Today Current Affairs: 9th July 2021 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
India’s Covid-19 Emergency Response Package: Phase II:
The Union Cabinet has approved a new scheme ‘India COVID-19 Emergency Response & Health System Preparedness Package: Phase-II’ amounting to Rs. 23,123 crore for FY 2021-22. The Phase-II of the Package has Central Sector (CS) and Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS) components.
Under the Central Sector components:
- National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) would be strengthened by providing Genome Sequencing machines, besides sanctioning Scientific Control room, Epidemic Intelligence Services (EIS) and INSACOG Secretariat support.
- Support would be provided for implementation of Hospital Management Information System (HMIS) in all the District Hospitals of the Country (presently, it is implemented only in 310 DHs).
- Support would also be provided for expanding the National Architecture of eSanjeevani Tele-consultation platform to provide upto 5 lakhs tele-consultations per day from the present 50,000 Tele-consultations per day.
- Support would also be provided for IT interventions, including strengthening the Central War room at DoHFW, strengthening Country’s COVID-19 Portal, 1075 COVID help lines and COWIN platform.
- Under the CSS components, States/UTs would be supported to:
- Create Paediatric units in all 736 districts and also, to establish Paediatric Centre of Excellence (PaediatricCoE) in each State/UT, for providing Tele-ICU services, mentoring and technical hand-holding to the District Paediatric units.
- Augment 20,000 ICU beds in public healthcare system out of which 20% will be Pediatric ICU beds.
- Install 1050 numbers of Liquid Medical Oxygen Storage Tanks with Medical Gas Pipeline System (MGPS), with an aim to support at least one such unit per district.
- Augment the existing feet of ambulances – 8,800 ambulances will be added under the package.
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund:

The Union Cabinet gave its approval to the various modifications in Central Sector Scheme of Financing Facility under ‘Agriculture Infrastructure Fund’.
- Eligibility has now been extended to State Agencies/APMCs, National & State Federations of Cooperatives, Federations of Farmers Producers Organizations (FPOs) and Federations of Self Help Groups (SHGs).
- For APMCs, interest subvention for a loan upto Rs. 2 crore will be provided for each project of different infrastructure types e.g. cold storage, sorting, grading and assaying units, silos, et within the same market yard.
- The power has been delegated to Minister of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare to make necessary changes with regard to addition or deletion of beneficiary in such a manner so that basic spirit of the scheme is not altere
- The period of financial facility has been extended from 4 to 6 years upto 2025-26 and overall period of the scheme has been extended from 10 to 13 upto 2032-33.
Authorised Economic Operators Programme:

The Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs (CBIC) has inaugurated the online filing of Authorised Economic Operators (AEO).
- The new version (V 2.0) of the web application is designed to ensure continuous real-time and digital monitoring of physically filed applications for timely intervention and expedience.
Authorised Economic Operator (AEO) Programme:
- AEO is a programme under the aegis of the World Customs Organization (WCO) SAFE Framework of Standards to secure and facilitate Global Trade.
- The programme aims to enhance international supply chain security and facilitate movement of legitimate goods.
- AEO is a voluntary compliance programme.
- Under this programme, an entity engaged in international trade is approved by Customs as compliant with supply chain security standards and granted AEO status & certain benefits.
- Benefits of AEO status include expedited clearance times, fewer examinations, improved security and communication between supply chain partners.
SAFE Framework:
- In June 2005 the WCO Council adopted the Framework of Standards to Secure and Facilitate Global Trade (SAFE Framework) that would act as a deterrent to international terrorism, to secure revenue collections and to promote trade facilitation worldwide.
- It prescribes baseline standards that have been tested and are working well around the globe.
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft: Findings:

