Today Current Affairs: 6th November 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
India Raised A New Army Aviation Brigade: LAC
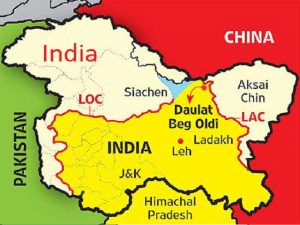
India raised a new army aviation brigade in the eastern sector of Line of Actual Control (LAC) in the Arunachal Pradesh sector.
- Also, China’s legislature has adopted a new border law that calls on the state and military to safeguard territory and “combat any acts” that undermine China’s territorial claims.
- The LAC is the demarcation that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory. The recent stand-off at Ladakh’s Galwan Valley has escalated due to the infrastructure projects that India has undertaken in recent years.
- The new army aviation brigade was raised in March 2021 at Missamari air base, close to Tezpur, Assam and has capabilities such as Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH), US’ Cheetah helicopters and Israel’s Heron drones.
- While the function of the new brigade is largely for Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR) activities of the Army, it has the capability to support the Army for other objectives as well on the LAC.
Line of Actual Control (LAC):
- Demarcation Line: Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh and the Union Territory of Ladakh share a border with China.
Sectors: The LAC is generally divided into three sectors namely: Western sector, Middle sector, and Eastern sector
Human papillomavirus (HPV) Vaccine:
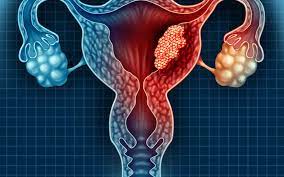
New Research has found that the Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine (Cervarix) reduces the risk of Cervical Cancer significantly in women.
- The results are important because the vaccine was introduced in the 2000s and studies confirming that it is effective against cancer have come up only recently.
- The Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine reduced cervical cancer cases by 87% among women in the U.K. who received the vaccine when they were 12 or 13 years old.
- It reduced the risk by 34% in women who were aged 16-18 years when they were offered the jab.
- Over a period of 11 years (since 2006), the vaccine prevented around 450 cervical cancers and around 17,200 cases of precancerous conditions.
Cervical Cancer:
- It is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix – the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina.
- Various strains of the Human papillomavirus (HPV) play a role in causing most cervical cancer.
- When exposed to HPV, the body’s immune system typically prevents the virus from doing harm. In a small percentage of people, however, the virus survives for years, contributing to the process that causes some cervical cells to become cancer cells.
- The HPV vaccine (Cervarix) protects against two of the cancer-causing strains, which are HPV 16 and 18.
Human papillomavirus:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common viral infection of the reproductive tract.
- There are more than 100 types of HPV.
- More than 40 types of HPV are spread through direct sexual contact.
- Out of these 40, two cause genital warts, while about a dozen of HPV cause different types of cancer including cervical, anal, oropharyngeal, penile, vulvar and vaginal.
16th East Asia Summit:

The Prime Minister attended the 16th East Asia Summit (EAS).
- The 16th EAS discussed important regional and international issues including Indo-Pacific, South China Sea, UNCLOS, terrorism, and situation in Korean Peninsula and Myanmar.
- Indo-Pacific:
- Reaffirmed India’s focus on a free, open and inclusive Indo-Pacific and the principle of “ASEAN Centrality” in the region.
- Highlighted the synergies between ASEAN Outlook on Indo-Pacific (AOIP) and India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Resilient Global Value Chain:
- Emphasised the importance of a resilient global value chain and reiterated India’s commitment to providing Quad-sponsored vaccines to Indo-Pacific countries.
- Quad countries (India, Japan, Australia and US) are on track to help produce at least 1 billion vaccine doses in India to boost the global supply by the end of 2022.
- Recalled India’s support of USD1 million to the ASEAN Covid-19 Recovery Fund.
- Multilateralism:
- India remained committed to strengthening respect for shared values of multilateralism, rules-based international order, international law and sovereignty and territorial integrity of all nations.
- Cyber Security:
- The idea of developing global standards on cyber security has also been raised.
- The EAS leaders adopted three statements on mental health, economic recovery through tourism, and sustainable recovery, which have been co-sponsored by India.
East Asia Summit:
- Established in 2005, it is a forum of 18 regional leaders for strategic dialogue and cooperation on the key political, security, and economic challenges facing the Indo-Pacific region.
- The concept of an East Asia Grouping was first promoted in 1991 by the then Malaysian Prime Minister, Mahathir bin Mohamad.
- There are six priority areas of regional cooperation within the framework of the EAS.
- These are – Environment and Energy, Education, Finance, Global Health Issues and Pandemic Diseases, Natural Disaster Management, and ASEAN Connectivity.
- It comprises the ten member states of the ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) which are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam, along with 8 other countries namely Australia, China, Japan, India, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Russia and the USA.
- It is an ASEAN-centred forum so it can only be chaired by an ASEAN member.
- Brunei Darussalam is the chair for 2021.
Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) Framework: RBI

