Today’s Current Affairs: 22nd December 2025 for UPSC IAS exams, State PSC exams, SSC CGL, State SSC, RRB, Railways, Banking Exam & IBPS, etc
Table of Contents
Dark Eagle Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW):

The US Army and Navy recently completed integrated testing of the Dark Eagle Long-Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW).
- Dark Eagle Long Range Hypersonic Weapon (LRHW) is a hypersonic missile system of the United States Army.
- It is a non-nuclear, ground-launched hypersonic missile weapon system.
- The missile component of the LRHW is reportedly being developed by Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman.
- Built for strategic attack missions, the weapon is capable of penetrating anti-access/area-denial (A2/AD) defenses, suppressing long-range enemy fires, and delivering rapid precision effects when and where they are needed.
- It is a land-based hypersonic weapon designed to strike targets at distances of up to 2,735 kilometers.
- It comprises a mobile ground-based battery equipped with Transporter Erector Launchers (TEL), supported by command and control elements.
- The system’s ballistic missile features two stages, one of which includes a hypersonic glide warhead (C-HGB), an unpowered but highly maneuverable vehicle capable of reaching extreme speeds of Mach 17, making interception particularly difficult.
- The missile climbs to the edge of space, flies through the upper atmosphere out of reach of most enemy defenses, then maneuvers toward its target.
- Each hypersonic missile is powered by a solid-fueled two-stage rocket booster.
Kavachi Volcano: News

Scientists recently reported a rare footage showing sharks living inside Kavachi volcano near the Solomon Islands, challenging assumptions about marine survival in extreme volcanic environments.
- It is a shallow submarine volcano located in the South Pacific Ocean, south of the remote Vangunu Island in the Solomon Islands.
- It sits on the Pacific Ring of Fire, a tectonically active region.
- It is one of the world’s few active and visible undersea volcanoes.
- It has been erupting on a regular (though thoroughly unpredictable) basis for many years, including several temporary island-building events.
- Eruptions typically produce steam plumes, ash, lava, and water discoloration due to volcanic gas release.
- The new islands formed are not large enough and coated with solid lava flows to be able to resist wave erosion.
- Notable eruptive activity has been recorded repeatedly since it was first documented in 1939.
Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB):

The Prime Minister of India recently extended his greetings to all personnel associated with the Sashastra Seema Bal on their Raising Day.
- The Sashastra Seema Bal, previously known as the Special Service Bureau, was established in 1963 after the Sino–Indian Conflict of 1962.
- It was created with the objective of guarding India’s international borders with Nepal and Bhutan.
- SSB is a part of the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) and falls under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The primary responsibility of SSB is to protect the safety of India’s designated borders with neighbouring nations Nepal and Bhutan.
- To foster an understanding of security among people residing in those border communities.
- To stop smuggling, illegal immigration, and other transnational crimes.
- To stop unlawful entry or exit on or from the Indian Border.
- To implement social responsibility initiatives in the relevant jurisdiction, for instance, establishing schools, buildings, restrooms, and roads by a border region development plan.
- To perform any additional tasks, such as UN missions, Law & Order missions, Counter The uprising Operations, Election duty, the central government may assign.
- Headed by a Director General (IPS officer or senior CAPF officer); includes infantry-style battalions, specialized units (engineering, signals, medical, dog squads), and training centers.
Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve: In News

Forest authorities recently arrested 53 persons for attempting to encroach upon protected land within the Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve, Chhattisgarh.
- It is located in Chhattisgarh.
- It was established by joining the regions represented by Sitanadi and Udanti wildlife sanctuaries.
- The drainage system of the reserve consists of the Mahanadi as the main river, along with the Udanti, Sitanadi, Indravan, and Pairi Rivers as tributaries.
- The location of the reserve is strategic since it also connects with the Kanker and North Kondagaon forest divisions, forming a contiguous forest corridor to Indravati Tiger Reserve in the Bastar region.
- The forest type here is predominantly tropical dry and moist deciduous.
- The forest is dominated by Sal (Shorea robusta), which forms dense patches across the landscape.
- Alongside, species such as Teak (Tectona grandis), Bamboo, Tendu, Mahua, Bija, and Harra contribute to the green diversity of the region.
- Along with the Indravati Tiger Reserve, the Udanti Sitanadi Tiger Reserve is an important refuge for the last few herds of the highly endangered Wild Buffalo.
- Apart from the tiger, other endangered and rare species are the Indian Wolf, Leopard, Sloth Bear, and Mouse Deer.
Autophagy:
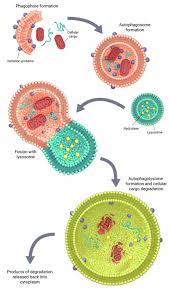
Researchers have uncovered a surprising player in autophagy process that can pave the way for developing therapies for diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and cancer.
- It is a key biological process where cells clear out damaged and unwanted materials.
- The autophagy pathway, which removes damaged material and defends against infections, is disrupted in diseases like Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s.
- When a cell fails to clear waste, its health suffers, especially in long-lived neurons.
- Autophagy is body’s cellular recycling system.
- It allows a cell to disassemble its junk parts and repurpose the salvageable bits and pieces into new, usable cell parts.
- Autophagy recycles damaged cell parts into fully functioning cell parts.
- It gets rid of nonfunctional cell parts that take up space and slow performance.
- It destroys pathogens in a cell that can damage it, like viruses and bacteria.
- Autophagy plays an important role when it comes to aging and longevity, too.
- Autophagy initially prevents cancer but later supports tumour growth and acts as a tumour suppressor by maintaining genome integrity and cellular homeostasis.
- In certain types of cancer, cells hijack autophagy for their own survival and propagation.
Tundra Biome:

According to a study conducted in Arctic Alaska, wildfires in the tundra have been more active this past century than at any time in the past 3,000 years.
- Tundra ecosystems are treeless regions found in the Arctic and on the top of mountains, where the climate is cold and rainfall is scanty.
- Characteristics of Tundra Biome:
- Low temperatures: The average temperature is -34 to -6 degrees Celsius.
- Permafrost: A layer of permanently frozen soil lies beneath the surface, which can be a few inches to several feet thick.
- Minimal precipitation: Despite often being compared to deserts in terms of moisture, the tundra receives low levels of precipitation, often as snow.
- Limited biodiversity: The harsh conditions of the tundra result in fewer plant and animal species compared to other biomes.
- Carbon sink: The tundra acts as a significant carbon storage area due to slow decomposition rates in the cold environment.
- The world has three types of Tundra:
- Arctic Tundra: It occurs north of the taiga belt in the far Northern Hemisphere.
- Alpine tundra: It prevails above the tree line in mountains worldwide.
- Antarctic tundra: It includes several sub-Antarctic islands and parts of the continent of Antarctica.
- Flora: Mosses, lichens, sedges, cotton grass, birches etc.
- Fauna: Arctic foxes, snow geese, polar bears etc.
National Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe Hub (NSSH) Scheme:

The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) has intensified efforts to promote entrepreneurship among SC and ST communities through the National Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe Hub (NSSH) Scheme.
- It is one of the flagship schemes of the Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises.
- It is implemented by the National Small Industries Corporation Ltd. (NSIC).
- NSSH is aimed at capacity enhancement of SC/ST entrepreneurs and promoting “entrepreneurship culture” amongst the SC/ST population.
- The Scheme empowers the SC/ST population to participate in the public procurement process and fulfill the mandated target of 4% procurement from SC/ST enterprises under the Public Procurement Policy by the Ministries, Departments, and CPSEs (Central Public Sector Enterprises).
- The initiative provides financial assistance and facilitates access to credit for SC/ST entrepreneurs.
- It collaborates with financial institutions, banks, and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) to ensure that entrepreneurs from these communities have access to affordable and timely financial resources for their business ventures.
- It also focuses on skill development and capacity building of SC/ST entrepreneurs.
Jiyo Parsi Scheme:

According to a recent report submitted by the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS), the Jiyo Parsi Scheme has been largely successful in reaching its intended population.
- It is a unique Central Sector Scheme implemented by the Ministry of Minority Affairs for arresting the population decline of the Parsi Community.
- The scheme was launched in 2013-14.
- The objective of the scheme is to reverse the declining trend of the Parsi population by adopting a scientific protocol and structured interventions, stabilize their population, and to increase the population of Parsis in India.
- The scheme has three components:
- Medical Component: to provide financial assistance for medical treatment under standard medical protocol.
- Health of the Community: To motivate Parsi Couples to have more children, financial assistance would be available to couples to take care of their dependent elderly family members and children.
- Advocacy: Enhancing support for Parsi couples with infertility and family-related concerns involves counseling sessions and outreach programmes i.e., seminars, medical camps, publicity brochures, advocacy films, etc.
- The utilization of social media networks for publicity to effectively reach eligible Parsi couples, ensuring access to the benefits of the scheme.
- The Scheme will be implemented through the State Governments with the assistance of respective Parsi Institutions.
- Eligible Parsi couples would be provided financial assistance under the various components of the schemes through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode.
- The State Governments would get the necessary verification, including biometric authentication of all beneficiaries done.
Indian Coast Guard (ICG) Ship Amulya:

The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) Ship ‘Amulya’ was commissioned in Goa.
- It is the third in the series of eight new-generation Adamya-class Fast Patrol Vessels.
- It has more than 60% indigenous components, designed and built by the Goa Shipyard Limited.
- It integrates modern design philosophy focused on efficiency, endurance, and rapid response capability.
- It will be based at Paradip, Odisha, operating under the administrative and operational control of the Commander, Coast Guard Region (North East).
- It will undertake functions like surveillance, interdiction, search & rescue, anti-smuggling operations, and pollution response.
- Features of Indian Coast Guard (ICG) Ship Amulya:
- Propulsion: It is powered by advanced diesel engines.
- Speed: The ship delivers a top speed of 27 knots and an operational endurance of 1,500 nautical miles.
- Armaments: It is fitted with indigenous state-of-the-art weapons/systems, offering superior manoeuvrability, operational flexibility and enhanced performance at sea.
India’s foreign exchange reserves increased:
India’s external sector position strengthened further as the country’s foreign exchange reserves rose by $1.68 billion to $688.94 billion for the week which ended December 12, 2025. According to data released by the Reserve Bank of India. The increase was primarily supported by a sharp rise in gold reserves and a modest gain in foreign currency assets (FCAs).As per the RBI’s weekly statistical release, India’s forex reserves increased from $687.26 billion to $688.94 billion during the reporting week.This follows a rise of nearly $1.03 billion in the previous week ending December 5, 2025.The steady upward trend indicates relative stability in India’s external accounts despite global economic uncertainties, including geopolitical tensions and fluctuating capital flows.
PM Modi To Inaugurates New Terminal at Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport:
Prime Minister Narendra Modi to inaugurate the new terminal building of Lokpriya Gopinath Bordoloi International Airport in Guwahati in Assam, on December 20, 2025. The inauguration marks a major milestone in strengthening aviation infrastructure in Northeast India and is expected to significantly boost connectivity, tourism, and economic activity in the region.The newly inaugurated terminal is designed to handle 13.1 million passengers annually which making it one of the most advanced airports in eastern India.According to official statements the integrated terminal is supported by major upgrades in runway, aprons, taxiways, and airfield systems, ensuring smoother aircraft operations.The terminal is being described as India’s first nature-themed airport terminal, setting a new benchmark in sustainable and passenger-friendly design.
RBI Slaps ₹62 Lakh Penalty on Kotak Mahindra Bank:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has imposed a monetary penalty of INR 61.95 lakh on Kotak Mahindra Bank for non-compliance with multiple regulatory norms. The action follows RBI’s supervisory inspection of the bank’s operations and highlights the central bank focus on customer protection and data accuracy.RBI stated that after reviewing the bank’s response to the show-cause notice and additional submissions, the violations were sustained, warranting a monetary penalty.The regulator clarified that the penalty is based on compliance failures and does not question the validity of customer transactions or agreements.
ADB commits $4.26 billion in sovereign lending to India in 2025:
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has committed $4.26 billion in sovereign lending to India in 2025. Supporting various projects across skilling, clean energy, urban development, transport, healthcare, and tourism. The funding aligns closely with India’s priority development goals and long-term growth strategy.ADB approved 16 new sovereign projects for India. These investments aim to strengthen human capital, accelerate renewable energy adoption, modernize cities, and improve essential services.
Sector-wise distribution of projects,
- Human & Social Development: Roundly 32%
- Energy (mainly renewables): Nearly 26%
- Urban Development: Over 18%
Hurun Rich List 2025 ranks Zomato (Eternal) founder Deepinder Goyal as India’s top self-made entrepreneur:
The Hurun Rich List 2025 has once again highlighted India’s dynamic startup and business ecosystem. This year, Deepinder Goyal, founder and CEO of Eternal (formerly Zomato), has emerged as India’s top self-made entrepreneur, overtaking veteran businessman Radhakishan Damani of D-Mart. The list reflects rapid wealth creation in new-age technology companies and underlines the growing dominance of startup-led enterprises in India’s economy. Deepinder Goyal secured the first position after Eternal’s valuation rose by 27% over the past year to ₹3.2 lakh crore.This growth helped him surpass Radhakishan Damani, whose company Avenue Supermarts (DMart) saw a 13% decline in valuation to around ₹3 lakh crore, placing him second on the list.Goyal’s rise highlights the growing influence of digital platforms, food delivery, and consumer internet businesses in India’s wealth landscape.
SEBI Allows Zero-Coupon Bonds to Be Issued in Smaller Denominations:
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has allowed zero-coupon bonds to be issued in smaller denominations of INR 10,000. Announced on 18 December 2025, this decision is aimed at widening investor participation, improving accessibility to debt instruments, and strengthening India’s corporate bond market. The move aligns with SEBI’s broader objective of deepening financial markets and encouraging retail investment in fixed-income securities.Non-convertible debt securities (NCDs) and non-convertible redeemable preference shares (NCRPS) in India are often issued through private placement, traditionally with high face values that limited retail participation.SEBI had allowed issuers to reduce the face value of such instruments to INR10,000, but only for interest- or dividend-bearing securities with fixed maturity and no structured obligations.This condition effectively excluded zero-coupon bonds, as they do not offer periodic interest payments.