NASA’s Cassini spacecraft has made the following discoveries in the moons of Saturn by flying through their plumes:
- Titan has methane in its atmosphere.
- Enceladus has a liquid ocean with erupting plumes of gas and water.
- Researchers have concluded that there may be unknown methane-producing processes on Enceladus that await discovery.
- Most of the methane on Earth has a biological origin. Microorganisms called methanogens are capable of generating methane as a metabolic byproduct.
- They do not require oxygen to live and are widely distributed in nature.
- Methanogens are found in swamps, dead organic matter, and even in the human gut. They are known to survive in high temperatures and simulation studies have shown that they can live in Martian conditions.
- Methane could be formed by the chemical breakdown of organic matter present in Enceladus’ core.
- Hydrothermal processes could help the formation of carbon dioxide and methane.
About Cassini Mission:
- Launched in 1997.
- The mission is a cooperation between NASA, the European Space Agency and the Italian Space Agency.
- This was the first landing ever accomplished in the outer Solar System.
- Cassini is the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter orbit.
- Its design includes a Saturn orbiter and a lander for the moon Titan. The lander, called Huygens, landed on Titan in 2005.
A Future For All – The Need For Human-Wildlife Coexistence: WWF And UNEP Report:

A report titled, A future for all – the need for human-wildlife coexistence, was recently released by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) and the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
Highlights of the Report:
- Conflict between humans and animals is one of the main threats to the long-term survival of some of the world’s most iconic species.
- Globally, conflict-related killing affects more than 75 per cent of the world’s wild cat species. It also affects polar bears and Mediterranean monk seals as well as large herbivores such as elephants.
- Global wildlife populations have fallen an average of 68 per cent since 1970.
Indian scenario:
- Over 500 elephants were killed between 2014-2015 and 2018-2019, mostly due to human-elephant conflict.
- During the same period, 2,361 people were killed as a result of conflict with elephants.
- India will be most-affected by human-wildlife conflict because it had the world’s second-largest human population as well as large populations of tigers, Asian elephants, one-horned rhinos, Asiatic lions and other species.
Youth And Food System: UN Report:

A new UN report on youth and agriculture underscores the urgent need to make agri-food systems more appealing to young people to secure the future of global food security and nutrition.
- The report ‘Promoting youth engagement and employment in agriculture and food systems’ is prepared and shared to the UN by the Committee on World Food Security (CFS).
- CFS is an inclusive international and intergovernmental platform for all stakeholders to work together on food security and nutrition for all. The CFS is hosted by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations (UN).
Youth in Numbers:
- Youth aged between 15 and 24 years accounted for 16% of the world’s population in 2019.
- Young people were concentrated in Asia, Central and Southern Asia with 361 million youth and Eastern and South-Eastern Asia with 307 million youth, followed by sub-Saharan Africa (211 million youth).
- The International Labour Organization (ILO) estimated that 440 million youth from the African continent would enter the labour market between 2015 and 2030.
Key Findings:
- Food systems are the largest employer: Particularly in the developing countries, yet they often do not provide decent and meaningful work or adequate livelihood opportunities, nor maintain a balance between the needs and rights of different generations.
- Food systems are a complex web of activities involving production, processing, handling, preparation, storage, distribution, marketing, access, purchase, consumption, food loss and waste, as well as the outputs of these activities, including social, economic and environmental outcomes.
- More Employment Opportunities: Covid-19 has affected labour markets around the world, hurting employment prospects for the youth more than those belonging to other age groups. Globally, employment among the youth fell 8.7% in 2020 compared with 3.7% for adults.
- Agri-food systems, if made more appealing and equitable to youth, are a large, untapped reservoir of employment opportunities.
- Importance of Focusing on Developing Countries: As almost 88% of the world’s 1.2 billion youth live, particularly in Africa, where over 70% of youth subsist on USD 2 per day or less.
- Achieving Sustainable Development Goals: The youth engagement and employment in sustainable agri-food systems is simultaneously a goal to be realized and a means for the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals, and of economic well-being.
- Youth are on the front lines to build the food systems of the future, while also bearing significant risks from climate change, social and economic inequities, and political marginalization.
Indian Scenario:
Youth in Numbers:
- The youth (18-29 years) constitute 22% of India’s population, which is more than 261 million people.
- According to the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation, the median age of Indian population is around 28 years in 2021 and will become 31 years by 2031.
- India is also going through the stage of demographic dividend.
- Hardly 5% of the youth are engaged in agriculture though over 60% of the rural people derive their livelihood fully or partly from farming and its related activities.
- Clearly, the modern youth are disenchanted with agriculture and are shunning it as a profession.
Organisation Of Islamic Cooperation’s (OIC):