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced a revised Prompt Corrective Action (PCA) framework.
- The PCA framework enables supervisory intervention of RBI over Banks at an appropriate time and ensures effective market discipline.
- The framework applies to all banks operating in India, including foreign banks operating through branches or subsidiaries based on breach of risk thresholds of identified indicators.
- However, payments banks and small finance banks (SFBs) have been removed from the list of lenders where prompt corrective action can be initiated.
- The new provisions will be effective from January, 2022.
- Capital, Asset Quality and Capital-To-Risk Weighted Assets Ratio(CRAR), NPA ratio, Tier I Leverage Ratio, will be the key areas for monitoring in the revised framework.
- However, the revised framework excludes return on assets as a parameter that may trigger action under the framework.
Invocation of PCA: - The breach of any risk threshold may result in the invocation of the PCA. Stressed banks may not be allowed to expand credit/investment portfolios.
- However, they are allowed to invest in government securities/other high-quality liquid investments.
- In the case of a default on the part of a bank in meeting the obligations to its depositors, possible resolution processes may be resorted to without reference to the PCA matrix.
Prompt Corrective Action:
- PCA is a framework under which banks with weak financial metrics are put under watch by the RBI.
- The RBI introduced the PCA framework in 2002 as a structured early-intervention mechanism for banks that become undercapitalised due to poor asset quality, or vulnerable due to loss of profitability.
- The framework was reviewed in 2017 based on the recommendations of the working group of the Financial Stability and Development Council on Resolution Regimes for Financial Institutions in India and the Financial Sector Legislative Reforms Commission.
- Objective: The objective of the PCA framework is to enable supervisory intervention at an appropriate time and require the supervised entity to initiate and implement remedial measures in a timely manner, so as to restore its financial health.
- It aims to check the problem of Non-Performing Assets (NPAs) in the Indian banking sector.
- It is intended to help alert the regulator as well as investors and depositors if a bank is heading for trouble.
- The idea is to head off problems before they attain crisis proportions.
Mass Fish Death In The Kameng River In Arunachal Pradesh:

Studies have indicated that landslides caused by an earthquake of 3.4 magnitude close to the border with China led to mass fish death in the Kameng river in Arunachal Pradesh.
- The landslips dumped several tonnes of mud and rock into the river, substantially reducing the flow of water.
- The river turned blackish due to very high turbidity resulting in low dissolved oxygen that killed the fish.
The Kameng River:
- It is the right-bank tributary of the Brahmaputra river.
- It rises in the Tawang district in the eastern Himalayas. It forms the border between the East Kameng district and the West Kameng district of Arunachal Pradesh.
- In Assam, it flows through the Sonitpur district before joining the Brahmaputra at Tezpur.
- The Kameng River consists of two sections- the west consisting of the Akka hills and resided by the Akka tribes and the east consisting of the Dafla hills resided by the Daphla tribe.
- The Kaziranga National Park and the Pakkhui Wildlife Sanctuary are located near the Kameng river.
Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT):

