terror related crimes across states without special permission from the states under written proclamation from the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
- In the wake of the 26/11 Mumbai terror attack in November 2008, which shocked the entire world, the then United Progressive Alliance government decided to establish the NIA.
- In December 2008, former Union Home Minister P. Chidambaram introduced the National Investigation Agency Bill.
- The agency came into existence on 31st December 2008, and started its functioning in 2009.
- Till date, the NIA has registered 447 cases.
- The law under which the agency operates extends to the whole of India and also applies to Indian citizens outside the country.
- Persons in the service of the government wherever they are posted.
- Persons on ships and aircraft registered in India wherever they may be.
- Persons who commit a scheduled offence beyond India against the Indian citizen or affecting the interest of India.
Kai Chutney:

In Odisha, scientists are now fine-tuning their research to make a presentation for the Geographical Indications (GI) registry of Kai chutney.
- Applied under food category, the GI tag will help develop a structured hygiene protocol in the preparation of Kai chutney for standard wider use.
- Geographical Indications labels enhance the reputation and value of local products and support local businesses.
- People often keep a safe distance from red weaver ants as their sting inflicts a sharp pain and reddish bumps on the skin.
- Despite this, weaver ants are popular among the tribes of Mayurbhanj district in Odisha for the mouth-watering dish made of them — the Kai chutney.
- This savoury food item, rich in proteins, calcium, zinc, vitamin B-12, iron, magnesium, potassium, sodium, copper, fibre and 18 amino acids, is known to boost the immune system.
- Weaver ants, Oecophylla smaragdina, are abundantly found in Mayurbhanj throughout the year.
- They make nests with leaves of host trees.
New Pathway To Regulate Nitrate Absorption In Plants:
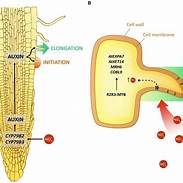
Researchers led by those from the National Centre of Biological Sciences, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bengaluru (NCBS-TIFR), have found a new pathway that regulates nitrate absorption in plants.
- The gene MADS27, which regulates nitrate absorption, root development and stress tolerance, is activated by the micro-RNA, miR444, therefore offers a way to control these properties of the plant.
- The researchers studied this mechanism in both rice (monocot) and tobacco (dicot) plants.
- The research is published in Journal of Experimental Botany.
- Nitrogen is one of the most important macronutrients needed for development of a plant.
- It is a part of chlorophyll, amino acids and nucleic acids, among others.
- It is mostly sourced from the soil where it is mainly absorbed in the form of nitrates and ammonium by the roots.
- Nitrates also play a role in controlling genome-wide gene expression that in turn regulates root system architecture, flowering time, leaf development, etc.
- Thus, while a lot of action takes place in the roots to absorb and convert nitrogen into useful nitrates, the absorbed nitrates in turn regulate plant development apart from being useful as a macronutrient.