The Ministry of External Affairs rejected the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation’s (OIC) proposal to assist a dialogue between India and Pakistan.
- Earlier in December 2020, India also rejected the criticism of its Kashmir policy by the OIC.
- OIC’s Offered to arrange a meeting between India and Pakistan and proposed to send a delegation to Jammu & Kashmir in line with resolutions of the OIC council of foreign ministers.
- Pakistan has repeatedly sought to raise the Kashmir issue at the OIC against the backdrop of India’s dramatically improved relations with several key players in West Asia and in the Islamic organisation, including Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain, Qatar, Indonesia and Bangladesh.
- India’s Response: The OIC should be watchful that their platform is not subverted by “vested interests” such as Pakistan to interfere in internal affairs of India or for anti-India propaganda through biased and one-sided resolutions.
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
- It is the second largest intergovernmental organization after the United Nations (UN) with a membership of 57 states.
- It is the collective voice of the Muslim world. It endeavors to safeguard and protect the interests of the Muslim world in the spirit of promoting international peace and harmony among various people of the world.
India is not a member of the OIC. - It was established upon a decision of the historical summit which took place in Rabat, Kingdom of Morocco in September 1969.
- Headquarters: Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Zika Virus Disease:
Zika Virus Disease (ZVD) was reported for the first time in Kerala.
- Zika virus is a mosquito-borne flavivirus that was first identified in Uganda in 1947 in monkeys. It was later identified in humans in 1952 in Uganda and the United Republic of Tanzania.
- ZVD is caused by a virus transmitted primarily by Aedes mosquitoes (AM), mainly Aedes aegypti.
- This is the same mosquito that transmits dengue, chikungunya and yellow fever.
- Zika virus is also transmitted from mother to fetus during pregnancy, through sexual contact, transfusion of blood and blood products, and organ transplantation.
- Symptoms are generally mild and include fever, rash, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, malaise or headache. Most people with Zika virus infection do not develop symptoms.
- Zika virus infection during pregnancy can cause infants to be born with microcephaly (smaller than normal head size) and other congenital malformations, known as congenital Zika syndrome.
- There is no vaccine or medicine for Zika. Instead, the focus is on relieving symptoms and includes rest, rehydration and acetaminophen for fever and pain.
Emvolio:
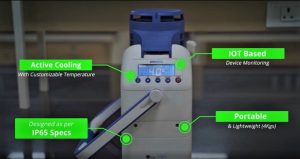
DBT-BIRAC supported startup Blackfrog Technologies has developed Emvolio.
- Emvólio is a portable, battery-powered medical-grade refrigeration device that improves the efficiency of the immunization by strictly maintaining preset temperature for up to 12 hours, thus enabling the safe and efficient transportation of vaccines to the last mile.
- Emvólio has a 2-litre capacity, enabling it to carry 30-50 vials, the standard for a daylong immunization campaign.
- The device also includes continuous temperature monitoring, location tracking, state-of-charge indication, communication with headquarters via live-tracking, and vital statistics for improved coverage.
- Blackfrog is an ISO-13485 certified manufacturer of medical devices, and Emvólio has been designed in accordance with WHO-PQS E003 standards.
About BIRAC:
- Set up by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), is a not-for-profit Section 8, Schedule B, Public Sector Enterprise.
Madurai Malli:

Consignments of Geographical Indications (GI) certified Madurai malli and other traditional flowers such as button rose, lily, chamanthi and marigold were exported to USA and Dubai from Tamil Nadu.
- Indian community in Dubai and USA would be able to offer freshflowers to Hindu deities both at home and temples while celebrating religious and cultural festivals after exports of flowers from India continue at regular interval.
- During 2020-2021, fresh cut flowers jasmine flowers and bouquets (comprising of jasmine and other traditional flowers) valued at Rs 66.28 crores were exported to countries like USA,UAE, Singapore, etc.
- Jasmine (Jasminum Officinale) is one of the most popular flowers found across the world. The scent of Jasmine is synonymous with the splendor of Madurai’s Meenakshi temple.
- Madurai has emerged as a major market for the malligai grown in its neighbourhood, and has evolved into the ‘jasmine capital’ of India.