Canadian Pension Plan Investment Board and Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan will be the anchor investors for the Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvIT) of the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) with each picking up 25% stake.
- Besides, NHAI would retain a minimum of 15% equity and the rest would be offered to domestic institutional investors.
- The InvIT will initially have a portfolio of five operating toll roads with an aggregate length of 390 kilometers, with more roads planned to be added later.
Infrastructure investment trusts (InvITs):
- They are institutions similar to mutual funds, which pool investment from various categories of investors and invest them into completed and revenue-generating infrastructure projects, thereby creating returns for the investor.
- They are regulated under the Sebi (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) Regulations, 2014 and the Indian Trust Act, 1882.
- InvITs have a trustee, sponsor(s), investment manager and project manager.
- Trustee (certified by Sebi) has the responsibility of inspecting the performance of an InvIT.
- Sponsor(s) are promoters of the company that set up the InvIT.
- Investment manager is entrusted with the task of supervising the assets and investments of the InvIT.
- Project manager is responsible for the execution of the project.
- The key features of InvITs are:
- Mandatory distribution of 90% of net distributable cash flows to the unit investors, leverage cap of 70% on the net asset value, and a cap on exposure to assets under construction (for publicly placed InvITs).
- The sponsor of the InvIT is responsible for setting up the InvIT and appointing the trustee.
- The sponsor should hold a minimum 15% of the units issued by the InvIT with a lock-in period of three years from the date of issuance.
Emergency Use Listing (EUL) For Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin Vaccine:
The World Health Organization (WHO) has given pre-qualification, or Emergency Use Listing (EUL) for Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin vaccine.
- The approval has been given by the Technical Advisory Group (TAG), an independent advisory panel of the WHO.
- The approval was expected on October 26, but the WHO had deferred its decision and sought additional clarifications from Bharat Biotech to conduct a final risk-benefit assessment.
- The WHO has already approved six vaccines for emergency use: AstraZeneca’s Covishield, Moderna’s mRNA-1273, Sinopharm’s BBIBP-CorV, Sinovac’s CoronaVac, Pfizer/BioNTech’s Comirnaty, and Johnson & Johnson’s vaccine.
- It has been granted EUL for use in persons 18 years and above, over two doses spaced four weeks apart.
- However, no recommendation has been made for use in children, and available data for use on pregnant women is insufficient to assess safety or efficacy.
- The move is expected to ease international travel for Indians who have opted for the vaccine but experts say that this would be subjected to countries clearing Covaxin through their regulatory processes.
- Covaxin is a whole virion-inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, developed in partnership with the Indian Council of Medical Research and the National Institute of Virology, Pune.
- The EUL is a prerequisite for the COVAX initiative in vaccine supply, and allows countries to expedite their own regulatory approval to import and administer COVID-19 vaccines.
- It is a risk-based procedure for assessing and listing unlicensed vaccines, therapeutics and in vitro diagnostics with the ultimate aim of expediting the availability of these products to people affected by a public health emergency.
Tax Dispute:

Cairn Energy has entered into certain undertakings with India which would allow for the refund of taxes under a billion-dollar dispute.
- In December 2020, a three-member international arbitral tribunal at the Permanent Court of Arbitration in the Netherlands ruled unanimously that the Indian government was “in breach of the guarantee of fair and equitable treatment”, and against the India-UK Bilateral Investment Treaty, and that the breach caused a loss to the British energy company and ordered compensation of $1.2 billion.
- Cairn had challenged the Indian government seeking taxes over an internal business reorganisation using the 2012 retrospective tax law, under the UK-India Bilateral Investment Treaty.
- In 2014, the Indian tax department had demanded Rs 10,247 crore in taxes.
- In 2015, Cairn Energy Plc commenced international arbitration proceedings against the Indian government.
Retrospective Taxation:
- It allows a country to pass a rule on taxing certain products, items or services and deals and charge companies from a time behind the date on which the law is passed.
- Countries use this route to correct any anomalies in their taxation policies that have, in the past, allowed companies to take advantage of such loopholes.
- Retrospective Taxation hurts companies that had knowingly or unknowingly interpreted the tax rules differently.
COP26:

Vinisha Umashankar from Tamil Nadu recently spoke on clean energy at a meeting that discussed clean technology and innovation as part of the 26th UN Climate Change Conference of Parties (COP26) in Glasgow.
- Among her audience were world leaders, including British Prime Minister Boris Johnson, U.S. President Joe Biden, and Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- She say Young people have every reason to be angry and frustrated at leaders who have made empty promises and failed to deliver. None of what we discuss today is practical for me. We need actions rather than promises to live in a habitable world.
- She urged everyone – world leaders, business leaders, international organization as well as the civil society – to immediately “stop talking and start acting” when it comes to tackling climate change.
- We will act even if you delay and we’ll build the future even if you’re still stuck in the past,” the teenager said while requesting all present to accept her invite and assured that no-one will regret doing so.
- Winding up her speech, she said, “When it comes to climate change there’s no stop button. We can’t hit pause or even rewind. We can only move together towards the future so united we rise and together we will definitely succeed”.
- She is one of the finalists for the Earthshot Prize.
- She is the founder of the solar-powered ironing cart, which would replace the conventional charcoal ironing box.
- Her innovation brought her laurels from around the world, including the prestigious Children’s Climate Prize in November 2021




