Today’s Current Affairs: 5th July 2024 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Vanuatu:

The government of Vanuatu will soon settle into a suite of new buildings funded by China, a move which has reignited concerns about Beijing’s reach in the South Pacific nation.
- This initiative underscores China’s strategic interests in the Pacific islands, where it has funded major infrastructure upgrades across the archipelago, competing with Western rivals for influence.
- Vanuatu is an island country consisting of a chain of 13 principal and many smaller islands located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
- These islands are situated approximately east of Australia.
- The islands extend north-south in an irregular Y shape.
- The northernmost group is the Torres Islands, and southward from there, the main islands include Vanua Lava, Santa Maria (Gaua), Espiritu Santo, Aoba (Ambae), Maéwo, Pentecost, Malakula, Ambrym, Épi, Éfaté, Erromango, Tanna, and Anatom.
- Formerly the jointly administered Anglo-French condominium of the New Hebrides, Vanuatu achieved independence in 1980.
- The capital, largest city, and commercial centre is Port-Vila (Vila), on Éfaté.
Death Anniversary Of Swami Vivekananda:

Every year, 4th July is observed as the death anniversary of Swami Vivekananda.
- He is considered as the father of modern Indian nationalism and is also credited with raising interfaith awareness and bringing Hinduism to the status of a major world religion in the late 19th century.
- Vivekananda was born as Narendranath Datta on 12th January 1863 in Calcutta.
- In 1893, upon the request of Maharaja Ajit Singh of the Khetri State, he took the name ‘Vivekananda.’
- He is credited for introducing yoga and Vedanta to the West.
- He died at Belur Math (1902) in West Bengal. It is the headquarters of Ramakrishna Math & Ramakrishna Mission.
- National Youth Day is held every year on 12th January to observe the birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda.
Steel Slag : Guidelines

The member (Science) of Niti Aayog released the Guidelines for the Utilization and Processing of Steel Slag as Processed Steel Slag Aggregates in Road Construction.
- Steel Slag is an industrial byproduct obtained from the steel manufacturing industry.
- It is produced in large quantities during steel-making operations that use electric arc furnaces.
- It can also be produced by smelting iron ore in a basic oxygen furnace.
- Primarily, slag consists of calcium, magnesium, manganese and aluminium silicates and oxides in various combinations.
- The cooling process of slag is responsible mainly for generating different types of slags required for various end-use consumers.
- It has found use as a barrier material remedy for waste sites where heavy metals tend to leach into the surrounding environment.
- Steel slag forces the heavy metals to drop out of solution in water run off because of its high oxide mineral content.
World Drug Report 2024:

The United Nations (UN) agency tackling crime and drug abuse (UNODC) released its annual World Drug Report recently.
Highlights of the Report:
- The number of people who use drugs has risen to 292 million in 2022, a 20 percent increase over the past ten years.
- Cannabis remains the most widely used drug worldwide (228 million users), followed by opioids (60 million users), amphetamines (30 million users), cocaine (23 million users) and ecstasy (20 million users).
- Nitazenes, a group of highly potent synthetic opioids, have recently emerged in several high-income countries, resulting in an increase in overdose deaths.
- Though an estimated 64 million people worldwide suffer from drug use disorders, only one in 11 is in treatment.
- Women receive less access to treatment than men, with only one in 18 women with drug use disorders in treatment versus one in seven men.
- In 2022, an estimated 7 million people were in formal contact with the police (arrests, cautions, and warnings) for drug offences, with about two-thirds of this total due to drug use or possession for use.
- In addition, 7 million people were prosecuted for drug offences and over 1.6 million were convicted globally in 2022.
Indian Gaur : Spotted

After several decades, the locally extinct Indian gaur has been spotted in the Nagarjunasagar Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NSTR) in Andhra Pradesh.
- The Indian Bison of Gaur is the largest and tallest in the family of wild cattle.
- Scientific Name: Bos gaurus
- Gaurs are indigenous to the South and Southeast parts of Asia.
- Gaurs are primarily the denizens of evergreen and semi-evergreen forests along with moist deciduous forests with open grasslands.
- They prefer hilly-terrains below an altitude of 1,500-1,800 m with large and undisturbed forest tracts and abundant water.
Nightjars:

A team of scientists recently described a new species of nightjar, named Caprimulgus ritae, living in the tropical forests Timor and Wetar, Lesser Sunda Islands.
- Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal insectivorous birds in the family Caprimulgidae and the order Caprimulgiformes.
- These birds are found all around the world, with the exception of Antarctica and certain island groups, such as the Seychelles.
- They are characterized by long wings, short legs, and very short bills.
- They feed on flying insects that they catch on the wing at night.
- Their grey-brown, mottled, streaked, and stripey plumage provides ideal camouflage in the daytime.
- During the day, they sleep on the ground or perched, usually lengthwise, on a branch.
- They are among the most difficult bird species to study due to their unobtrusive and nocturnal behavior and cryptic plumage.
Lesser Sunda Islands:
- The Lesser Sunda Islands are an archipelago in maritime Southeast Asia.
- It is located to the immediate east of Java and to the north of Western Australia.
- Major islands in the group include Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Flores, Sumba, and Timor.
Junk DNA:
Using artificial intelligence, researchers have found potential cancer drivers hidden in so-called ‘junk’ regions of DNA.
- Junk DNA refers to regions of DNA that are noncoding.
- DNA contains instructions (coding) that are used to create proteins in the cell.
- However, the amount of DNA contained inside each cell is vast, and not all of the genetic sequences present within a DNA molecule actually code for a protein.
- Some of this noncoding DNA is used to produce non-coding RNA components such as transfer RNA, regulatory RNA and ribosomal RNA.
- However, other DNA regions are not transcribed into proteins, nor are they used to produce RNA molecules and their function is unknown. These are known as junk regions of DNA.
- The proportion of coding versus noncoding DNA varies significantly between species.
- In the human genome, for example, almost all (98%) of the DNA is noncoding, while in bacteria, only 2% of the genetic material does not code for anything.
- However, over the years, researchers have found evidence to suggest that junk DNA may provide some form of functional activity.
Rudram-1 Missile:

India has successfully test-fired its first indigenous anti-radiation missile, the Rudram-1, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- Rudram-1 Missile is an air–to–surface missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
- It is integrated with the IAF’s Sukhoi-30MKI fighter jets, serving as the launch platform.
- It is India’s first indigenous anti-radiation missile.
- It features Inertial Navigation Systems (INS)-GPS navigation and a Passive Homing Head for the final attack, allowing it to accurately hit radiation-emitting targets.
- INS-GPS navigation provides a technological edge, enabling accurate targeting over a wide range of frequencies.
- The missile can be launched from varying altitudes, ranging from 500 meters to 15 kilometers and has a range of up to 250 kilometers depending on the launch conditions.
- This flexibility allows the IAF to adapt to different operational scenarios, enhancing its combat effectiveness.
- This precision is crucial for Suppression of Enemy Air Defence (SEAD) operations, enabling the destruction of enemy radars and communication sites from long standoff ranges.
Metal-Organic Frameworks:
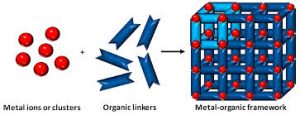
Researchers have carried out an in-depth analysis of the mechanisms underlying the flexibility of crystals of Metal-Organic frameworks (MOFs) and introduced a novel quantitative measure of mechanical flexibility for crystals.
- Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) are a class of porous, crystalline materials with a broad range of applications.
- They are composed of metal ions or clusters, which act as the joints, bound by multidirectional organic ligands, which act as linkers in the network structure.
- These crystalline materials possess the remarkable ability to absorb gases, such as carbon dioxide, and store them as well as act as filters for crude oil purification.
- MOFs derive their ability from the presence of nanopores, enhancing their surface areas that, in turn, make them adept at absorbing and storing gases.
- Flexibility in crystals has been assessed in terms of a parameter called elastic modulus, which is a measure of a material’s resistance to strain-induced deformation.




